Crusades
... • {At the end of the 4th Crusade Europe was in control of Constantinople} • After about 60 years of European control, the Byzantines eventually regained control. Until 1453 when the Turks took it again ...
... • {At the end of the 4th Crusade Europe was in control of Constantinople} • After about 60 years of European control, the Byzantines eventually regained control. Until 1453 when the Turks took it again ...
Crusades - Summary and King Richard powerpoint
... in both body and soul now work for a double honor. Behold! on this side will be the sorrowful and poor, on that, the rich; on this side, the enemies of the Lord, on that, his friends. Let those who …..eagerly set out on the way with God as their guide." ...
... in both body and soul now work for a double honor. Behold! on this side will be the sorrowful and poor, on that, the rich; on this side, the enemies of the Lord, on that, his friends. Let those who …..eagerly set out on the way with God as their guide." ...
The Crusades - Alena Pettit
... reconquer the Holy Land from Saladin. • Called by Pope Gregory VIII and led by Europe's most important leaders: - Philip II of France (left after capturing Acre) - Richard I of England - Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor (Drowned,creating instability between English and French) • Inability of the Crus ...
... reconquer the Holy Land from Saladin. • Called by Pope Gregory VIII and led by Europe's most important leaders: - Philip II of France (left after capturing Acre) - Richard I of England - Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor (Drowned,creating instability between English and French) • Inability of the Crus ...
Chapter_14_Powerpoint
... • The French king died in 1328, made the English want to rule both England and France. • Edward III invaded France in 1337, starting the Hundred Years’ War. ...
... • The French king died in 1328, made the English want to rule both England and France. • Edward III invaded France in 1337, starting the Hundred Years’ War. ...
Chapter 14 - World History and Honors History 9
... Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. The goal of the First Crusade was to take Jerusalem and the area around it, known as the Holy Land, away from the Muslims who controlled it. 2. Peasants on the First Crusade slaughtered entire communities of Jews in Germany. 3. During the Second Cr ...
... Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. The goal of the First Crusade was to take Jerusalem and the area around it, known as the Holy Land, away from the Muslims who controlled it. 2. Peasants on the First Crusade slaughtered entire communities of Jews in Germany. 3. During the Second Cr ...
The Crusader Chronicles
... Europeans Attempt to Strengthen the Christian Hold on Jerusalem In response to the Muslim forces attacking Edessa, groups of soldiers such as the Teutonic Knights, Knights Hospitaller, and Knights Templar rode to defend the Holy Lands. Leading this Crusade were monarchs Louis VII of France and Conr ...
... Europeans Attempt to Strengthen the Christian Hold on Jerusalem In response to the Muslim forces attacking Edessa, groups of soldiers such as the Teutonic Knights, Knights Hospitaller, and Knights Templar rode to defend the Holy Lands. Leading this Crusade were monarchs Louis VII of France and Conr ...
SALAH AL DIN LISTENING ACTIVITY. NAME: GRADE: Saladin and
... Gregory VIII, ordered another crusade immediately to regain the Holy City for the CHRISTIANS. This was the start of the Third Crusade. It was led by Richard I (Richard the Lionheart), EMPEROR Frederick Barbarossa of Germany and King Philip II of France. These were possibly the three most important m ...
... Gregory VIII, ordered another crusade immediately to regain the Holy City for the CHRISTIANS. This was the start of the Third Crusade. It was led by Richard I (Richard the Lionheart), EMPEROR Frederick Barbarossa of Germany and King Philip II of France. These were possibly the three most important m ...
The Crusades - Nutley Public Schools
... The Crusades • The Crusades were an attempt by the European Church to “reclaim the Holy Land” • Jerusalem had been conquered by Arabs around 640 AD • 1095 Pope Urban called for first Crusade ...
... The Crusades • The Crusades were an attempt by the European Church to “reclaim the Holy Land” • Jerusalem had been conquered by Arabs around 640 AD • 1095 Pope Urban called for first Crusade ...
14.1 Church Reform and the Crusades
... • Younger sons hope to earn land or win glory by fighting (although historian Rodney Stark in God’s Battalions: The Case for the Crusades disagrees with that theory because the first three crusades were led by the heads of the royal families of Europe). • Later, merchants join Crusades to try to gai ...
... • Younger sons hope to earn land or win glory by fighting (although historian Rodney Stark in God’s Battalions: The Case for the Crusades disagrees with that theory because the first three crusades were led by the heads of the royal families of Europe). • Later, merchants join Crusades to try to gai ...
14.1 church reform and the crusades
... • Younger sons hope to earn land or win glory by fighting (although historian Rodney Stark in God’s Battalions: The Case for the Crusades disagrees with that theory because the first three crusades were led by the heads of the royal families of Europe). • Later, merchants join Crusades to try to gai ...
... • Younger sons hope to earn land or win glory by fighting (although historian Rodney Stark in God’s Battalions: The Case for the Crusades disagrees with that theory because the first three crusades were led by the heads of the royal families of Europe). • Later, merchants join Crusades to try to gai ...
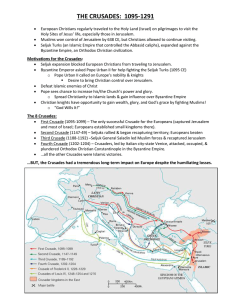
the crusades: 1095-1291
... Byzantine Emperor asked Pope Urban II for help fighting the Seljuk Turks (1095 CE) o Pope Urban II called on Europe’s nobility & knights Desire to bring Christian control over Jerusalem. Defeat Islamic enemies of Christ Pope sees chance to increase his/the Church’s power and glory. o Spread ...
... Byzantine Emperor asked Pope Urban II for help fighting the Seljuk Turks (1095 CE) o Pope Urban II called on Europe’s nobility & knights Desire to bring Christian control over Jerusalem. Defeat Islamic enemies of Christ Pope sees chance to increase his/the Church’s power and glory. o Spread ...
The Crusades: Military expeditions from Christian Europe to
... • (4) Peasants wanted a chance for adventure, treasures, and win favor with God. ...
... • (4) Peasants wanted a chance for adventure, treasures, and win favor with God. ...
The Crusades 1095-1204
... Failure highlighted with the death of a German king and the capture of the English king Aftermath: King Richard of England (the Lionhearted) managed to gain guarantees for the safety of Christians visiting Jerusalem ...
... Failure highlighted with the death of a German king and the capture of the English king Aftermath: King Richard of England (the Lionhearted) managed to gain guarantees for the safety of Christians visiting Jerusalem ...
SS8 - Middle Ages
... a. Why did people and knights travel so far to fight in the Crusades? (2 marks) b. What was the People’s Crusade and who were their leaders? (2 marks) c. Although they lost control of the Holy Land what did the Christians gain from contact with the Muslims during the crusades (provide specific examp ...
... a. Why did people and knights travel so far to fight in the Crusades? (2 marks) b. What was the People’s Crusade and who were their leaders? (2 marks) c. Although they lost control of the Holy Land what did the Christians gain from contact with the Muslims during the crusades (provide specific examp ...
HISTORY 3137(Fall 2012) – Crusade and Jihad
... unprecedented campaign, involving people from many parts of Europe, in an effort to recover the Holy Sepulcher for Christendom. Some modern historians tend to deemphasize the speech, but there's no doubt that contemporaries, once Jerusalem had been taken, looked back to this one incident as a turnin ...
... unprecedented campaign, involving people from many parts of Europe, in an effort to recover the Holy Sepulcher for Christendom. Some modern historians tend to deemphasize the speech, but there's no doubt that contemporaries, once Jerusalem had been taken, looked back to this one incident as a turnin ...
The Crusades
... Europe to prepare for a holy war Urban II believed Europe had to gain control of the Holy Land for all Christians He also wanted to reunite the two churches, and stop the constant wars in Europe ...
... Europe to prepare for a holy war Urban II believed Europe had to gain control of the Holy Land for all Christians He also wanted to reunite the two churches, and stop the constant wars in Europe ...
the crusades
... The people of Constantinople became filled with hatred for the west. The Children's Crusade in 12I2 C.E w.as a terrible tragedy. Many thousands of French and German children died trying to reach Jerusalem. They believed that God would help them because they were children. Many died of hunger. Others ...
... The people of Constantinople became filled with hatred for the west. The Children's Crusade in 12I2 C.E w.as a terrible tragedy. Many thousands of French and German children died trying to reach Jerusalem. They believed that God would help them because they were children. Many died of hunger. Others ...
Station 2 Resources
... accomplishment of) such an undertaking, as a preparation for the remission of all their sins. And we have constituted our most beloved son, Adhemar, Bishop of Puy, leader of this expedition and undertaking in our stead, so that those who, perchance, may wish to undertake this journey should comply W ...
... accomplishment of) such an undertaking, as a preparation for the remission of all their sins. And we have constituted our most beloved son, Adhemar, Bishop of Puy, leader of this expedition and undertaking in our stead, so that those who, perchance, may wish to undertake this journey should comply W ...
The Causes of the Crusades
... The Causes and Course of the Crusades What were the Crusades? The Crusades were holy wars fought between Christians in Europe and Muslims in the Middle East between 1095 and 1291. Although the main goal of the Crusades was to take control of Jerusalem away from the Muslims, there were many reasons w ...
... The Causes and Course of the Crusades What were the Crusades? The Crusades were holy wars fought between Christians in Europe and Muslims in the Middle East between 1095 and 1291. Although the main goal of the Crusades was to take control of Jerusalem away from the Muslims, there were many reasons w ...
File - Mr. Butts World History
... departed. To govern the conquered territory, those who remained established (13) _______________ large western settlements, or Crusader states, in Jerusalem, Edessa, Antioch and Tripoli. Guarded by formidable castles, the Crusader states retained the upper hand in the region until around 1130, when ...
... departed. To govern the conquered territory, those who remained established (13) _______________ large western settlements, or Crusader states, in Jerusalem, Edessa, Antioch and Tripoli. Guarded by formidable castles, the Crusader states retained the upper hand in the region until around 1130, when ...
The Crusades
... knights to help fight Muslim Turks • Even though popes/emperors were rivals—he agreed ...
... knights to help fight Muslim Turks • Even though popes/emperors were rivals—he agreed ...
the crusades - qasocialstudies
... long series of wars between Christians and Muslims in SW Asia Holy Land – the region where Jesus lived, preached, and died (Palestine at this time in history) When Turkish Muslims take over the Holy Land, Christian pilgrims begin to report of being attacked in Jerusalem. ...
... long series of wars between Christians and Muslims in SW Asia Holy Land – the region where Jesus lived, preached, and died (Palestine at this time in history) When Turkish Muslims take over the Holy Land, Christian pilgrims begin to report of being attacked in Jerusalem. ...
The Causes and Course of the Crusades
... The possibility of opening up new trade routes between Europe and the Middle East. Take another look at the reasons why Europeans were willing to fight. Which one would have convinced you most to go on a crusade? Why? ...
... The possibility of opening up new trade routes between Europe and the Middle East. Take another look at the reasons why Europeans were willing to fight. Which one would have convinced you most to go on a crusade? Why? ...
File
... What part of the world did Saladin originally conquer and unite? By the mid-1180’s Saladin’s empire stretched from the Nile to the _______________________ River. How did Saladin’s near-death illness change him? What creative tactic(s) did Saladin use to help him win the Battle of Hattin? When he too ...
... What part of the world did Saladin originally conquer and unite? By the mid-1180’s Saladin’s empire stretched from the Nile to the _______________________ River. How did Saladin’s near-death illness change him? What creative tactic(s) did Saladin use to help him win the Battle of Hattin? When he too ...
Despenser's Crusade

Despenser's Crusade (or the Bishop of Norwich's Crusade, sometimes just Norwich Crusade) of 1383 was a military expedition led by Henry le Despenser that aimed to assist the city of Ghent in its struggle against the supporters of Antipope Clement VII. It took place during the great Papal schism and the Hundred Years' War between England and France. While France supported Clement, whose court was based in Avignon, the English supported Pope Urban VI in Rome. Popular at the time among the lower and middle classes, Despenser's Crusade ""was only widely criticised in hindsight"", and ""for all its canonical propriety, [it] was the Hundred Years' War thinly disguised"". Among contemporary critics of the crusade were John Wyclif and the French chronicler Jean Froissart, who charged its leaders with hypocrisy.