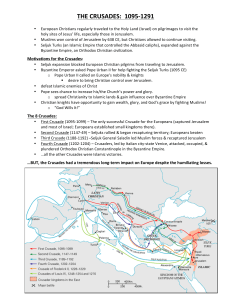
THE CRUSADES: 1095
... Byzantine Emperor asked Pope Urban II for help fighting the Seljuk Turks (1095 CE) o Pope Urban II called on Europe’s nobility & knights § desire to bring Christian control over Jerusalem. defeat Islamic ...
... Byzantine Emperor asked Pope Urban II for help fighting the Seljuk Turks (1095 CE) o Pope Urban II called on Europe’s nobility & knights § desire to bring Christian control over Jerusalem. defeat Islamic ...
Crusades Mrs. Tepel So what is a Crusade? A vigorous concerted
... • He calls for the Crusades to do something with the knights who are causing havoc in Europe. ...
... • He calls for the Crusades to do something with the knights who are causing havoc in Europe. ...
The Crusades
... • Eastern Roman Empire, centered around Constantinople, existed long after Western Roman Empire • Became known as the Byzantine Empire • Lasted until 1453 • Both Greek and Christian state • Christian Church of Byzantine Empire came to be known as Eastern Orthodox Church • Did not believe that pope w ...
... • Eastern Roman Empire, centered around Constantinople, existed long after Western Roman Empire • Became known as the Byzantine Empire • Lasted until 1453 • Both Greek and Christian state • Christian Church of Byzantine Empire came to be known as Eastern Orthodox Church • Did not believe that pope w ...
CrusadesC-E - PVS
... acceptable, and they were filled with hatred for the west. The Children's Crusade in 1212 was a terrible tragedy. Many thousands of French and German children died trying to reach Jerusalem. They believed God would help them because they were children. Many died of hunger. Other froze to death. When ...
... acceptable, and they were filled with hatred for the west. The Children's Crusade in 1212 was a terrible tragedy. Many thousands of French and German children died trying to reach Jerusalem. They believed God would help them because they were children. Many died of hunger. Other froze to death. When ...
Slide 1
... • Small Crusades sprouted up throughout the 13th century and they failed for three reasons • Political schemes • Poor preparation • Deaths of key western rulers ...
... • Small Crusades sprouted up throughout the 13th century and they failed for three reasons • Political schemes • Poor preparation • Deaths of key western rulers ...
The Crusades
... led by Peter the Hermit set out for battle. They settled in Constantinople and were advised to wait for help. The people rebelled and attacked the Turks. They were defeated as only a small part of his army survived. ...
... led by Peter the Hermit set out for battle. They settled in Constantinople and were advised to wait for help. The people rebelled and attacked the Turks. They were defeated as only a small part of his army survived. ...
The Crusades
... Parties Involved • Richard the Lionheart • King Philip Augustus of France • Emperor Frederick Barbarossa of Germany ...
... Parties Involved • Richard the Lionheart • King Philip Augustus of France • Emperor Frederick Barbarossa of Germany ...
Crusades
... 1. Arabs (Muslims) closed Jerusalem to Christians and Jews. 2. Pope called for a crusade. 3. Knights wanted to use fighting skills. 4. Peasants wanted to escape feudal system. 5. Adventure! ...
... 1. Arabs (Muslims) closed Jerusalem to Christians and Jews. 2. Pope called for a crusade. 3. Knights wanted to use fighting skills. 4. Peasants wanted to escape feudal system. 5. Adventure! ...
Chapter 14 Section 1
... The Inquisition was a court used to suppress what? These were people whose beliefs differed from what? What happened if you were suspected? If you confessed? Other than Muslims, what other group was expelled from Spain? Effects of the Crusades The Crusades show the power of the church during the ___ ...
... The Inquisition was a court used to suppress what? These were people whose beliefs differed from what? What happened if you were suspected? If you confessed? Other than Muslims, what other group was expelled from Spain? Effects of the Crusades The Crusades show the power of the church during the ___ ...
The Fourth Crusade (1000)
... enthusiastic, and ambitious for the glory of the Papacy, he revived the plans of Pope Urban II and sought once more to unite the forces of Christendom against Islam. No emperor or king answered his summons, but a number of knights (chiefly French) took the crusader's vow. None of the Crusades, after ...
... enthusiastic, and ambitious for the glory of the Papacy, he revived the plans of Pope Urban II and sought once more to unite the forces of Christendom against Islam. No emperor or king answered his summons, but a number of knights (chiefly French) took the crusader's vow. None of the Crusades, after ...
The Crusades
... • Why might so many people have taken part in the Crusades, not only knights and soldiers but also ordinary people and even children? ...
... • Why might so many people have taken part in the Crusades, not only knights and soldiers but also ordinary people and even children? ...
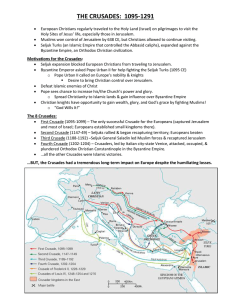
the crusades: 1095-1291
... Seljuk expansion blocked European Christians from traveling to Jerusalem. Byzantine Emperor asked Pope Urban II for help fighting the Seljuk Turks (1095 CE) o Pope Urban II called on Europe’s nobility & knights Desire to bring Christian control over Jerusalem. Defeat Islamic enemies of Chris ...
... Seljuk expansion blocked European Christians from traveling to Jerusalem. Byzantine Emperor asked Pope Urban II for help fighting the Seljuk Turks (1095 CE) o Pope Urban II called on Europe’s nobility & knights Desire to bring Christian control over Jerusalem. Defeat Islamic enemies of Chris ...
Middle Ages Learning Portfolio
... his Crusade would receive a special form of religious pardon called an indulgence. Crusaders who joined the holy war would be forgiven for all their sins, and if they died in battle, they would go straight to heaven. However, despite this incentive the Crusaders accomplished nothing. After the first ...
... his Crusade would receive a special form of religious pardon called an indulgence. Crusaders who joined the holy war would be forgiven for all their sins, and if they died in battle, they would go straight to heaven. However, despite this incentive the Crusaders accomplished nothing. After the first ...
The Crusades & Church Reform
... Philip & Richard quarreled (Philip went home) Richard was outmatched ...
... Philip & Richard quarreled (Philip went home) Richard was outmatched ...
www.historyforkids.net
... 1. Religion influenced many things such as education, customs, morals, and routines. 2. The center of faith for followers of Christianity, Judaism, and Islam was the city of Jerusalem. 3. The First Crusade began in 1096 and lasted until 1099. 4. Richard the Lionheart was able to reach a treaty with ...
... 1. Religion influenced many things such as education, customs, morals, and routines. 2. The center of faith for followers of Christianity, Judaism, and Islam was the city of Jerusalem. 3. The First Crusade began in 1096 and lasted until 1099. 4. Richard the Lionheart was able to reach a treaty with ...
Word - Saint Mary`s Press
... Belief and Violence: The Crusades Church leaders, secular rulers, and common folk alike came together in an attempt to change things in a far-off land they believed should rightfully be ruled by Christians—specifically, European Christians. The impetus behind the Crusades was the desire to free the ...
... Belief and Violence: The Crusades Church leaders, secular rulers, and common folk alike came together in an attempt to change things in a far-off land they believed should rightfully be ruled by Christians—specifically, European Christians. The impetus behind the Crusades was the desire to free the ...
Belief and Violence: The Crusades
... Belief and Violence: The Crusades Church leaders, secular rulers, and common folk alike came together in an attempt to change things in a far-off land they believed should rightfully be ruled by Christians—specifically, European Christians. The impetus behind the Crusades was the desire to free the ...
... Belief and Violence: The Crusades Church leaders, secular rulers, and common folk alike came together in an attempt to change things in a far-off land they believed should rightfully be ruled by Christians—specifically, European Christians. The impetus behind the Crusades was the desire to free the ...
The Crusades
... to the Byzantine Empire. The emperor of Constantinople, Alexius I (1081–1118), sent envoys to Rome asking Pope Urban II to send help. The response was immediate and overwhelming. Thousands of devoted Christians joined the First Crusade. Pope Urban encouraged the crusade because he hoped it would hel ...
... to the Byzantine Empire. The emperor of Constantinople, Alexius I (1081–1118), sent envoys to Rome asking Pope Urban II to send help. The response was immediate and overwhelming. Thousands of devoted Christians joined the First Crusade. Pope Urban encouraged the crusade because he hoped it would hel ...
1/13 Aim: Why did Western Europe fight the Crusades
... Europeans fight the Crusades? Do Now: In 1095 A.D Pope Urban II called upon Christians in Western Europe to fight the Muslims for control of the holy land, Jerusalem. Why were many willing to fight in the Crusades knowing that there was good chance that they might never return? On your handout, matc ...
... Europeans fight the Crusades? Do Now: In 1095 A.D Pope Urban II called upon Christians in Western Europe to fight the Muslims for control of the holy land, Jerusalem. Why were many willing to fight in the Crusades knowing that there was good chance that they might never return? On your handout, matc ...
Pilgrims in Arms [VOD]
... as you watch it. The emphasis will be on the origins of the First Crusade, and its first few years in the late 11th century (ca. 1095-1097). You may also want to compare the documentary with the class readings (textbook or handouts). Background of Emperor Alexius I’s letter role of Seljuk Turks ...
... as you watch it. The emphasis will be on the origins of the First Crusade, and its first few years in the late 11th century (ca. 1095-1097). You may also want to compare the documentary with the class readings (textbook or handouts). Background of Emperor Alexius I’s letter role of Seljuk Turks ...
Crusades1
... •1099 – Jerusalem fell to Crusaders after 2 months •Many knights returned home, some set up homes •Only Crusade that Christians won ...
... •1099 – Jerusalem fell to Crusaders after 2 months •Many knights returned home, some set up homes •Only Crusade that Christians won ...
The Crusades
... Crusades- A series of “Holy Wars” that were undertaken to recapture the Holy Land. ...
... Crusades- A series of “Holy Wars” that were undertaken to recapture the Holy Land. ...
















![Pilgrims in Arms [VOD]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005347787_1-11e216de7a422ffbd1d23e4375229286-300x300.png)

