Inbreeding and the incidence of childhood genetic disorders in
... Human Biology, King's College, London WC2R 2LS. SUMMARY Consanguineous marriages are strongly favoured among the populations of South India. In a study conducted on 407 infants and children, a total of 35 genetic diseases was diagnosed in 63 persons: 44 with single gene defects, 12 with polygenic di ...
... Human Biology, King's College, London WC2R 2LS. SUMMARY Consanguineous marriages are strongly favoured among the populations of South India. In a study conducted on 407 infants and children, a total of 35 genetic diseases was diagnosed in 63 persons: 44 with single gene defects, 12 with polygenic di ...
Mechanisms of Evolution
... population to change B. Natural selection affects smaller populations more often than larger populations C. Natural selection depends on some traits helping individuals in their environment ...
... population to change B. Natural selection affects smaller populations more often than larger populations C. Natural selection depends on some traits helping individuals in their environment ...
Genetic Drift
... Attributed to population bottleneck in Middle Ages Population was dramatically reduced at this time Individuals who remained alive & reproduced just happened to be ones who carried Tay-Sachs ...
... Attributed to population bottleneck in Middle Ages Population was dramatically reduced at this time Individuals who remained alive & reproduced just happened to be ones who carried Tay-Sachs ...
Probability and Punnett Squares
... Since, in humans, there are many more genes on the X than there are on the Y, there are many more X-linked traits than there are Y-linked traits. ...
... Since, in humans, there are many more genes on the X than there are on the Y, there are many more X-linked traits than there are Y-linked traits. ...
Factors that Cause Evolutionary Change
... select mates, often on the basis of their phenotypes. E: Increases the proportion of homozygous individuals in a population, but does not affect the frequency of alleles. D: Refers to random change in genetic variation from generation to generation due to chance (“experimental probability”). E: In s ...
... select mates, often on the basis of their phenotypes. E: Increases the proportion of homozygous individuals in a population, but does not affect the frequency of alleles. D: Refers to random change in genetic variation from generation to generation due to chance (“experimental probability”). E: In s ...
Recessive and dominant heredity in humans
... general population is homozygous dominant for the normal condition and therefore only passes on a normal allele. ...
... general population is homozygous dominant for the normal condition and therefore only passes on a normal allele. ...
The Evolution of Populations
... Plant Disease Resistance is a genetic trait that allows plants to survive against infections. High genetic diversity allows for plant population to respond to environment stimuli, unlike low diversity in which the few organisms of the species may perish if they can’t adapt to new environments. ...
... Plant Disease Resistance is a genetic trait that allows plants to survive against infections. High genetic diversity allows for plant population to respond to environment stimuli, unlike low diversity in which the few organisms of the species may perish if they can’t adapt to new environments. ...
Mendelian Inheritance - Santa Susana High School
... F1Generation = hybrid offspring of the P cross F2Generation = self-pollinated offspring of the F1 allele - alternate versions of a gene dominant allele - codes for a trait that is always expressed (symbolized by a capital letter) recessive allele - has no noticeable contribution to an organism's app ...
... F1Generation = hybrid offspring of the P cross F2Generation = self-pollinated offspring of the F1 allele - alternate versions of a gene dominant allele - codes for a trait that is always expressed (symbolized by a capital letter) recessive allele - has no noticeable contribution to an organism's app ...
Unit 6 Genetics - centralmountainbiology
... is a carrier, doesn’t express trait. Aa • Horizontal bar connecting two individuals represents a set of parents. • Vertical bar represents offspring. ...
... is a carrier, doesn’t express trait. Aa • Horizontal bar connecting two individuals represents a set of parents. • Vertical bar represents offspring. ...
9 Genetics Vocabulary
... 18. dihybrid cross—predicts the inheritance of TWO traits together (16 boxes) 19. codominance—both alleles are expressed in the heterozygote 20. incomplete dominance—neither allele is expressed; instead, the phenotype of the heterozygote is in between that of the two homozygotes 21. multiple alleles ...
... 18. dihybrid cross—predicts the inheritance of TWO traits together (16 boxes) 19. codominance—both alleles are expressed in the heterozygote 20. incomplete dominance—neither allele is expressed; instead, the phenotype of the heterozygote is in between that of the two homozygotes 21. multiple alleles ...
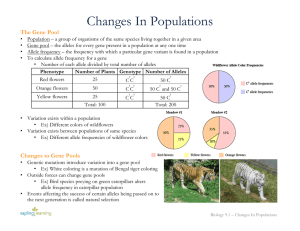
Changes In Populations
... • Ex) Different colors of wildflowers • Variation exists between populations of same species • Ex) Different allele frequencies of wildflower colors ...
... • Ex) Different colors of wildflowers • Variation exists between populations of same species • Ex) Different allele frequencies of wildflower colors ...
Inheritance Patterns Name Definition Visual Example Punnett
... for blood type. 2 alleles produce surface antigens A or B. The third allele O produces no antigens. Both alleles inherited from your parents are expressed. That is why some people can have type AB blood. ...
... for blood type. 2 alleles produce surface antigens A or B. The third allele O produces no antigens. Both alleles inherited from your parents are expressed. That is why some people can have type AB blood. ...
natural selection
... • GENETIC DRIFT – in small populations the frequencies of alleles can be drastically affected by chance events – BOTTLENECK EFFECT – if populations are driven to the point of extinction the remaining individuals do not carry a true representation of the original gene pool. – FOUNDER EFFECT – when a ...
... • GENETIC DRIFT – in small populations the frequencies of alleles can be drastically affected by chance events – BOTTLENECK EFFECT – if populations are driven to the point of extinction the remaining individuals do not carry a true representation of the original gene pool. – FOUNDER EFFECT – when a ...
Genetic Equilibrium Honors Biology Mr. Lee Room 320
... (group of individuals of the same species that interbreed) Gene pool- consists of all the genes, and alleles, that are present in a population Relative frequency of an alleles is the number of times that an allele occurs in a gene pool ...
... (group of individuals of the same species that interbreed) Gene pool- consists of all the genes, and alleles, that are present in a population Relative frequency of an alleles is the number of times that an allele occurs in a gene pool ...
Bio Inquiry - GEOCITIES.ws
... found a smaller population. This group of people usually has certain gene frequencies ...
... found a smaller population. This group of people usually has certain gene frequencies ...
Name: Chapter 11: Introduction to Genetics Exam Matching: Match
... states that genes for different traits can segregate during the formation of gametes. helps account for the many genetic variations observed in plants, animals, and other organisms. 11. Many genes have more than two alleles and are therefore said to have . This does not mean that an individual can h ...
... states that genes for different traits can segregate during the formation of gametes. helps account for the many genetic variations observed in plants, animals, and other organisms. 11. Many genes have more than two alleles and are therefore said to have . This does not mean that an individual can h ...
X-LINKED INHERITANCE
... Overall, the risk associated with having a child affected with a recessive disease as a result of a first cousin mating is approximately 3 percent, in addition to a baseline risk of 3 to 4 % all ...
... Overall, the risk associated with having a child affected with a recessive disease as a result of a first cousin mating is approximately 3 percent, in addition to a baseline risk of 3 to 4 % all ...
Genetics test vocabulary Review Name: Class: ______ 1. Gregor
... 8. An alternate form of a gene: ____allele__________ 9. Having non identical alleles (not pure; ex. Aa): __heterozygous___ 10. Having identical alleles (pure, ex. AA): _homozygous_________ 11. Square used to determine probability and results of cross: punnett 12. The allele that is masked or covered ...
... 8. An alternate form of a gene: ____allele__________ 9. Having non identical alleles (not pure; ex. Aa): __heterozygous___ 10. Having identical alleles (pure, ex. AA): _homozygous_________ 11. Square used to determine probability and results of cross: punnett 12. The allele that is masked or covered ...