Evolution fib notes
... How did all these different organisms arise? How are they all related? Evolution = ____________________ o All living things share a common ancestor. o We can draw a Tree of Life to show how every species is related. Evolution: ________________________; the process by which modern species ___________ ...
... How did all these different organisms arise? How are they all related? Evolution = ____________________ o All living things share a common ancestor. o We can draw a Tree of Life to show how every species is related. Evolution: ________________________; the process by which modern species ___________ ...
Evolution & Natural Selection
... early atmospheric compounds could produce simple organic compounds found in living things Rise of oxygen drove some life forms to extinction but many evolved and used oxygen for respiration and ...
... early atmospheric compounds could produce simple organic compounds found in living things Rise of oxygen drove some life forms to extinction but many evolved and used oxygen for respiration and ...
devonian presentation
... Cooling of Earth due to CO2 Decreases 1) Chemical Weathering- This process creates Calcium and Magnesium, removing CO2 from the atmosphere, and cooling Earth. 2) Carbon Storage- Plants convert CO2 to Carbon which is then stored inside the plant structure. When it dies, the Carbon is released into so ...
... Cooling of Earth due to CO2 Decreases 1) Chemical Weathering- This process creates Calcium and Magnesium, removing CO2 from the atmosphere, and cooling Earth. 2) Carbon Storage- Plants convert CO2 to Carbon which is then stored inside the plant structure. When it dies, the Carbon is released into so ...
Introduction to Animals Crosswords
... 19. Middle germ layer that forms muscles 21. Back side 22. Symmetry where body parts are in a circle arranged around a central axis 25. Sponges have this symmetry 26. Respiratory structures that remove oxygen from water 28. Specialized nerve cells 29. How animals take in food 30. Number of tissue la ...
... 19. Middle germ layer that forms muscles 21. Back side 22. Symmetry where body parts are in a circle arranged around a central axis 25. Sponges have this symmetry 26. Respiratory structures that remove oxygen from water 28. Specialized nerve cells 29. How animals take in food 30. Number of tissue la ...
Cryolophosaurus ellioti
... 225 MYA- one super continent Laurasia & Gonwanaland: 200 MYA- Pangaea separated into 2 continents Today: 7 major continents due to plate movement Evidence: Polar Dinosaur Cryolophosaurus ellioti: fossils found in S. Australia and in Antarctica ...
... 225 MYA- one super continent Laurasia & Gonwanaland: 200 MYA- Pangaea separated into 2 continents Today: 7 major continents due to plate movement Evidence: Polar Dinosaur Cryolophosaurus ellioti: fossils found in S. Australia and in Antarctica ...
G1-2 Evolution Ch 15
... one amino acid/ human and frog hemoglobin differ by 67 amino acids). II Patterns of Evolution A. Coevolution 1. Predators and their prey often coevolve 2. Plant-eating animals and plants often coevolve (example: bats feed on nectar, flowers are light in color to see at night) B. Convergent Evolution ...
... one amino acid/ human and frog hemoglobin differ by 67 amino acids). II Patterns of Evolution A. Coevolution 1. Predators and their prey often coevolve 2. Plant-eating animals and plants often coevolve (example: bats feed on nectar, flowers are light in color to see at night) B. Convergent Evolution ...
October 4 2016 Bellringer Intro to Living Planet
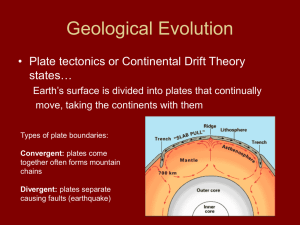
... Bellringer Intro to Living Planet ■ What are the three layers of the earth. And what do they consist of? ■ What is the biosphere, and what are its three main parts? ■ What is continental drift hypothesis? ...
... Bellringer Intro to Living Planet ■ What are the three layers of the earth. And what do they consist of? ■ What is the biosphere, and what are its three main parts? ■ What is continental drift hypothesis? ...
Charles Darwin`s Theory of Evolution
... Charles Darwin's Theory of Evolution Brief Summary Darwin's theory of evolution is based on five key observations and inferences drawn from them. These observations and inferences have been summarized by the great biologist Ernst Mayr as follows: 1) Species have great fertility. They make more offsp ...
... Charles Darwin's Theory of Evolution Brief Summary Darwin's theory of evolution is based on five key observations and inferences drawn from them. These observations and inferences have been summarized by the great biologist Ernst Mayr as follows: 1) Species have great fertility. They make more offsp ...
Evolution of Evolution
... Used comparative anatomy to create replicas of extinct animals in which only a few fossils were found Hypothesized that animals became extinct due to catastrophes in history…BUT what about humans?? ...
... Used comparative anatomy to create replicas of extinct animals in which only a few fossils were found Hypothesized that animals became extinct due to catastrophes in history…BUT what about humans?? ...
Chapter 14
... Theory stated- Proposed that selective use or disuse of organs caused organisms to acquire or lose certain traits during their lifetime Then these could be passed to offspring and over time could lead to a change in species (Ex. Giraffes long necks) What is wrong with this idea? ...
... Theory stated- Proposed that selective use or disuse of organs caused organisms to acquire or lose certain traits during their lifetime Then these could be passed to offspring and over time could lead to a change in species (Ex. Giraffes long necks) What is wrong with this idea? ...
Chapter 5 Outline APES
... range of tolerance to different physical and chemical conditions. types of competitors. Habitat is the location where a species lives. convergent evolution. is species belonging to different taxonomic groups may develop a resemblance resulting from adaptation to similar environments. ...
... range of tolerance to different physical and chemical conditions. types of competitors. Habitat is the location where a species lives. convergent evolution. is species belonging to different taxonomic groups may develop a resemblance resulting from adaptation to similar environments. ...
File
... 30. Any two of the following: Mutation; genetic recombination through sexual reproduction; introduction of new genes due to migration; 31. Organisms can be preserved in ice, amber, or tar as well as rock. 32. Fossils found near the surface would generally be considered younger than those found deepe ...
... 30. Any two of the following: Mutation; genetic recombination through sexual reproduction; introduction of new genes due to migration; 31. Organisms can be preserved in ice, amber, or tar as well as rock. 32. Fossils found near the surface would generally be considered younger than those found deepe ...
Evolution Unit Test Review with answers
... 18. What is a vestigial structure? How does this give evidence of evolution? Organ that currently serves no useful function in an organism, but most likely had a function in an ancestor. 19. Organisms that are the most alike in body structure, reproductive processes, and feeding patterns most likely ...
... 18. What is a vestigial structure? How does this give evidence of evolution? Organ that currently serves no useful function in an organism, but most likely had a function in an ancestor. 19. Organisms that are the most alike in body structure, reproductive processes, and feeding patterns most likely ...
Facts you need to know to pass the Living Environment
... 25.___________ is any condition that prevents the body from working as it should. 26.___________ certain genetic mutations in a cell can result in uncontrolled cell division. 27.____________system is the body's primary defense against disease-causing pathogens. 28._____________- a molecule found on ...
... 25.___________ is any condition that prevents the body from working as it should. 26.___________ certain genetic mutations in a cell can result in uncontrolled cell division. 27.____________system is the body's primary defense against disease-causing pathogens. 28._____________- a molecule found on ...
TAKS Review - Greenslime
... D. more sugar is produced E. water is pumped out of the cells F. more sugar is consumed ...
... D. more sugar is produced E. water is pumped out of the cells F. more sugar is consumed ...
vocabularyPART1
... EVOLUTION is change over time. EVOLUTIONARY THEORY is an explanation of phenomena supported by a collection of scientific facts, observation and hypothesis. FOSSILS are preserved remains of ancient organisms found in sedimentary rock (soil type). ...
... EVOLUTION is change over time. EVOLUTIONARY THEORY is an explanation of phenomena supported by a collection of scientific facts, observation and hypothesis. FOSSILS are preserved remains of ancient organisms found in sedimentary rock (soil type). ...
Evolution Notes
... From fossils we can infer, – Adjacent/Horizontal Layering • Different organisms lived at different times. – Radioactive Dating – Half-lives – Relate Age Dating ...
... From fossils we can infer, – Adjacent/Horizontal Layering • Different organisms lived at different times. – Radioactive Dating – Half-lives – Relate Age Dating ...
Evolution Study Guide: Chapters 16
... cells use information coded in RNA__and _DNA__to carry information from one generation to the next and to direct PROTEIN synthesis 12) P 472-3 Peter & Rosemary Grant have spent more that 35 years studying Galapagos finches. They found that the different variations in beak size and shape produced dif ...
... cells use information coded in RNA__and _DNA__to carry information from one generation to the next and to direct PROTEIN synthesis 12) P 472-3 Peter & Rosemary Grant have spent more that 35 years studying Galapagos finches. They found that the different variations in beak size and shape produced dif ...
Evolution Power Point
... strongest): Those with more adaptive traits tend to survive longer and/or produce the most offspring. ...
... strongest): Those with more adaptive traits tend to survive longer and/or produce the most offspring. ...
Evolutionary history of life

The evolutionary history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and fossil organisms have evolved since life appeared on the planet, until the present day. Earth formed about 4.5 Ga (billion years ago) and life appeared on its surface within 1 billion years. The similarities between all present-day organisms indicate the presence of a common ancestor from which all known species have diverged through the process of evolution. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.