practice questions
... 7. When Darwin returned from the voyage of the Beagle, he a. immediately published his ideas about evolution. b. realized his ideas about evolution were wrong. c. wrote about his ideas but waited many years to publish them. d. copied the evolutionary theory of Wallace. 8. When lions prey on a herd o ...
... 7. When Darwin returned from the voyage of the Beagle, he a. immediately published his ideas about evolution. b. realized his ideas about evolution were wrong. c. wrote about his ideas but waited many years to publish them. d. copied the evolutionary theory of Wallace. 8. When lions prey on a herd o ...
Life Science (Diversity and Natural Selection)
... LS.1.2.c Throughout Earth’s history, extinction of a species has occurred when the environment changes and the individual organisms of that species do not have the traits necessary to survive and reproduce in the changed environment. Most species (approximately 99 percent) that have lived on Earth a ...
... LS.1.2.c Throughout Earth’s history, extinction of a species has occurred when the environment changes and the individual organisms of that species do not have the traits necessary to survive and reproduce in the changed environment. Most species (approximately 99 percent) that have lived on Earth a ...
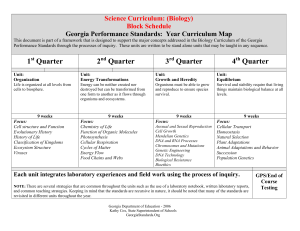
Curriculum Map - Biology
... Georgia Performance Standards: Year Curriculum Map This document is part of a framework that is designed to support the major concepts addressed in the Biology Curriculum of the Georgia Performance Standards through the processes of inquiry. These units are written to be stand alone units that may b ...
... Georgia Performance Standards: Year Curriculum Map This document is part of a framework that is designed to support the major concepts addressed in the Biology Curriculum of the Georgia Performance Standards through the processes of inquiry. These units are written to be stand alone units that may b ...
Bio 152 – Summer 2006 Week 2 OBJECTIVES: Lecture 5 1. What is
... 1. Describe reproduction in prokaryotes. 2. Briefly summarize the mitosis cycle. 3. What is the purpose of mitosis? 4. Briefly summarize the meiosis cycle. 5. What are the unique features of meiosis? 6. When do mitosis and meiosis occur during the life of an organism? 7. Explain the term nondisjunct ...
... 1. Describe reproduction in prokaryotes. 2. Briefly summarize the mitosis cycle. 3. What is the purpose of mitosis? 4. Briefly summarize the meiosis cycle. 5. What are the unique features of meiosis? 6. When do mitosis and meiosis occur during the life of an organism? 7. Explain the term nondisjunct ...
File eoct review with answers
... b. Geographic isolation: rivers, oceans, mountain ranges, and other land forms separate members of the same species c. Temporal isolation: reproduce at different times. 55. What is the combined genetic information of all members of a particular population called? Gene pool 56. What is extinction. Gi ...
... b. Geographic isolation: rivers, oceans, mountain ranges, and other land forms separate members of the same species c. Temporal isolation: reproduce at different times. 55. What is the combined genetic information of all members of a particular population called? Gene pool 56. What is extinction. Gi ...
Multifactorial Traits
... • The further you go back in time, the more proteins (and DNA) are different. • Differences in protein sequences and DNA can be used to estimate time when two species shared a common ancestor ...
... • The further you go back in time, the more proteins (and DNA) are different. • Differences in protein sequences and DNA can be used to estimate time when two species shared a common ancestor ...
1) Which of the following is not true of
... B Fungi are multicellular autotrophs. C Fungi lack hydrolytic enzymes within their protoplasm. D Fungi are unable to make food from inorganic materials. ...
... B Fungi are multicellular autotrophs. C Fungi lack hydrolytic enzymes within their protoplasm. D Fungi are unable to make food from inorganic materials. ...
T-1 Chapter One: Biology- Study of Life
... a) All organisms are made up of one or more cells. - A cell is the basic unit of life. Single-celled organisms are the most common organisms on Earth, while multi-cellular organisms are the other type. Cells in multi-cellular organisms specialize to perform specific functions within the organism (ie ...
... a) All organisms are made up of one or more cells. - A cell is the basic unit of life. Single-celled organisms are the most common organisms on Earth, while multi-cellular organisms are the other type. Cells in multi-cellular organisms specialize to perform specific functions within the organism (ie ...
Final Exam Free Response Review 1. Errors in mitosis and meiosis
... b. How can the H-W principle of genetic equilibrium be used to determine whether this population is evolving? 7. In order for a new species to form, members of a population must become genetically separated from one another until genes can no longer flow between them. a. Identify and explain two met ...
... b. How can the H-W principle of genetic equilibrium be used to determine whether this population is evolving? 7. In order for a new species to form, members of a population must become genetically separated from one another until genes can no longer flow between them. a. Identify and explain two met ...
Structure and Function in Living Systems Chapter 8: Systems in
... each doing something different in order to produce and serve the meals. In a complicated process like this one, it helps to have different ...
... each doing something different in order to produce and serve the meals. In a complicated process like this one, it helps to have different ...
Cells Study Guide
... Heredity – the passing of trait from parents to offspring o Asexual reproduction - organisms that reproduce with only one parent (one set of genetic material) and offspring are identical to parent o Benefits of asexual reproduction include the ability to reproduce rapidly and they do not need to spe ...
... Heredity – the passing of trait from parents to offspring o Asexual reproduction - organisms that reproduce with only one parent (one set of genetic material) and offspring are identical to parent o Benefits of asexual reproduction include the ability to reproduce rapidly and they do not need to spe ...
Analogous Structures
... The banana bunch eventually washes up on an island off the coast of the mainland. The fruit flies mature and emerge from their slimy nursery onto the lonely island. At this point, speciation has not occurred — any fruit flies that got back to the mainland could mate and produce healthy offspring wit ...
... The banana bunch eventually washes up on an island off the coast of the mainland. The fruit flies mature and emerge from their slimy nursery onto the lonely island. At this point, speciation has not occurred — any fruit flies that got back to the mainland could mate and produce healthy offspring wit ...
Animals
... other, many of them have similar features that allow us to put them into groups. • Putting different species into different groups according to their features is called classification. ...
... other, many of them have similar features that allow us to put them into groups. • Putting different species into different groups according to their features is called classification. ...
Natural Selection - Madeira City Schools
... • We know that acquired traits on not passed on through the dna • But the fact that species change, and the idea that an organism’s traits help it survive, really shaped Darwin’s ideas ...
... • We know that acquired traits on not passed on through the dna • But the fact that species change, and the idea that an organism’s traits help it survive, really shaped Darwin’s ideas ...
Review for BCT
... to support evolution and shared common ancestors: DNA/Protein structures (molecular) – more similar the sequences or structure the more closely related two organisms are Anatomy – similar body structures can provide information about relationships and ancestry Embryonic development – the stages ...
... to support evolution and shared common ancestors: DNA/Protein structures (molecular) – more similar the sequences or structure the more closely related two organisms are Anatomy – similar body structures can provide information about relationships and ancestry Embryonic development – the stages ...
REVIEW 6: EVOLUTION 1. Define evolution
... b. “The organism evolved to live in its environment.” Individual organisms do not evolve. Only populations can evolve. Individual organisms are selected to survive or not to survive. c. “The organism could not adapt and it went extinct.” Individual organisms die; they cannot go extinct. Only species ...
... b. “The organism evolved to live in its environment.” Individual organisms do not evolve. Only populations can evolve. Individual organisms are selected to survive or not to survive. c. “The organism could not adapt and it went extinct.” Individual organisms die; they cannot go extinct. Only species ...
No Slide Title - Hightower Trail
... Why do evolutionary biologists think that related species have similar body structures and development patterns? ...
... Why do evolutionary biologists think that related species have similar body structures and development patterns? ...
Theories of Evolution
... Microevolution: Small-scale evolutionary changes, usually on the molecular level, that occur over the span of a few generations and can therefore be detected in living populations. ...
... Microevolution: Small-scale evolutionary changes, usually on the molecular level, that occur over the span of a few generations and can therefore be detected in living populations. ...
Review - Evolution (2014)
... visited 4 different types of organisms that live in the Galapagos Islands. Explain how Darwin’s finches help to support the theory of natural selection ~ USE ...
... visited 4 different types of organisms that live in the Galapagos Islands. Explain how Darwin’s finches help to support the theory of natural selection ~ USE ...
Crossword and vocabulary
... provide recognizable evidence of organisms that lived long ago 15. Random changes in DNA molecules making up genes that can alter anatomy and physiology in offspring 18. Species that is found in only one area 20. Parts of the fundamental niche of a species that are actually used by that species 21. ...
... provide recognizable evidence of organisms that lived long ago 15. Random changes in DNA molecules making up genes that can alter anatomy and physiology in offspring 18. Species that is found in only one area 20. Parts of the fundamental niche of a species that are actually used by that species 21. ...
Evolution - NVHSIntroBioPiper1
... C demonstrating altruistic behavior are the ones with the most mutations D remain unchanged over a period of time 2. Which of the following best defines common descent? A All organisms came from the same ancestor. B All organisms have certain traits in common. C All organisms descended from organism ...
... C demonstrating altruistic behavior are the ones with the most mutations D remain unchanged over a period of time 2. Which of the following best defines common descent? A All organisms came from the same ancestor. B All organisms have certain traits in common. C All organisms descended from organism ...
Darwin`s Theory of Evolution
... slow and gradual process. Still, if evolution is gradual, there should be a fossilized record of small, incremental changes on the way to a new species. His conclusion was that the fossil record lacked these transitional stages because it was incomplete. • In 1972, evolutionary scientists Stephen Ja ...
... slow and gradual process. Still, if evolution is gradual, there should be a fossilized record of small, incremental changes on the way to a new species. His conclusion was that the fossil record lacked these transitional stages because it was incomplete. • In 1972, evolutionary scientists Stephen Ja ...
Evolution by Natural Selection
... Earth over time 2. Charles Lyell hypothesized that small changes in rock have collected over hundreds of millions of years ...
... Earth over time 2. Charles Lyell hypothesized that small changes in rock have collected over hundreds of millions of years ...
Evolutionary history of life

The evolutionary history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and fossil organisms have evolved since life appeared on the planet, until the present day. Earth formed about 4.5 Ga (billion years ago) and life appeared on its surface within 1 billion years. The similarities between all present-day organisms indicate the presence of a common ancestor from which all known species have diverged through the process of evolution. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.