Marine Biology Name: Osmoregulation WebQuest Period: ______
... Osmoregulation is the active regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism's fluids to maintain the homeostasis of the organism's water content; that is, it keeps the organism's fluids from becoming too diluted or too concentrated. Osmotic pressure is a measure of the tendency of water to move i ...
... Osmoregulation is the active regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism's fluids to maintain the homeostasis of the organism's water content; that is, it keeps the organism's fluids from becoming too diluted or too concentrated. Osmotic pressure is a measure of the tendency of water to move i ...
Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 1: The Changing Earth Lesson 1
... 1. A river carries sediments into a shallow sea and deposits them on the bottom. Layers build up. 2. Dead animals sink to the bottom. Layer after layer of sediments are deposited on top. 3. Over time, the lower layers form sedimentary rock. The remains of the dead animals form fossils. 4. Fossils in ...
... 1. A river carries sediments into a shallow sea and deposits them on the bottom. Layers build up. 2. Dead animals sink to the bottom. Layer after layer of sediments are deposited on top. 3. Over time, the lower layers form sedimentary rock. The remains of the dead animals form fossils. 4. Fossils in ...
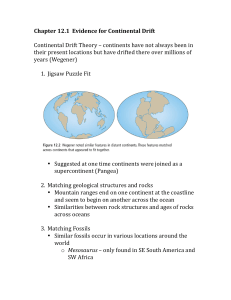
Chapter 12.1 Evidence for Continental Drift Continental Drift Theory
... Chapter 12.1 Evidence for Continental Drift ...
... Chapter 12.1 Evidence for Continental Drift ...
Bio II Chapter 32 - Marissa Junior/Senior High School
... All except fishes spend part or all of their life on land In order to adapt to life on land: Support of the body Conservation of water ...
... All except fishes spend part or all of their life on land In order to adapt to life on land: Support of the body Conservation of water ...
What Is an Animal?
... Muscle contraction enables animals to move around, usually by working in combination with a skeleton. ...
... Muscle contraction enables animals to move around, usually by working in combination with a skeleton. ...
ECOLOGY SPRING 2009 - Florida International University
... The taxonomic group “apes” is paraphyletic Some apes are more closely related to hominids than to other apes. Living apes consist of gibbons, orangutans, gorillas and chimpanzees Hominids consist of humans and their direct ancestors Common ancestor was more like a chimpanzee than a gorilla ...
... The taxonomic group “apes” is paraphyletic Some apes are more closely related to hominids than to other apes. Living apes consist of gibbons, orangutans, gorillas and chimpanzees Hominids consist of humans and their direct ancestors Common ancestor was more like a chimpanzee than a gorilla ...
Unit 6: Adaptations Over Time
... most organisms do not become • The _______ fossils simpler • By looking at fossils scientists conclude that many _________ forms of life existed ________ earlier in Earth’s history, and more _________ complex forms of life appeared ________ later indirect evidence that evolution has occurred • Fossi ...
... most organisms do not become • The _______ fossils simpler • By looking at fossils scientists conclude that many _________ forms of life existed ________ earlier in Earth’s history, and more _________ complex forms of life appeared ________ later indirect evidence that evolution has occurred • Fossi ...
Unit 6: Adaptations Over Time
... most organisms do not become • The _______ fossils simpler • By looking at fossils scientists conclude that many _________ forms of life existed ________ earlier in Earth’s history, and more _________ complex forms of life appeared ________ later indirect evidence that evolution has occurred • Fossi ...
... most organisms do not become • The _______ fossils simpler • By looking at fossils scientists conclude that many _________ forms of life existed ________ earlier in Earth’s history, and more _________ complex forms of life appeared ________ later indirect evidence that evolution has occurred • Fossi ...
1 EARTH SCIENCE Lithosphere is the earth`s rock layer
... In an energy pyramid, producers/plants are found at the bottom because they contain the most energy in an ecosystem. The producers use the sun’s energy directly for the process of photosynthesis ...
... In an energy pyramid, producers/plants are found at the bottom because they contain the most energy in an ecosystem. The producers use the sun’s energy directly for the process of photosynthesis ...
IB Biology Name Problem Set Unit 5 – Evolution 1. What is evolution
... A physical change during an organism’s life that is inherited by its offspring D. A random change in the proportions of alleles from generation to generation ...
... A physical change during an organism’s life that is inherited by its offspring D. A random change in the proportions of alleles from generation to generation ...
Unit 1 Evolution Chp 22 Module 2
... 18. Below are three different images. The first image is of the Galapagos finches. The second image is of the Galapagos Islands and the third image is illustrating the process of colonization and speciation of an archipelago. Give a brief “Darwinian” explanation of how the 14 species of finches cam ...
... 18. Below are three different images. The first image is of the Galapagos finches. The second image is of the Galapagos Islands and the third image is illustrating the process of colonization and speciation of an archipelago. Give a brief “Darwinian” explanation of how the 14 species of finches cam ...
History of Earth
... • Collection of all types of fossilized organisms that have been discovered • Millions of species of fossilized organisms have been discovered – Estimated to be about 2% of all species that have lived on Earth – New species are still being found ...
... • Collection of all types of fossilized organisms that have been discovered • Millions of species of fossilized organisms have been discovered – Estimated to be about 2% of all species that have lived on Earth – New species are still being found ...
Kinds, individuals, organisms
... essential properties. Historically it is related to the pre-evolutionary stage based on the description and classification of organic types. The second rejects the notion of class and is attached to the mereological notion of individual. Organisms, as well as species (and other categories in the hie ...
... essential properties. Historically it is related to the pre-evolutionary stage based on the description and classification of organic types. The second rejects the notion of class and is attached to the mereological notion of individual. Organisms, as well as species (and other categories in the hie ...
9554Terms and Definitions
... ecosystem consists of producers and consumers. Plants are producers in the ecosystem chain. Animals that are consumers are next in the ecosystem. Some of these animals are known as herbivores, which eat only plants. Carnivores are the animals that get their energy from eating other animals. The next ...
... ecosystem consists of producers and consumers. Plants are producers in the ecosystem chain. Animals that are consumers are next in the ecosystem. Some of these animals are known as herbivores, which eat only plants. Carnivores are the animals that get their energy from eating other animals. The next ...
The Four Spheres of the Earth
... The atmosphere is the body of air which surrounds our planet. Most of our atmosphere is located close to the earth's surface where it is most dense. The air of our planet is 79% nitrogen and just under 21% oxygen; the small amount remaining is composed of carbon dioxide and other gasses. It also inc ...
... The atmosphere is the body of air which surrounds our planet. Most of our atmosphere is located close to the earth's surface where it is most dense. The air of our planet is 79% nitrogen and just under 21% oxygen; the small amount remaining is composed of carbon dioxide and other gasses. It also inc ...
evolution - Laurel County Schools
... • Organisms produce more offspring than can survive. For example fish sometime lay millions of eggs • In any population, individuals have variations. (size, color, speed) • Individuals, with certain useful variations, such as speed or being able to avoid predators, will survive in their environment, ...
... • Organisms produce more offspring than can survive. For example fish sometime lay millions of eggs • In any population, individuals have variations. (size, color, speed) • Individuals, with certain useful variations, such as speed or being able to avoid predators, will survive in their environment, ...
powerpoint notes - Social Circle City Schools
... only two cell layers (no tissues, organs, or systems) Sometimes considered a colony of cells ...
... only two cell layers (no tissues, organs, or systems) Sometimes considered a colony of cells ...
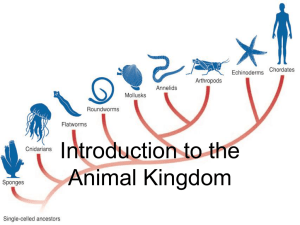
Introduction to the Animal Kingdom
... Introduction to the Animal Kingdom • Animals are multicellular eukaryotic heterotroph whose cells lack cell walls • Vertebrates: 5% of animal species with backbones • Invertebrates: 95% of animal species WITHOUT backbones • Cell specialization – special shape, physical structure, and chemical compo ...
... Introduction to the Animal Kingdom • Animals are multicellular eukaryotic heterotroph whose cells lack cell walls • Vertebrates: 5% of animal species with backbones • Invertebrates: 95% of animal species WITHOUT backbones • Cell specialization – special shape, physical structure, and chemical compo ...
File - Science 10 Enriched
... Evidence of ___________ in parts of the world that are now tropical, such as parts of India and Africa. ...
... Evidence of ___________ in parts of the world that are now tropical, such as parts of India and Africa. ...
GRADE 6 SCIENCE NOTES
... Very Short answer questions: 1. All living things move and all non-living things do not move .True or false? False. 2. Which of these grow through their life-plants or animals? Plants. 3. What is the process of removal of waste products from the body called? Excretion. 4.When oxygen and food combine ...
... Very Short answer questions: 1. All living things move and all non-living things do not move .True or false? False. 2. Which of these grow through their life-plants or animals? Plants. 3. What is the process of removal of waste products from the body called? Excretion. 4.When oxygen and food combine ...
Evolutionary history of life

The evolutionary history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and fossil organisms have evolved since life appeared on the planet, until the present day. Earth formed about 4.5 Ga (billion years ago) and life appeared on its surface within 1 billion years. The similarities between all present-day organisms indicate the presence of a common ancestor from which all known species have diverged through the process of evolution. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.