organisms - Lyndhurst Schools
... • BIOLOGY is the study of life. • Living things are called ORGANISMS. o Include animals, plants, fungi, protist, and bacteria. ...
... • BIOLOGY is the study of life. • Living things are called ORGANISMS. o Include animals, plants, fungi, protist, and bacteria. ...
Evolution as Theory and Fact
... Genetic code of chimps and gorillas is almost identical to humans • If evolution is true then we might also expect that closely related organisms will be more similar to one another than more distantly related organisms. • Comparison of the human genetic code with that of other organisms show that c ...
... Genetic code of chimps and gorillas is almost identical to humans • If evolution is true then we might also expect that closely related organisms will be more similar to one another than more distantly related organisms. • Comparison of the human genetic code with that of other organisms show that c ...
Notes: Chapter 15 Darwin`s Theory of Evolution
... D. “Survival of the fittest” E. Natural selection is how evolution occurs F. Natural selection results in changes in the inherited traits of a population G. Cannot be seen directly – takes place over many generations over a long period of time IV. Descent with modification – natural selection produc ...
... D. “Survival of the fittest” E. Natural selection is how evolution occurs F. Natural selection results in changes in the inherited traits of a population G. Cannot be seen directly – takes place over many generations over a long period of time IV. Descent with modification – natural selection produc ...
Evolution Review Game
... evolution by natural selection, organisms with adaptations are more likely to survive and _____. ...
... evolution by natural selection, organisms with adaptations are more likely to survive and _____. ...
Notes on Evolution
... The Modern Theory of Evolution a. An attempt to explain WHY evolution happens b. Lamarck’s Theory i. Use and disuse 1. The more an organ is used, the bigger and more developed it becomes; the less an organ is used, the small and less developed it becomes ii. Inheritance of acquired characteristics 1 ...
... The Modern Theory of Evolution a. An attempt to explain WHY evolution happens b. Lamarck’s Theory i. Use and disuse 1. The more an organ is used, the bigger and more developed it becomes; the less an organ is used, the small and less developed it becomes ii. Inheritance of acquired characteristics 1 ...
2013 Taxonomy Notes ppt
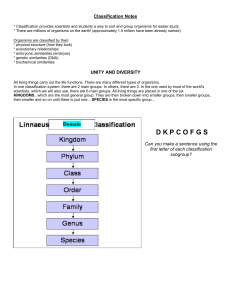
... Classification Notes * Classification provides scientists and students a way to sort and group organisms for easier study. * There are millions of organisms on the earth! (approximately 1.5 million have been already named) Organisms are classified by their: * physical structure (how they look) * evo ...
... Classification Notes * Classification provides scientists and students a way to sort and group organisms for easier study. * There are millions of organisms on the earth! (approximately 1.5 million have been already named) Organisms are classified by their: * physical structure (how they look) * evo ...
Evolution - flickbio
... • Virus from outer space – kills blueeyed people (but does not change a person’s eyes to blue) • Spadefoot toad – must bury itself in the ground and mate quickly when it comes to the surface, therefore, it has a loud croak and long toes! ...
... • Virus from outer space – kills blueeyed people (but does not change a person’s eyes to blue) • Spadefoot toad – must bury itself in the ground and mate quickly when it comes to the surface, therefore, it has a loud croak and long toes! ...
Natual Selection and Evolution - ahs-honorsbio2009-1
... Evaluate hypotheses about the origin of life and identify the probable characteristics of early life-forms Distinguish between chemical and biological evolution Describe the fossil record for prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Explain homology and give examples of homologous structures Describe how the gen ...
... Evaluate hypotheses about the origin of life and identify the probable characteristics of early life-forms Distinguish between chemical and biological evolution Describe the fossil record for prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Explain homology and give examples of homologous structures Describe how the gen ...
15-1 The Puzzle of Life*s Diversity
... Darwin’s Observations populations tend to remain stable in size ...
... Darwin’s Observations populations tend to remain stable in size ...
Evolution - Angelfire
... Organisms that share more similar enzymes, DNA sequences, etc. are more closely related ...
... Organisms that share more similar enzymes, DNA sequences, etc. are more closely related ...
Topic 3 Notes - Gouverneur Central School District
... Types of Deformed strata1. Folded: (bend) by compressional forces, syncline (smile) and anticline (frown) 2. Tilted: uplift or subsidence, strata is at an angle 3. Faulted: crack or break in the strata with displacement (they have moved) types of fault: reverse fault- caused by compressional forces ...
... Types of Deformed strata1. Folded: (bend) by compressional forces, syncline (smile) and anticline (frown) 2. Tilted: uplift or subsidence, strata is at an angle 3. Faulted: crack or break in the strata with displacement (they have moved) types of fault: reverse fault- caused by compressional forces ...
CH15 PowerPoint
... 1. Fossil Record 2. Biogeography (Geographic Distribution of Living Species) ...
... 1. Fossil Record 2. Biogeography (Geographic Distribution of Living Species) ...
Homeostasis
... Explain why large active animals such as humans also require a circulatory system Say what factors control the rate of gaseous exchange and excretory functions. ...
... Explain why large active animals such as humans also require a circulatory system Say what factors control the rate of gaseous exchange and excretory functions. ...
Indirect Evidence of Evolution
... Features that are similar in appearance and function, but do not appear to have the same evolutionary origin Example: wings of a insect and wings of a bird ...
... Features that are similar in appearance and function, but do not appear to have the same evolutionary origin Example: wings of a insect and wings of a bird ...
Fossils
... – Observation #2: All species can produce more offspring than the environment can support, and many of these offspring fail to survive and reproduce – Inference #2: This unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce will lead to the accumulation of favorable traits in the ...
... – Observation #2: All species can produce more offspring than the environment can support, and many of these offspring fail to survive and reproduce – Inference #2: This unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce will lead to the accumulation of favorable traits in the ...
Evolution - Jessamine County Schools
... have genetically based traits that cause them to survive and produce more offspring than other individuals Gene flow – involves movement of genes between populations and can lead to changes in the genetic composition of local populations. Genetic drift – involves changes in the genetic composition o ...
... have genetically based traits that cause them to survive and produce more offspring than other individuals Gene flow – involves movement of genes between populations and can lead to changes in the genetic composition of local populations. Genetic drift – involves changes in the genetic composition o ...
Ch. 14.1: Darwin developed a Theory of Evolution
... • Adaptation: Some variations provide an advantage that increases chances of survival. • Survival of the Fittest: Those with the adaptations are more likely to survive and reproduce • Descent with Modification: Genes for beneficial adaptations are passed on & trait becomes more common in each new ...
... • Adaptation: Some variations provide an advantage that increases chances of survival. • Survival of the Fittest: Those with the adaptations are more likely to survive and reproduce • Descent with Modification: Genes for beneficial adaptations are passed on & trait becomes more common in each new ...
What Can Changes Inside Earth Communicate? Pre/Post Test 1
... a layer of rock that forms Earth’s outer skin ...
... a layer of rock that forms Earth’s outer skin ...
Earth and Space Science (The Rock and Fossil Record)
... Radioactive Decay Radiometric Dating Half-life Fossil Trace Fossil Mold Cast Index Fossil ...
... Radioactive Decay Radiometric Dating Half-life Fossil Trace Fossil Mold Cast Index Fossil ...
Evolution - Ardsley Schools
... – Individuals Do Not evolve, only populations evolve – Change in the frequency of alleles in a population of time ...
... – Individuals Do Not evolve, only populations evolve – Change in the frequency of alleles in a population of time ...
evolutionpowerpoint_1
... • Sir Charles Lyell (Father of modern geology)-popularized idea of uniformitariansm including that the Earth is much older than originally believed and changes continually • Erasmus Darwin (Grandpa Darwin) wrote of Evolution before Charles was born • Patrick Matthew writes about principles of natura ...
... • Sir Charles Lyell (Father of modern geology)-popularized idea of uniformitariansm including that the Earth is much older than originally believed and changes continually • Erasmus Darwin (Grandpa Darwin) wrote of Evolution before Charles was born • Patrick Matthew writes about principles of natura ...
Paleontology

Paleontology or palaeontology (/ˌpeɪlɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpeɪlɪənˈtɒlədʒi/ or /ˌpælɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpælɪənˈtɒlədʒi/) is the scientific study of life existent prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene Epoch roughly 11,700 years before present. It includes the study of fossils to determine organisms' evolution and interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek παλαιός, palaios, i.e. ""old, ancient"", ὄν, on (gen. ontos), i.e. ""being, creature"" and λόγος, logos, i.e. ""speech, thought, study"".Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of morphologically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics and engineering. Use of all these techniques has enabled paleontologists to discover much of the evolutionary history of life, almost all the way back to when Earth became capable of supporting life, about 3,800 million years ago. As knowledge has increased, paleontology has developed specialised sub-divisions, some of which focus on different types of fossil organisms while others study ecology and environmental history, such as ancient climates.Body fossils and trace fossils are the principal types of evidence about ancient life, and geochemical evidence has helped to decipher the evolution of life before there were organisms large enough to leave body fossils. Estimating the dates of these remains is essential but difficult: sometimes adjacent rock layers allow radiometric dating, which provides absolute dates that are accurate to within 0.5%, but more often paleontologists have to rely on relative dating by solving the ""jigsaw puzzles"" of biostratigraphy. Classifying ancient organisms is also difficult, as many do not fit well into the Linnean taxonomy that is commonly used for classifying living organisms, and paleontologists more often use cladistics to draw up evolutionary ""family trees"". The final quarter of the 20th century saw the development of molecular phylogenetics, which investigates how closely organisms are related by measuring how similar the DNA is in their genomes. Molecular phylogenetics has also been used to estimate the dates when species diverged, but there is controversy about the reliability of the molecular clock on which such estimates depend.