Natural selection and adaptation
... Uniformitarianism • Hutton’s theories got to a frontal attack on a popular contemporary school of thought called catastrophism ...
... Uniformitarianism • Hutton’s theories got to a frontal attack on a popular contemporary school of thought called catastrophism ...
01 - Cobb Learning
... b. Earth changes only at certain times and only after certain events. c. Earth is uniform and unchanging; it has always been as it is now. d. the same geologic processes have been at work throughout Earth’s history. 3. Which of the following processes was NOT observed by Hutton when he developed the ...
... b. Earth changes only at certain times and only after certain events. c. Earth is uniform and unchanging; it has always been as it is now. d. the same geologic processes have been at work throughout Earth’s history. 3. Which of the following processes was NOT observed by Hutton when he developed the ...
The Geologic Time Scale
... The remains and evidence of plants and animals that once lived on Earth are called fossils. Fossils preserved in the rock record provide information about past environmental conditions, evolutionary changes in life-forms, and help geologists to correlate rock layers from one area to another. ...
... The remains and evidence of plants and animals that once lived on Earth are called fossils. Fossils preserved in the rock record provide information about past environmental conditions, evolutionary changes in life-forms, and help geologists to correlate rock layers from one area to another. ...
natural selection
... so the more variety there is, the more there can be in the future. But evolution does not necessitate long term progress in some set direction. Evolutionary change appears to be like the growth of a bush: Some branches survive from the beginning with little or no change, many die out altogether, and ...
... so the more variety there is, the more there can be in the future. But evolution does not necessitate long term progress in some set direction. Evolutionary change appears to be like the growth of a bush: Some branches survive from the beginning with little or no change, many die out altogether, and ...
Greater Latrobe School District Weekly Lesson Plan
... Objective(s): Summarize the concept of evolution and the five assumptions of Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium. Instructional Strategies: 1. Complete the Flashy Fish online activity investigating the impact of natural selection and sexual selection on a population. 2. Continue to investigate the interactio ...
... Objective(s): Summarize the concept of evolution and the five assumptions of Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium. Instructional Strategies: 1. Complete the Flashy Fish online activity investigating the impact of natural selection and sexual selection on a population. 2. Continue to investigate the interactio ...
File
... • From seismic and other geophysical evidence and laboratory experiments, scientists agree with the theory that the plate-driving force is the slow movement of hot, softened mantle that lies below the rigid plates • Below the lithospheric plates, at some depth the mantle is partially molten and can ...
... • From seismic and other geophysical evidence and laboratory experiments, scientists agree with the theory that the plate-driving force is the slow movement of hot, softened mantle that lies below the rigid plates • Below the lithospheric plates, at some depth the mantle is partially molten and can ...
Evolutionary Theory 3
... What Darwin Explained • Darwin presented a unifying explanation for data from multiple fields of science. • Today, those fields include geology, geography, ecology, developmental biology, anatomy, genetics, and biochemistry. • Scientists continue to draw on the power of Darwin’s explanations. ...
... What Darwin Explained • Darwin presented a unifying explanation for data from multiple fields of science. • Today, those fields include geology, geography, ecology, developmental biology, anatomy, genetics, and biochemistry. • Scientists continue to draw on the power of Darwin’s explanations. ...
chapter 16 practice test evolution
... necessary. Evolutionary theory is like all of the other sciences in this respect. Science is always trying to improve our knowledge. At present, evolution is the only well-supported natural explanation for all of life’s diversity. The Theory is Flawed o Science is an extremely competitive field – if ...
... necessary. Evolutionary theory is like all of the other sciences in this respect. Science is always trying to improve our knowledge. At present, evolution is the only well-supported natural explanation for all of life’s diversity. The Theory is Flawed o Science is an extremely competitive field – if ...
CHAPTER 16 PRACTICE TEST EVOLUTION
... necessary. Evolutionary theory is like all of the other sciences in this respect. Science is always trying to improve our knowledge. At present, evolution is the only well-supported natural explanation for all of life’s diversity. The Theory is Flawed o Science is an extremely competitive field – if ...
... necessary. Evolutionary theory is like all of the other sciences in this respect. Science is always trying to improve our knowledge. At present, evolution is the only well-supported natural explanation for all of life’s diversity. The Theory is Flawed o Science is an extremely competitive field – if ...
Evolution - clarkdanderson
... Natural selection - tendency of organisms with favorable adaptations to their environment to survive and produce new generations • Theory proposed by Charles Darwin, 1859, On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life. ...
... Natural selection - tendency of organisms with favorable adaptations to their environment to survive and produce new generations • Theory proposed by Charles Darwin, 1859, On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life. ...
History of Life - CHS
... RNA probably predated DNA Difficult to obtain data to support this idea because RNA is more complex than a protein (like what was produced in Primordial Soup experiments) ...
... RNA probably predated DNA Difficult to obtain data to support this idea because RNA is more complex than a protein (like what was produced in Primordial Soup experiments) ...
INSTRUCTIONAL COMPONENT 1 CALIFORNIA
... a) How biodiversity is the sum total of different kinds of organisms and is affected by alterations of habitats? b) How to analyze the changes in an ecosystem resulting from changes in climate, human activity, introduction of nonnative species, or changes in population size? c) How fluctuations in p ...
... a) How biodiversity is the sum total of different kinds of organisms and is affected by alterations of habitats? b) How to analyze the changes in an ecosystem resulting from changes in climate, human activity, introduction of nonnative species, or changes in population size? c) How fluctuations in p ...
change in species over time
... b. Close together but very different climates c. Characteristics of animals/plants varied noticeably C. Hypothesis life changes over time Now a Theory ...
... b. Close together but very different climates c. Characteristics of animals/plants varied noticeably C. Hypothesis life changes over time Now a Theory ...
STERNGRR Examples in representative organisms
... sensory hairs, and PHEROMONES (chemicals used by species to communicate with each other) to obtain information from their environment. Draw and label the compound eye and the pheromone image in the space provided. ...
... sensory hairs, and PHEROMONES (chemicals used by species to communicate with each other) to obtain information from their environment. Draw and label the compound eye and the pheromone image in the space provided. ...
Geology Assessment Study Guide
... ○ Human beings could be found on Earth. ____________________ ○ Pangaea begins to break apart. ____________________ ○ Earth was bombarded with asteroids. ____________________ ● Was the first life on Earth in oceans or on land? ____________________ ● Were humans and dinosaurs ever around at the same t ...
... ○ Human beings could be found on Earth. ____________________ ○ Pangaea begins to break apart. ____________________ ○ Earth was bombarded with asteroids. ____________________ ● Was the first life on Earth in oceans or on land? ____________________ ● Were humans and dinosaurs ever around at the same t ...
Do Now: Answer these 2 questions in your notebook.
... traits. In fact, they do. Compare the forelimbs of the human, the bat, the penguin, and the alligator. Find the humerus, radius, ulna, and carpals in each forelimb. Though the limbs look strikingly different on the outside and though they vary in function, they are very similar in skeletal structure ...
... traits. In fact, they do. Compare the forelimbs of the human, the bat, the penguin, and the alligator. Find the humerus, radius, ulna, and carpals in each forelimb. Though the limbs look strikingly different on the outside and though they vary in function, they are very similar in skeletal structure ...
HB Unit 1 Foundations of Biology
... group (independent/tested variable) to a control group (no tested variable). *dependent variable= variable that is measured quantitatively (numbers) • Experiments can only disprove an hypothesis • Inference= conclusion drawn from facts and previous data, not on direct observation • Theory= set of re ...
... group (independent/tested variable) to a control group (no tested variable). *dependent variable= variable that is measured quantitatively (numbers) • Experiments can only disprove an hypothesis • Inference= conclusion drawn from facts and previous data, not on direct observation • Theory= set of re ...
LIVING ENVIRONMENT SUMMER PACKET Ecology
... 3) According to Darwin's theory of evolution, differences between species may be the result of 4) Two nucleotide sequences found in two different species are almost exactly the same. This suggests that these species 5) The diagram below shows undisturbed sedimentary strata at the bottom of an ocean ...
... 3) According to Darwin's theory of evolution, differences between species may be the result of 4) Two nucleotide sequences found in two different species are almost exactly the same. This suggests that these species 5) The diagram below shows undisturbed sedimentary strata at the bottom of an ocean ...
Glossary - Queensland Museum
... India and smaller pieces. It was subsequently broken apart by continental drift. An animal that eats only plants. A large group of small, agile, herbivorous dinosaurs. A group of aquatic reptiles that lived from the Triassic Period to the Cretaceous. Their body shape is similar to modern dolphins, w ...
... India and smaller pieces. It was subsequently broken apart by continental drift. An animal that eats only plants. A large group of small, agile, herbivorous dinosaurs. A group of aquatic reptiles that lived from the Triassic Period to the Cretaceous. Their body shape is similar to modern dolphins, w ...
Unit 6A
... Species change most as they arise from ancestral species Relatively little change occurs after Eldredge & Gould’s model contrasts with the model of gradualism ...
... Species change most as they arise from ancestral species Relatively little change occurs after Eldredge & Gould’s model contrasts with the model of gradualism ...
The Dynamic Earth: Plate Tectonics (PowerPoint)
... Meet Alfred Wegener, who first proposed this notion in ...
... Meet Alfred Wegener, who first proposed this notion in ...
Chap 6 - Maria Regina School
... – Result from permanent changes, or mutations, in organism’s genes – Over time, more and more individuals may inherit these variations, and if they continue to survive and reproduce, can create new species ...
... – Result from permanent changes, or mutations, in organism’s genes – Over time, more and more individuals may inherit these variations, and if they continue to survive and reproduce, can create new species ...
Theme 8 – The Dynamic Earth: Plate Tectonics
... Meet Alfred Wegener, who first proposed this notion in ...
... Meet Alfred Wegener, who first proposed this notion in ...
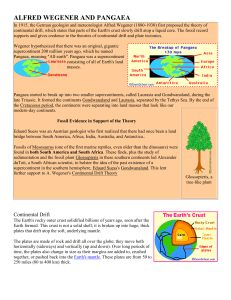
ALFRED WEGENER AND PANGAEA In 1915, the German geologist
... Continental Drift The Earth's rocky outer crust solidified billions of years ago, soon after the Earth formed. This crust is not a solid shell; it is broken up into huge, thick plates that drift atop the soft, underlying mantle. The plates are made of rock and drift all over the globe; they move bot ...
... Continental Drift The Earth's rocky outer crust solidified billions of years ago, soon after the Earth formed. This crust is not a solid shell; it is broken up into huge, thick plates that drift atop the soft, underlying mantle. The plates are made of rock and drift all over the globe; they move bot ...
Paleontology

Paleontology or palaeontology (/ˌpeɪlɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpeɪlɪənˈtɒlədʒi/ or /ˌpælɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpælɪənˈtɒlədʒi/) is the scientific study of life existent prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene Epoch roughly 11,700 years before present. It includes the study of fossils to determine organisms' evolution and interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek παλαιός, palaios, i.e. ""old, ancient"", ὄν, on (gen. ontos), i.e. ""being, creature"" and λόγος, logos, i.e. ""speech, thought, study"".Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of morphologically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics and engineering. Use of all these techniques has enabled paleontologists to discover much of the evolutionary history of life, almost all the way back to when Earth became capable of supporting life, about 3,800 million years ago. As knowledge has increased, paleontology has developed specialised sub-divisions, some of which focus on different types of fossil organisms while others study ecology and environmental history, such as ancient climates.Body fossils and trace fossils are the principal types of evidence about ancient life, and geochemical evidence has helped to decipher the evolution of life before there were organisms large enough to leave body fossils. Estimating the dates of these remains is essential but difficult: sometimes adjacent rock layers allow radiometric dating, which provides absolute dates that are accurate to within 0.5%, but more often paleontologists have to rely on relative dating by solving the ""jigsaw puzzles"" of biostratigraphy. Classifying ancient organisms is also difficult, as many do not fit well into the Linnean taxonomy that is commonly used for classifying living organisms, and paleontologists more often use cladistics to draw up evolutionary ""family trees"". The final quarter of the 20th century saw the development of molecular phylogenetics, which investigates how closely organisms are related by measuring how similar the DNA is in their genomes. Molecular phylogenetics has also been used to estimate the dates when species diverged, but there is controversy about the reliability of the molecular clock on which such estimates depend.