Year 6 Science Key Skills
... Explore colours using light. Recognise that Isaac Newton discovered information about light and colour. Explain that objects block light to form shadows. ...
... Explore colours using light. Recognise that Isaac Newton discovered information about light and colour. Explain that objects block light to form shadows. ...
Evolution Study Guide
... 4. Understand how vestigial structures show evidence of evolution. What are some examples of vestigial structures (remember, vestigial structures are NOT used, therefore penguin wings are not considered vestigial structures because they use them to swim). Speciation through Isolation (section 11 ...
... 4. Understand how vestigial structures show evidence of evolution. What are some examples of vestigial structures (remember, vestigial structures are NOT used, therefore penguin wings are not considered vestigial structures because they use them to swim). Speciation through Isolation (section 11 ...
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
... Disruptive: eliminates intermediate Group Beak sizes in finches ...
... Disruptive: eliminates intermediate Group Beak sizes in finches ...
Chapter 2: The need for Earth Heritage Conservation
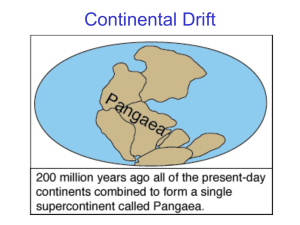
... Much of the early knowledge of the history of the Earth was developed in Britain and many British sites have played a part in the development of now universally-applied principles of geology. These sites have great historical importance. For example, many of the names of periods of geological time a ...
... Much of the early knowledge of the history of the Earth was developed in Britain and many British sites have played a part in the development of now universally-applied principles of geology. These sites have great historical importance. For example, many of the names of periods of geological time a ...
On the Galápagos Islands, Charles Darwin observed
... 1. On the Galápagos Islands, Charles Darwin observed a. completely unrelated species on each of the islands. b. species exactly like those found in mainland South America. c. somewhat similar species to those on the mainland, with traits that suited their particular environments. d. species complete ...
... 1. On the Galápagos Islands, Charles Darwin observed a. completely unrelated species on each of the islands. b. species exactly like those found in mainland South America. c. somewhat similar species to those on the mainland, with traits that suited their particular environments. d. species complete ...
Evolution - WordPress.com
... another. Some of this variation is inherited. • Organisms in nature produce more offspring than can survive, and many of those that survive do not reproduce. ...
... another. Some of this variation is inherited. • Organisms in nature produce more offspring than can survive, and many of those that survive do not reproduce. ...
ORIGINS Genesis 1: 20-25 Session 7: Evolution Part 1
... a genome that had no known functions and were called "Junk DNA". This junk DNA was therefore evidence of common ancestors. However, we now know they all have a use. Common descent or Common designer? ...
... a genome that had no known functions and were called "Junk DNA". This junk DNA was therefore evidence of common ancestors. However, we now know they all have a use. Common descent or Common designer? ...
Descent with Modification: A Darwinian View of Life
... Jean Baptiste Lamarck placed fossils in an evolutionary context and was the first person to present a functional mechanism describing evolution He used two common ideas of his time: ...
... Jean Baptiste Lamarck placed fossils in an evolutionary context and was the first person to present a functional mechanism describing evolution He used two common ideas of his time: ...
Biology 14.2 How Biologists Classify Organisms
... evolutionary relationships using cladistics. Cladistics is a method of analysis that reconstructs phylogenies (evolutionary histories) by inferring relationships based on shared characteristics. Inferring means to make an educated guess based on examining ...
... evolutionary relationships using cladistics. Cladistics is a method of analysis that reconstructs phylogenies (evolutionary histories) by inferring relationships based on shared characteristics. Inferring means to make an educated guess based on examining ...
Ecology
... Many scientists point to 4 principles that summarize Mendel’s work. They are: Traits are inherited by individual units called genes If there are 2 or more forms of a gene, some forms may be dominant, others recessive In most organisms that have sexual reproduction, there are 2 copies of each g ...
... Many scientists point to 4 principles that summarize Mendel’s work. They are: Traits are inherited by individual units called genes If there are 2 or more forms of a gene, some forms may be dominant, others recessive In most organisms that have sexual reproduction, there are 2 copies of each g ...
a Introduction to Geology
... and then flutters its wings. A week later, the weather in New York is affected. No instruments presently known could measure the perturbation, but it happens. It is called “the Butterfly Effect.” This strange effect promotes the idea that in a chaotic system, a very small change to that system appli ...
... and then flutters its wings. A week later, the weather in New York is affected. No instruments presently known could measure the perturbation, but it happens. It is called “the Butterfly Effect.” This strange effect promotes the idea that in a chaotic system, a very small change to that system appli ...
The Vertebrate Genealogy
... “Let’s first dispose of the myth that our ancestors were chimpanzees or any other modern apes. Chimpanzees and humans represent two divergent branches of the anthropoid tree that evolved from a common, less-specialized ancestor.” ...
... “Let’s first dispose of the myth that our ancestors were chimpanzees or any other modern apes. Chimpanzees and humans represent two divergent branches of the anthropoid tree that evolved from a common, less-specialized ancestor.” ...
Plate tectonics, 9-2..
... History of life on earth • 4.6 bya—when it all began (Precambrian) • Earth’s atmosphere changed over time • First organisms were likely prokaryotes (3.4 by old fossils) • Photosynthetic organisms probably evolved next ...
... History of life on earth • 4.6 bya—when it all began (Precambrian) • Earth’s atmosphere changed over time • First organisms were likely prokaryotes (3.4 by old fossils) • Photosynthetic organisms probably evolved next ...
Describe an example of how natural selection influenced the
... species. Include outside sources if applicable. Review a classmate’s post and discuss additional conditions that might have contributed to the selection process. The peppered moth is a classic example of how natural selection has influenced the evolution of a particular species. Prior to the industr ...
... species. Include outside sources if applicable. Review a classmate’s post and discuss additional conditions that might have contributed to the selection process. The peppered moth is a classic example of how natural selection has influenced the evolution of a particular species. Prior to the industr ...
Chapter 7 - Diversity - NCERT Ques Ans
... 1. What are the advantages of classifying organisms? Following are the advantages of classifying organisms: → It makes us aware of and gives us information regarding the diversity of plants and animals. → It makes the study of different kinds of organisms much easier. → It tells us about the inter-r ...
... 1. What are the advantages of classifying organisms? Following are the advantages of classifying organisms: → It makes us aware of and gives us information regarding the diversity of plants and animals. → It makes the study of different kinds of organisms much easier. → It tells us about the inter-r ...
Heterotroph Theory
... experiment looking at where bacteria came from, but instead he used a flask with a curved neck- so air could get in but bacteria could not He found bacteria did not spontaneously generate ...
... experiment looking at where bacteria came from, but instead he used a flask with a curved neck- so air could get in but bacteria could not He found bacteria did not spontaneously generate ...
Study Guide Geo Time Test
... Part B Using a Geological Timelscale Chart: Use Handout I to complete questions 24 24. Create a timeline showing the 4 major eras in chronological order including time spans. ...
... Part B Using a Geological Timelscale Chart: Use Handout I to complete questions 24 24. Create a timeline showing the 4 major eras in chronological order including time spans. ...
BioB 6W2 Review (divide by 4.9)
... the following key to identify the organisms' above: 1a The critter has flat sides – go to 3 1b The critter has rounded sides – go to 2 2a The critter is open in the center - Foramen aperire 2b The critter is solid in the center - Implevit circuli 3a The critter is triangular in shape – Triangulum iu ...
... the following key to identify the organisms' above: 1a The critter has flat sides – go to 3 1b The critter has rounded sides – go to 2 2a The critter is open in the center - Foramen aperire 2b The critter is solid in the center - Implevit circuli 3a The critter is triangular in shape – Triangulum iu ...
File
... Communicate how plants convert energy from the Sun through photosynthesis Photosynthesis: The process of plants making their own food *in order to make food, plants need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide (the gas humans breathe out) *plants will make sugar and release oxygen (the gas humans brea ...
... Communicate how plants convert energy from the Sun through photosynthesis Photosynthesis: The process of plants making their own food *in order to make food, plants need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide (the gas humans breathe out) *plants will make sugar and release oxygen (the gas humans brea ...
Year 8 Praising stars 2 revision Electrical circuits
... Plants compete for light, water, nutrients (mineral salts) and space. If there are not enough resources the population will decrease. Disease can kill organisms. The populations of predators and prey are linked. When there are a lot of prey organisms, the number of predators increases because they h ...
... Plants compete for light, water, nutrients (mineral salts) and space. If there are not enough resources the population will decrease. Disease can kill organisms. The populations of predators and prey are linked. When there are a lot of prey organisms, the number of predators increases because they h ...
Unit 17 STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH
... because the crystals have enough time to grow to a large size • ex. - granite ...
... because the crystals have enough time to grow to a large size • ex. - granite ...
Unit7Notes
... evolved from just one species. Begin with the Founder effect & Geographic Isolation. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ ...
... evolved from just one species. Begin with the Founder effect & Geographic Isolation. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ ...
Evolution
... Evolution by Natural Selection • Postulate 2: At least some of the differences among members of a population are due to characteristics that may be passed from parent to offspring – However, the mechanism of inheritance was not understood at this point in time ...
... Evolution by Natural Selection • Postulate 2: At least some of the differences among members of a population are due to characteristics that may be passed from parent to offspring – However, the mechanism of inheritance was not understood at this point in time ...
Paleontology

Paleontology or palaeontology (/ˌpeɪlɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpeɪlɪənˈtɒlədʒi/ or /ˌpælɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpælɪənˈtɒlədʒi/) is the scientific study of life existent prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene Epoch roughly 11,700 years before present. It includes the study of fossils to determine organisms' evolution and interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek παλαιός, palaios, i.e. ""old, ancient"", ὄν, on (gen. ontos), i.e. ""being, creature"" and λόγος, logos, i.e. ""speech, thought, study"".Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of morphologically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics and engineering. Use of all these techniques has enabled paleontologists to discover much of the evolutionary history of life, almost all the way back to when Earth became capable of supporting life, about 3,800 million years ago. As knowledge has increased, paleontology has developed specialised sub-divisions, some of which focus on different types of fossil organisms while others study ecology and environmental history, such as ancient climates.Body fossils and trace fossils are the principal types of evidence about ancient life, and geochemical evidence has helped to decipher the evolution of life before there were organisms large enough to leave body fossils. Estimating the dates of these remains is essential but difficult: sometimes adjacent rock layers allow radiometric dating, which provides absolute dates that are accurate to within 0.5%, but more often paleontologists have to rely on relative dating by solving the ""jigsaw puzzles"" of biostratigraphy. Classifying ancient organisms is also difficult, as many do not fit well into the Linnean taxonomy that is commonly used for classifying living organisms, and paleontologists more often use cladistics to draw up evolutionary ""family trees"". The final quarter of the 20th century saw the development of molecular phylogenetics, which investigates how closely organisms are related by measuring how similar the DNA is in their genomes. Molecular phylogenetics has also been used to estimate the dates when species diverged, but there is controversy about the reliability of the molecular clock on which such estimates depend.