WinFinalDraftB
... Write the differential equation in terms of derivatives of y. Solve for the roots of the characteristic (or homogeneous) equation. Write the characteristic (or homogeneous) solution, yc, with undetermined coefficients. Write a particular solution yp, based on the nonhomogeneous part of the equation. ...
... Write the differential equation in terms of derivatives of y. Solve for the roots of the characteristic (or homogeneous) equation. Write the characteristic (or homogeneous) solution, yc, with undetermined coefficients. Write a particular solution yp, based on the nonhomogeneous part of the equation. ...
Physics Qualifying Examination – Part I 7-Minute Questions September 12, 2015
... For which values of ρ0 and R would you expect a black hole to be implied? (Hint: Escape speed?) Given that Newtonian gravity is fully described by the Poisson equation ∇ 2 Φ = 4π G ρ (x), formally derive the acceleration −∇Φ for this mass distribution using the divergence theorem. What is the veloci ...
... For which values of ρ0 and R would you expect a black hole to be implied? (Hint: Escape speed?) Given that Newtonian gravity is fully described by the Poisson equation ∇ 2 Φ = 4π G ρ (x), formally derive the acceleration −∇Φ for this mass distribution using the divergence theorem. What is the veloci ...
Quiz3 - 203 .tst
... A) entirely in the magnetic field. B) entirely in the electric field. C) equally divided between the magnetic and the electric fields. D) zero. Answer: C 10) If the magnetic field in a traveling electromagnetic wave has a maximum value of 16.5 nT, what is the maximum value of the electric field asso ...
... A) entirely in the magnetic field. B) entirely in the electric field. C) equally divided between the magnetic and the electric fields. D) zero. Answer: C 10) If the magnetic field in a traveling electromagnetic wave has a maximum value of 16.5 nT, what is the maximum value of the electric field asso ...
Lecture_22 - Quantum Mechanics (read Chap 40.2)
... •Notice this is a partial differential equation with v = velocity of wave propagation. ...
... •Notice this is a partial differential equation with v = velocity of wave propagation. ...
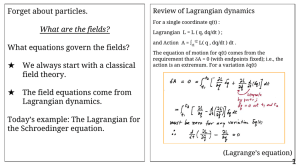
Forget about particles. What equations govern the fields? What are the fields?
... and Action A = ∫t1t2 L( q , dq/dt ) dt . The equation of motion for q(t) comes from the requirement that δA = 0 (with endpoints fixed); i.e., the action is an extremum. For a variation δq(t) ...
... and Action A = ∫t1t2 L( q , dq/dt ) dt . The equation of motion for q(t) comes from the requirement that δA = 0 (with endpoints fixed); i.e., the action is an extremum. For a variation δq(t) ...
Class work February 6
... pitcher at 54.0 m/s. If the contact time between bat and ball is 3.00 X 10-3 calculate the average force between the ball and bat during contact. ...
... pitcher at 54.0 m/s. If the contact time between bat and ball is 3.00 X 10-3 calculate the average force between the ball and bat during contact. ...
A PRIMER ON THE ANGULAR MOMENTUM AND PARITY
... Electrons, protons and neutrons all have an intrinsic angular momentum associated with them that is similar to the classical concept of spin. By analogy with orbital angular momentum, one can define a set of spin operators for the length and the z component of spin, Ŝ 2 and Ŝz respectively. These ...
... Electrons, protons and neutrons all have an intrinsic angular momentum associated with them that is similar to the classical concept of spin. By analogy with orbital angular momentum, one can define a set of spin operators for the length and the z component of spin, Ŝ 2 and Ŝz respectively. These ...
PPT
... As the electromagnetic wave moves rightward past the rectangle, the magnetic flux B through the rectangle changes and— according to Faraday’s law of induction— induced electric fields appear throughout the region of the rectangle. We take E and E + dE to be the induced fields along the two long side ...
... As the electromagnetic wave moves rightward past the rectangle, the magnetic flux B through the rectangle changes and— according to Faraday’s law of induction— induced electric fields appear throughout the region of the rectangle. We take E and E + dE to be the induced fields along the two long side ...
PHOTON WAVE MECHANICS: A DE BROGLIE
... of them (which is allowed by the continuity equation (4). Also, some difficulties suffered by the de Broglie - Bohm theory, related to “unusual” properties of the quantum potential, can be simply solved in the novel picture (for further details see [7]). 3. The motion of gauge particles In the previ ...
... of them (which is allowed by the continuity equation (4). Also, some difficulties suffered by the de Broglie - Bohm theory, related to “unusual” properties of the quantum potential, can be simply solved in the novel picture (for further details see [7]). 3. The motion of gauge particles In the previ ...
13. nuclear
... The gamma particle has no charge, so it will not be attracted to either side. The beta particle is negatively charged particle. The beta particle will be attracted to the positive end of the magnet. ...
... The gamma particle has no charge, so it will not be attracted to either side. The beta particle is negatively charged particle. The beta particle will be attracted to the positive end of the magnet. ...
Chapter 9a Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
... Compton scattering cannot be understood on the basis classical electromagnetic theory. On the basis of classical principles, the scattering mechanism is induced by motion of electrons in the material, caused by the incident radiation. This motion must have the same frequency as that of incident wav ...
... Compton scattering cannot be understood on the basis classical electromagnetic theory. On the basis of classical principles, the scattering mechanism is induced by motion of electrons in the material, caused by the incident radiation. This motion must have the same frequency as that of incident wav ...
Learning Goal: To learn about the impulse-momentum
... This equation is known as the impulse-momentum theorem. It states that the change in an object's momentum is equal to the impulse of the net force acting on the object. In the case of a constant net force acting along the direction of motion, the impulsemomentum theorem can be written as ...
... This equation is known as the impulse-momentum theorem. It states that the change in an object's momentum is equal to the impulse of the net force acting on the object. In the case of a constant net force acting along the direction of motion, the impulsemomentum theorem can be written as ...