... ( II ) A long cylindrical conductor of radius R carries total electric current /. The current density, J, is not uniform over the cross-section of the conductor but is a function of the radial distance r from the axis according to /= br2, where b is a positive constant. (a) What are the SI units of ...
Physical Chemistry Composite systems Adding angular momenta
... Angular Momentum of Composite Systems ...
... Angular Momentum of Composite Systems ...
here
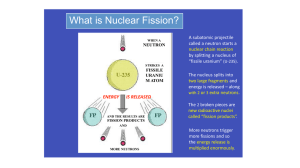
... The nucleus splits into two large fragments and energy is released – along with 2 or 3 extra neutrons. The 2 broken pieces are new radioactive nuclei called “fission products”. ...
... The nucleus splits into two large fragments and energy is released – along with 2 or 3 extra neutrons. The 2 broken pieces are new radioactive nuclei called “fission products”. ...
JCE0597 p605 Numerical Methods for Finding Momentum Space
... Department of Chemistry, Saint John’s University, Collegeville, MN 56321 For chemists, quantum mechanics consists to a large extent in solving Schrödinger’s equation in its position representation for a wide variety of problems of varying complexity. This activity yields quantized energy levels and ...
... Department of Chemistry, Saint John’s University, Collegeville, MN 56321 For chemists, quantum mechanics consists to a large extent in solving Schrödinger’s equation in its position representation for a wide variety of problems of varying complexity. This activity yields quantized energy levels and ...
SET 2 Option J — Particle physics J1. This question is about
... State one reason why the process e e is more likely to involve the electromagnetic interaction rather than the weak interaction. ...
... State one reason why the process e e is more likely to involve the electromagnetic interaction rather than the weak interaction. ...
Light - UDChemistry
... • It is impossible to know both the position and momentum of an electron simultaneously • The only way to know anything about an electron is to shoot it with a photon • The photon alters the position and/or momentum in an unpredictable manner, so the original position and ...
... • It is impossible to know both the position and momentum of an electron simultaneously • The only way to know anything about an electron is to shoot it with a photon • The photon alters the position and/or momentum in an unpredictable manner, so the original position and ...
How Are Electric And Magnetic Fields Used To Steer
... Force on a charged particle in a magnetic field equation: F = B q v sin θ F = force (N) B = magnetic field strength (T) q = charge on the particle (C) v = velocity of the particle (m/s) (Angle θ is between the direction of the beam and the magnetic field direction) ...
... Force on a charged particle in a magnetic field equation: F = B q v sin θ F = force (N) B = magnetic field strength (T) q = charge on the particle (C) v = velocity of the particle (m/s) (Angle θ is between the direction of the beam and the magnetic field direction) ...
Theoretical Physics T2 Quantum Mechanics
... A photocathode is irradiated with ultraviolet light which causes the emission of electrons thus generating an electric current, between the cathode and the electron collector, that is measured by a galvanometer. Additionally a voltage is installed such that the electrons are hindered in advancing th ...
... A photocathode is irradiated with ultraviolet light which causes the emission of electrons thus generating an electric current, between the cathode and the electron collector, that is measured by a galvanometer. Additionally a voltage is installed such that the electrons are hindered in advancing th ...
CHAPTER 7: The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom Energy
... travels through some material or through space. Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation is the emission and transmission of energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. It consists of electric and magnetic field. ...
... travels through some material or through space. Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation is the emission and transmission of energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. It consists of electric and magnetic field. ...
PPT
... h in Fig. 33-6 is fixed at point P on the x axis and in the xy plane. As the electromagnetic wave moves rightward past the rectangle, the magnetic flux B through the rectangle changes and— according to Faraday’s law of induction— induced electric fields appear throughout the region of the rectangle. ...
... h in Fig. 33-6 is fixed at point P on the x axis and in the xy plane. As the electromagnetic wave moves rightward past the rectangle, the magnetic flux B through the rectangle changes and— according to Faraday’s law of induction— induced electric fields appear throughout the region of the rectangle. ...
Electrons in Atoms Powerpoint
... Excited State – some electrons have more energy than usual, causing some electrons to be in a higher energy level than they should be in ...
... Excited State – some electrons have more energy than usual, causing some electrons to be in a higher energy level than they should be in ...
The hydrogen line spectrum explained as Raman shift
... explains and illustrates: if the excited-state atom is perturbed by the electric field of a photon with frequency ν, it may release a second photon of the same frequency, in phase with the first photon. The atom will again ...
... explains and illustrates: if the excited-state atom is perturbed by the electric field of a photon with frequency ν, it may release a second photon of the same frequency, in phase with the first photon. The atom will again ...