6.1.5. Number Representation: Operators
... where, to avoid ambiguity, we have used subscript to indicate the particle occupying the state. Taking the hermitian conjugate, we obtain the adjoint basis vector ...
... where, to avoid ambiguity, we have used subscript to indicate the particle occupying the state. Taking the hermitian conjugate, we obtain the adjoint basis vector ...
Chapter 9 review
... Boltzmann showed that the statistical factor exp(−βE) is a characteristic of any classical system. quantities other than molecular speeds may affect the energy of a given state. ...
... Boltzmann showed that the statistical factor exp(−βE) is a characteristic of any classical system. quantities other than molecular speeds may affect the energy of a given state. ...
Problem Set 9 - MIT OpenCourseWare
... that there are 3 bound energy eigenstates, and that their energy eigenvalues are discrete and non-degenerate. Record these values and sketch each eigenstate. (b) Keeping the shape of the potential fixed, change the number of wells to N =2. Begin with the separation between wells set to the maximum a ...
... that there are 3 bound energy eigenstates, and that their energy eigenvalues are discrete and non-degenerate. Record these values and sketch each eigenstate. (b) Keeping the shape of the potential fixed, change the number of wells to N =2. Begin with the separation between wells set to the maximum a ...
Magnetic Force on an electric current
... f = frequency of monochromatic light (a single photon) [Hz] c = speed of light in a vacuum = 3.0x108 ms-1, = wavelength of monochromatic light OR of an particle such as an electron [m] Electron Standing Wave Orbit: 2r = nnh/mv, n = wavelength number, r = orbit radius [m], mv = electron moment ...
... f = frequency of monochromatic light (a single photon) [Hz] c = speed of light in a vacuum = 3.0x108 ms-1, = wavelength of monochromatic light OR of an particle such as an electron [m] Electron Standing Wave Orbit: 2r = nnh/mv, n = wavelength number, r = orbit radius [m], mv = electron moment ...
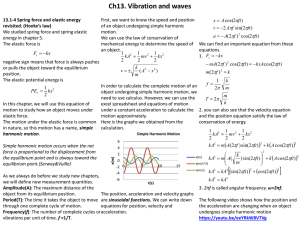
13.1-4 Spring force and elastic energy revisited. (Hooke’s law)
... Amplitude(A): The maximum distance of the object from its equilibrium position. The position, acceleration and velocity graphs Period(T): The time it takes the object to move are sinusoidal functions. We can write down through one complete cycle of motion. equations for position, velocity and Freque ...
... Amplitude(A): The maximum distance of the object from its equilibrium position. The position, acceleration and velocity graphs Period(T): The time it takes the object to move are sinusoidal functions. We can write down through one complete cycle of motion. equations for position, velocity and Freque ...
Atomic Structure and Periodicity
... What is one possible set of four quantum numbers for one of the outermost electrons in a strontium atom in the ground state ...
... What is one possible set of four quantum numbers for one of the outermost electrons in a strontium atom in the ground state ...
A Primer on Quantum Mechanics and Orbitals
... Actually, I lied a little. There is one physical situation that is reminiscent of the kind of 'double valued' wavefunction that I've so far said is forbidden by the rules of quantum mechanics. This situation is the case of electron (or proton, or neutron) spin. Spin is a kind of 'intrinsic' angular ...
... Actually, I lied a little. There is one physical situation that is reminiscent of the kind of 'double valued' wavefunction that I've so far said is forbidden by the rules of quantum mechanics. This situation is the case of electron (or proton, or neutron) spin. Spin is a kind of 'intrinsic' angular ...
Wednesday, March 3, 2010
... The potentials and the Schrödinger wave equation for the three regions are as follows: ...
... The potentials and the Schrödinger wave equation for the three regions are as follows: ...
Chapter 6 lecture 1
... 1.096776x107 m-1 is known as Rydberg’s constant (RH) Set n2 = 2, n1=3,4,5,6 and calculate wavelengths….. n1 ...
... 1.096776x107 m-1 is known as Rydberg’s constant (RH) Set n2 = 2, n1=3,4,5,6 and calculate wavelengths….. n1 ...
NATURAL UNITS AND PLANE WAVES Natural Units A.1
... they are a convenient substitute for a wave packet of definite momentum and are the conventional basis for expanding the wave function of an interacting particle. The wave functions of quantum mechanics form a Hilbert space, that is, a linear vector space of infinite dimension.' Whereas the dynamica ...
... they are a convenient substitute for a wave packet of definite momentum and are the conventional basis for expanding the wave function of an interacting particle. The wave functions of quantum mechanics form a Hilbert space, that is, a linear vector space of infinite dimension.' Whereas the dynamica ...