waves
... Experiments showed that a minimum frequency was needed before electrons would be emitted called the threshold frequency no dependence on intensity ...
... Experiments showed that a minimum frequency was needed before electrons would be emitted called the threshold frequency no dependence on intensity ...
I. Relativity
... Throughout the latter portion of the 19th century, experiments were performed to identify that preferred reference frame for light waves. The questions were, what is the medium in which light waves travel and in what reference frame is that medium at rest? That hypothetical medium was given the name ...
... Throughout the latter portion of the 19th century, experiments were performed to identify that preferred reference frame for light waves. The questions were, what is the medium in which light waves travel and in what reference frame is that medium at rest? That hypothetical medium was given the name ...
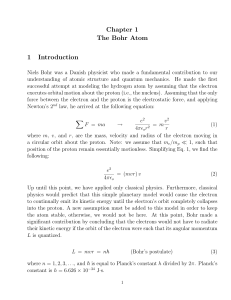
Chapter 1 The Bohr Atom 1 Introduction
... You will find that these three definitions are used over and over again in atomic physics, so, these are worth remembering. For example, these definitions can be used to simply the calculation performed in Eq. 6. Finally, a third parameter that can be calculated using the Bohr model is the total ene ...
... You will find that these three definitions are used over and over again in atomic physics, so, these are worth remembering. For example, these definitions can be used to simply the calculation performed in Eq. 6. Finally, a third parameter that can be calculated using the Bohr model is the total ene ...
Shou-Cheng Zhang, , 823 (2001); DOI: 10.1126/science.294.5543.823
... Here, ⌿␣ is a four-component complex spinor with ␣ ⫽ 1, 2, 3, 4, and xa is a five-component real vector. From the normalization condition of the ⌿ spinor it may be seen that x 2a ⫽ 1, therefore, Xa ⫽ Rxa describes a point of the 4D sphere S 4 with radius R. From this heuristic reasoning, one may hop ...
... Here, ⌿␣ is a four-component complex spinor with ␣ ⫽ 1, 2, 3, 4, and xa is a five-component real vector. From the normalization condition of the ⌿ spinor it may be seen that x 2a ⫽ 1, therefore, Xa ⫽ Rxa describes a point of the 4D sphere S 4 with radius R. From this heuristic reasoning, one may hop ...
Mid-Term Exam
... while “attentuation” describes the narrowing of the beam as it is refracted. (c) “Loss” describes energy absorbed by the material, while “attenuation” describes the decrease in wave strength across space, which may be caused by loss, but can be caused by other things. (d) “Loss” describes the portio ...
... while “attentuation” describes the narrowing of the beam as it is refracted. (c) “Loss” describes energy absorbed by the material, while “attenuation” describes the decrease in wave strength across space, which may be caused by loss, but can be caused by other things. (d) “Loss” describes the portio ...
The Exam 2 Solutions are also available now.
... For n = 1, the wavefunction is half a sine wave, extending from x = 0 to x = L. To have the probability of finding the particle in the region 0 ≤ x ≤ L/4 be equal to the probability of finding the particle in the region L/2 ≤ x ≤ 3L/4, the square of the wavefunction must be identical over these two ...
... For n = 1, the wavefunction is half a sine wave, extending from x = 0 to x = L. To have the probability of finding the particle in the region 0 ≤ x ≤ L/4 be equal to the probability of finding the particle in the region L/2 ≤ x ≤ 3L/4, the square of the wavefunction must be identical over these two ...
Notes-17
... When an atom or molecule is exposed to an electromagnetic field, it can undergo energy and momentum exchange with the photon field, i.e., it can absorb or emit radiations. To describe the electromagnetic field using the concept of photons, one has to use quantum electrodynamics (QED) where the elect ...
... When an atom or molecule is exposed to an electromagnetic field, it can undergo energy and momentum exchange with the photon field, i.e., it can absorb or emit radiations. To describe the electromagnetic field using the concept of photons, one has to use quantum electrodynamics (QED) where the elect ...
Momentum and impulse
... If the relative speeds are equal, e 1, the particles are said to be perfectly elastic (there will be no loss in kinetic energy). ...
... If the relative speeds are equal, e 1, the particles are said to be perfectly elastic (there will be no loss in kinetic energy). ...
The quantum mechanics of photon addition and subtraction
... tial modes out of a pump photon. If one photon is detected in one output mode, then we are sure that the other photon is in the other mode, without having to measure it. As shown in Figure 1(b), an initial field input to one mode will gain one extra photon heralded by a photon detected in the conjug ...
... tial modes out of a pump photon. If one photon is detected in one output mode, then we are sure that the other photon is in the other mode, without having to measure it. As shown in Figure 1(b), an initial field input to one mode will gain one extra photon heralded by a photon detected in the conjug ...
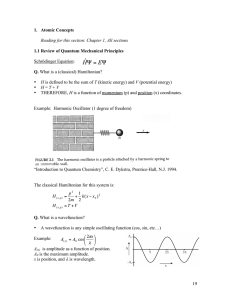
1.3 Atomic Concepts
... These energies cannot be calculated exactly as for the H-atom, as no closed form or analytical solution exists for the Schrödinger equation for three or more particles (same is true in classical mechanics – n-body problem with n > 3) ...
... These energies cannot be calculated exactly as for the H-atom, as no closed form or analytical solution exists for the Schrödinger equation for three or more particles (same is true in classical mechanics – n-body problem with n > 3) ...
Chapter6
... subplot(3,2,i),plot(xp,yp,xb(i),yb(i),'o');axis([0 xmax 0 ymax]); xlabel('x(m)');ylabel('y(m)') end ...
... subplot(3,2,i),plot(xp,yp,xb(i),yb(i),'o');axis([0 xmax 0 ymax]); xlabel('x(m)');ylabel('y(m)') end ...
Newtonian Dynamics y In the next few weeks, we’ll study two chapters
... entitled “Homework Set 2a” and “Homework Set 2b”. ...
... entitled “Homework Set 2a” and “Homework Set 2b”. ...
HW11: Ch.31 Q 2,5,7,9,12 P 4,7,11,19, 23, 26
... B=B0(R) Cos(2 π f t) where R is the radial distance from the capacitor’s central axis. (b) Determine the expression for the amplitude B0(R) of this time-dependent (sinusoidal) field when R<= R0 and when R>R0. (c) Plot B0(R) in tesla for the range 0
... B=B0(R) Cos(2 π f t) where R is the radial distance from the capacitor’s central axis. (b) Determine the expression for the amplitude B0(R) of this time-dependent (sinusoidal) field when R<= R0 and when R>R0. (c) Plot B0(R) in tesla for the range 0
Models of Light Student Worksheet
... 2) Pair Creation and Annihilation: The rules of quantum physics don’t seem to make sense. However, the mathematics works really well and it has brought us computers, lasers, solar cells and Positron Emission Tomography (PET). PET is a medical scan that allows us to see biochemical activity in living ...
... 2) Pair Creation and Annihilation: The rules of quantum physics don’t seem to make sense. However, the mathematics works really well and it has brought us computers, lasers, solar cells and Positron Emission Tomography (PET). PET is a medical scan that allows us to see biochemical activity in living ...