wave
... „One can even set up quite ridiculous cases. A cat is penned up in a steel chamber, along with the following device (which must be secured against direct interference by the cat): in a Geiger counter there is a tiny bit of radioactive substance, so small, that perhaps in the course of the hour one o ...
... „One can even set up quite ridiculous cases. A cat is penned up in a steel chamber, along with the following device (which must be secured against direct interference by the cat): in a Geiger counter there is a tiny bit of radioactive substance, so small, that perhaps in the course of the hour one o ...
Where are the electrons
... Dual wave-particle nature of light • Einstein expanded on Planck’s theory and said that electromagnetic radiation has a dual wave-particle nature. • While light exhibits wave like properties, it can also be thought of as a stream of particles. • Each particle carries a quantum of energy – these par ...
... Dual wave-particle nature of light • Einstein expanded on Planck’s theory and said that electromagnetic radiation has a dual wave-particle nature. • While light exhibits wave like properties, it can also be thought of as a stream of particles. • Each particle carries a quantum of energy – these par ...
Extension physics
... Show by substitution into the wave equation that expressions of the form ei(tkx) describe a wave of unity amplitude propagating along the negative/positive direction of the x-axis. ...
... Show by substitution into the wave equation that expressions of the form ei(tkx) describe a wave of unity amplitude propagating along the negative/positive direction of the x-axis. ...
Class 23_270_11
... statistics, form an intereference pattern. Their cumulative impact is wavelike. • This leads us to believe that the behavior of electrons is governed by probabilistic laws. ‐‐The wavefunction describes the probability that an electron will be found in a ...
... statistics, form an intereference pattern. Their cumulative impact is wavelike. • This leads us to believe that the behavior of electrons is governed by probabilistic laws. ‐‐The wavefunction describes the probability that an electron will be found in a ...
e-the-quantum-numberssv-2
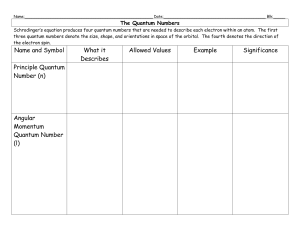
... Name:______________________________________________________ Date:___________________________________________ Blk:_____ ...
... Name:______________________________________________________ Date:___________________________________________ Blk:_____ ...
Honors Chemistry
... The statement indicates that the electron has absorbed energy and moved out further away from the nucleus (into a higher energy level). The absorption of energy gives the electron a higher potential energy than it had in the ground state. 5. What type of energy causes an electron to move from its gr ...
... The statement indicates that the electron has absorbed energy and moved out further away from the nucleus (into a higher energy level). The absorption of energy gives the electron a higher potential energy than it had in the ground state. 5. What type of energy causes an electron to move from its gr ...
Task 1
... 1. Since the distance between the Zeeman sub-levels is proportional to the magnetic field, this effect is used by astronomers to measure the magnetic field of the Sun and other stars. ...
... 1. Since the distance between the Zeeman sub-levels is proportional to the magnetic field, this effect is used by astronomers to measure the magnetic field of the Sun and other stars. ...
Higher Physics Content Statements
... The Bohr model of the atom. Electrons can be excited to higher energy levels by an input of energy. Ionisation level is the level at which an electron is free from the atom. Zero potential energy is defined as equal to that of the ionisation level, implying that other energy levels have negative val ...
... The Bohr model of the atom. Electrons can be excited to higher energy levels by an input of energy. Ionisation level is the level at which an electron is free from the atom. Zero potential energy is defined as equal to that of the ionisation level, implying that other energy levels have negative val ...
1. Define the vocabulary on page 88. Section 1
... 2. All forms of electromagnetic radiation form the ________________. 3. All forms of electromagnetic radiation move at a constant speed of _____________ through a vacuum. 4. _________ is the distance between corresponding points on adjacent waves. 5. What is the symbol for wavelength? 6. Frequency i ...
... 2. All forms of electromagnetic radiation form the ________________. 3. All forms of electromagnetic radiation move at a constant speed of _____________ through a vacuum. 4. _________ is the distance between corresponding points on adjacent waves. 5. What is the symbol for wavelength? 6. Frequency i ...
A Helium atom has a nuclear charge of Ze, where Z=2. One of the
... An electron is in the field of an EM plane wave. The electron is accelerated by the electric field, and therefore emits EM radiation. What would classical theory* predict is the wavelength of the emitted radiation? ...
... An electron is in the field of an EM plane wave. The electron is accelerated by the electric field, and therefore emits EM radiation. What would classical theory* predict is the wavelength of the emitted radiation? ...
Particle wavelength, Rutherford scattering
... to have particle characteristics (photons), matter proved to have wave characteristics. The wave nature of matter allows us to use electrons to make images (e.g. the viruses shown here on a bacterium). This picture is the output of an “electron ...
... to have particle characteristics (photons), matter proved to have wave characteristics. The wave nature of matter allows us to use electrons to make images (e.g. the viruses shown here on a bacterium). This picture is the output of an “electron ...
![L 35 Modern Physics [1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001036078_1-1a4f17b9367db590f7dcb987ef21bbe6-300x300.png)