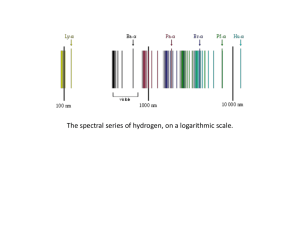
Degeneracy
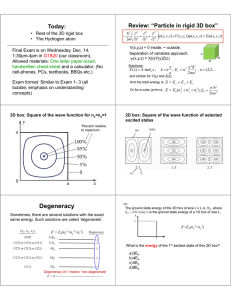
... The ground state energy of the 2D box of size L x L is 2E0, where E0 = π2ħ2/(2mL2) is the ground state energy of a 1D box of size L. y ...
... The ground state energy of the 2D box of size L x L is 2E0, where E0 = π2ħ2/(2mL2) is the ground state energy of a 1D box of size L. y ...
Lecture 15 (Slides) September 28
... • The PIAB wave functions exhibit nodes. As we move to higher energy (higher n) states the number of nodes increases. As well, as one moves to higher n values the characteristic wavelength decreases. (This is reminiscent of light where, again, the energy of a photon increases as the wavelength of th ...
... • The PIAB wave functions exhibit nodes. As we move to higher energy (higher n) states the number of nodes increases. As well, as one moves to higher n values the characteristic wavelength decreases. (This is reminiscent of light where, again, the energy of a photon increases as the wavelength of th ...
lecture 10
... quantum theory, on the other hand, there is a chance that the car could tunnel (leak) through the potential energy barrier between C and E and emerge on the other side of the hill at E . (b) The wavefunction of the electron incident on a potential energy barrier (Vo). The incident and reflected wave ...
... quantum theory, on the other hand, there is a chance that the car could tunnel (leak) through the potential energy barrier between C and E and emerge on the other side of the hill at E . (b) The wavefunction of the electron incident on a potential energy barrier (Vo). The incident and reflected wave ...
Problem set 2 A - De Broglie wavelength B
... with q = k′ −k, k′ the wavevector scattered in a direction (θ, ϕ) and with k = k ′ because the scattering is elastic. When the energy of the collision is very small, k → 0 and therefore q → 0. The scattering amplitude f is then independent of the energy of the particle and isotropic. The scattering ...
... with q = k′ −k, k′ the wavevector scattered in a direction (θ, ϕ) and with k = k ′ because the scattering is elastic. When the energy of the collision is very small, k → 0 and therefore q → 0. The scattering amplitude f is then independent of the energy of the particle and isotropic. The scattering ...
27-4 Photons Carry Momentum
... Thus, after the collision, the photon has lower energy, which means its frequency is lower while its wavelength !/ is higher. The photon’s direction changes by an angle #. Applying energy conservation to this situation gives one equation, while applying momentum conservation in two dimensions gives ...
... Thus, after the collision, the photon has lower energy, which means its frequency is lower while its wavelength !/ is higher. The photon’s direction changes by an angle #. Applying energy conservation to this situation gives one equation, while applying momentum conservation in two dimensions gives ...
Rutherford–Bohr model
... the negatively charged electron confined to an atomic shell encircles a small, positively charged atomic nucleus and where an electron jump between orbits is accompanied by an emitted or absorbed amount of electromagnetic energy (hν).[1] The orbits in which the electron may travel are shown as grey ...
... the negatively charged electron confined to an atomic shell encircles a small, positively charged atomic nucleus and where an electron jump between orbits is accompanied by an emitted or absorbed amount of electromagnetic energy (hν).[1] The orbits in which the electron may travel are shown as grey ...
Environmental Physics for Freshman Geography Students
... i.e. the speed of the wave is the ratio of the corresponding particle’s energy to its momentum. In Lecture 2 we learned that, being a massless particle, the photon has E = pc, where c is a constant equal to the speed of light in a vacuum. Eq. (7.13) thus tells us that all photons (no matter what the ...
... i.e. the speed of the wave is the ratio of the corresponding particle’s energy to its momentum. In Lecture 2 we learned that, being a massless particle, the photon has E = pc, where c is a constant equal to the speed of light in a vacuum. Eq. (7.13) thus tells us that all photons (no matter what the ...
sch4u-quantumtheory
... Rise of the Quantum Theory • Light – particles or waves? Greeks answer: particles • 17th century, Christian Huygens, proposed light can be best described as a wave; Isaac Newton vehemently opposed • Mid-19th century, James Maxwell proposed that light is an electromagnetic wave consisting of magnetic ...
... Rise of the Quantum Theory • Light – particles or waves? Greeks answer: particles • 17th century, Christian Huygens, proposed light can be best described as a wave; Isaac Newton vehemently opposed • Mid-19th century, James Maxwell proposed that light is an electromagnetic wave consisting of magnetic ...
Kinematics, Momentum and Energy
... An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will stay in motion unless acted on by an external force. ...
... An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will stay in motion unless acted on by an external force. ...
Blackbody Radiation
... • In fact, it predicts that the intensity of light at high frequencies will get higher and higher and the total energy radiated will approach infinity – but this is impossible • Great difference between theory and experimental values in UV region ...
... • In fact, it predicts that the intensity of light at high frequencies will get higher and higher and the total energy radiated will approach infinity – but this is impossible • Great difference between theory and experimental values in UV region ...
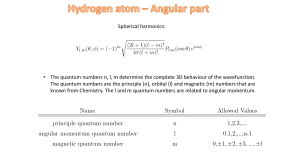
Many-Electron Atoms Thornton and Rex, Ch. 8
... Consider a 1-electron atom (or with just 1 electron outside closed shell). It has Orbital Angular momentum L and Spin Angular momentum S. These can be combined to give Total Angular momentum J = L + S . J is quantized with ...
... Consider a 1-electron atom (or with just 1 electron outside closed shell). It has Orbital Angular momentum L and Spin Angular momentum S. These can be combined to give Total Angular momentum J = L + S . J is quantized with ...
Double-Slit Experiment
... 1. Studies in which the frequency of the light is varied show that NO electrons are emitted by a given metal below a specific threshold frequency, v0 . 2. For light with frequency lower than the threshold frequency, no electrons are emitted regardless of the intensity (amplitude) 3. For light with f ...
... 1. Studies in which the frequency of the light is varied show that NO electrons are emitted by a given metal below a specific threshold frequency, v0 . 2. For light with frequency lower than the threshold frequency, no electrons are emitted regardless of the intensity (amplitude) 3. For light with f ...