somatoform disorders
... • 1. Four pain symptoms: a history of pain related to at least four different sites or functions (eg, head, abdomen, back, joints, extremities, chest, rectum, during menstruation, during sexual intercourse, or during urination) • 2. Two gastrointestinal symptoms: a history of at least two gastrointe ...
... • 1. Four pain symptoms: a history of pain related to at least four different sites or functions (eg, head, abdomen, back, joints, extremities, chest, rectum, during menstruation, during sexual intercourse, or during urination) • 2. Two gastrointestinal symptoms: a history of at least two gastrointe ...
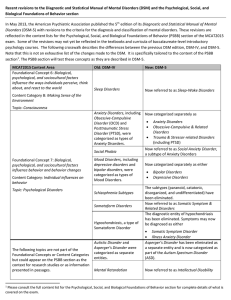
Recent revisions to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental
... Recent revisions to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) and the Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior section In May 2013, the American Psychiatric Association published the 5th edition of its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorder ...
... Recent revisions to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) and the Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior section In May 2013, the American Psychiatric Association published the 5th edition of its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorder ...
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS AND TREATMENT
... 1.2.12 Sexual dysfunctions 1.2.13 Gender dysphoria 1.2.14 Disruptive, impulse-control, and conduct disorders 1.2.15 Substance-related and addictive disorders 1.2.16 Neurocognitive disorders 1.2.17 Paraphilic disorders 1.2.18 Personality disorders "Major Depressive Disorder" Depressed mood most of th ...
... 1.2.12 Sexual dysfunctions 1.2.13 Gender dysphoria 1.2.14 Disruptive, impulse-control, and conduct disorders 1.2.15 Substance-related and addictive disorders 1.2.16 Neurocognitive disorders 1.2.17 Paraphilic disorders 1.2.18 Personality disorders "Major Depressive Disorder" Depressed mood most of th ...
citalopram-induced major depression in a patient with panic disorder
... treatment follows a temporal sequence similar to that of the clinical treatment response. That is, the onset of the antidepressant clinical response in depressed patients is delayed by 2-3 weeks (Blier & Montigny 1999, Kalia 2005). It is assumed (Humble & Wistedt 1992) that all states associated wit ...
... treatment follows a temporal sequence similar to that of the clinical treatment response. That is, the onset of the antidepressant clinical response in depressed patients is delayed by 2-3 weeks (Blier & Montigny 1999, Kalia 2005). It is assumed (Humble & Wistedt 1992) that all states associated wit ...
DSM-5 Released: The Big Changes
... research.). This exclusion was removed in the DSM5. Here are the reasons they gave: The first is to remove the implication that bereavement typically lasts only 2 months when both physicians and grief counselors recognize that the duration is more commonly 1–2 years. Second, bereavement is recogniz ...
... research.). This exclusion was removed in the DSM5. Here are the reasons they gave: The first is to remove the implication that bereavement typically lasts only 2 months when both physicians and grief counselors recognize that the duration is more commonly 1–2 years. Second, bereavement is recogniz ...
Psychatric Emergencies
... Death occurs in 4 to 20 percent of cases from complications such as hyperthermia, aspiration, or vascular collapse. Onset of withdrawal is usually 2 to 10 days after cessation or decreases in alcohol use and may last hours to days. Symptoms of uncomplicated alcohol withdrawal peak 24 to 48 hours aft ...
... Death occurs in 4 to 20 percent of cases from complications such as hyperthermia, aspiration, or vascular collapse. Onset of withdrawal is usually 2 to 10 days after cessation or decreases in alcohol use and may last hours to days. Symptoms of uncomplicated alcohol withdrawal peak 24 to 48 hours aft ...
General adult psychiatry
... to the baby. Risk is increased in first time mothers and instrumental deliveries. 3. Depressive episode in which the patient does complain of low mood, but appears to lack the biological and other associated features of depression. The patient can present with features such as hypersomnia, hyperphag ...
... to the baby. Risk is increased in first time mothers and instrumental deliveries. 3. Depressive episode in which the patient does complain of low mood, but appears to lack the biological and other associated features of depression. The patient can present with features such as hypersomnia, hyperphag ...
Chapter 14, Psych Disorders
... depression is diagnosed when an individual experiences at least five of the following nine symptoms (at least one has to be from the first two on the list): ...
... depression is diagnosed when an individual experiences at least five of the following nine symptoms (at least one has to be from the first two on the list): ...
Mental Disorders
... rationally and their judgments are impaired. Living their daily life becomes very, very difficult. However, for even the worst of these disorders there is treatment available. The most prevalent symptoms of these diseases are usually delusions and hallucinations. Delusions believe certain facts even ...
... rationally and their judgments are impaired. Living their daily life becomes very, very difficult. However, for even the worst of these disorders there is treatment available. The most prevalent symptoms of these diseases are usually delusions and hallucinations. Delusions believe certain facts even ...
Abnormal Psychology - Rutgers Psychology
... .We will compare various current theories of the development of behavioral and cognitive disorders as defined by the Diagnostic Statistical Manual V (DSM-V) as well as the efficacy of various treatment modalities including pharmacological interventions. As a result, you will be better able to recogn ...
... .We will compare various current theories of the development of behavioral and cognitive disorders as defined by the Diagnostic Statistical Manual V (DSM-V) as well as the efficacy of various treatment modalities including pharmacological interventions. As a result, you will be better able to recogn ...
Obsessive Compulsive and Related Disorders - DSM-5
... picking, which must cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational or other important areas of functioning. The symptoms must not be better explained by symptoms of another mental disorder. This disorder is included in DSM-5 because of substantial scientific literature o ...
... picking, which must cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational or other important areas of functioning. The symptoms must not be better explained by symptoms of another mental disorder. This disorder is included in DSM-5 because of substantial scientific literature o ...
The CBQ and the Core Phenotype - Juvenile Bipolar Research
... goofy giddy, elated, euphoric, overly-optimistic, self-aggrandizing, grandiose); depressed (withdrawn, bored/anhedonic, irritable, sad, dysphoric, or overly pessimistic, self-critical). Episodes are defined by DSM-IV symptom criteria but not by DSM-IV duration criteria; manic/hypomanic or mixed epis ...
... goofy giddy, elated, euphoric, overly-optimistic, self-aggrandizing, grandiose); depressed (withdrawn, bored/anhedonic, irritable, sad, dysphoric, or overly pessimistic, self-critical). Episodes are defined by DSM-IV symptom criteria but not by DSM-IV duration criteria; manic/hypomanic or mixed epis ...
Guide to Depression and Bipolar Disorder
... Types of Depression It is now believed that depression is the sign of an imbalance in brain chemicals called neurotransmitters. Although the direct causes of the illness are unclear, it is known that body chemistry can bring on a depressive disorder, due to the presence of another illness, altered h ...
... Types of Depression It is now believed that depression is the sign of an imbalance in brain chemicals called neurotransmitters. Although the direct causes of the illness are unclear, it is known that body chemistry can bring on a depressive disorder, due to the presence of another illness, altered h ...
The Initial Field Trials of DSM
... mood dysregulation disorder. This disorder has a more modest kappa statistic. Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder was more reliably assessed in the inpatient setting where it was examined, as was borderline personality disorder early in its history. Perhaps as clinical experience with this new ch ...
... mood dysregulation disorder. This disorder has a more modest kappa statistic. Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder was more reliably assessed in the inpatient setting where it was examined, as was borderline personality disorder early in its history. Perhaps as clinical experience with this new ch ...
Agoraphobia : A fear of going out to public places. Amnesia: A
... Conversion disorder: A somatoform disorder characterized by a significant loss of physical function (with no apparent organic basis), usually in a single organ system. Culture-bound disorders: Abnormal syndromes found only in a few cultural groups. Cyclothymic disorder: Exhibiting chronic but relati ...
... Conversion disorder: A somatoform disorder characterized by a significant loss of physical function (with no apparent organic basis), usually in a single organ system. Culture-bound disorders: Abnormal syndromes found only in a few cultural groups. Cyclothymic disorder: Exhibiting chronic but relati ...
PDF
... new eye for the prevalence of cyclelinked symptoms—one data set came from family pedigrees with early-onset major depression and another from a 10site study in families with bipolar disorder: 2,524 women in all. The results? Almost 68 percent of women with mood disorders reported premenstrual sympto ...
... new eye for the prevalence of cyclelinked symptoms—one data set came from family pedigrees with early-onset major depression and another from a 10site study in families with bipolar disorder: 2,524 women in all. The results? Almost 68 percent of women with mood disorders reported premenstrual sympto ...
Topics in Co-Occurring Disorders: The Disease of Addiction
... Type of Mental Disorder Anxiety disorder Major depressive disorder Substance use disorder Bipolar disorder Eating disorders Schizophrenia Any mental disorder ...
... Type of Mental Disorder Anxiety disorder Major depressive disorder Substance use disorder Bipolar disorder Eating disorders Schizophrenia Any mental disorder ...
Slide 1 - Barrington 220
... tendency to be unconcerned with social rewards lacking a sense of social responsibility reduced activity in frontal lobe ...
... tendency to be unconcerned with social rewards lacking a sense of social responsibility reduced activity in frontal lobe ...
Antisocial Personality Disorder
... Studies have shown that it is very difficult to treat because people with it may not even want or think that they need any type of treatment. Long term one on one therapy might work but getting the patient to stick to it is difficult. Treatment for depression & anxiety may be needed to be give ...
... Studies have shown that it is very difficult to treat because people with it may not even want or think that they need any type of treatment. Long term one on one therapy might work but getting the patient to stick to it is difficult. Treatment for depression & anxiety may be needed to be give ...
Psychological Disorders
... for no apparent reason, experiences two or more weeks of depressed moods, feelings of worthlessness, and diminished interest or pleasure in most activities ...
... for no apparent reason, experiences two or more weeks of depressed moods, feelings of worthlessness, and diminished interest or pleasure in most activities ...
Chapter 4 Review
... 23. Why is depression linked to suicide? Depression is an emotional state in which the person feels hopeless and worthless. Suicidal people usually have (or had in some cases) these symptoms. 24. List four common myths and then four facts about suicide. Myths Facts 1. People who talk about suicide 1 ...
... 23. Why is depression linked to suicide? Depression is an emotional state in which the person feels hopeless and worthless. Suicidal people usually have (or had in some cases) these symptoms. 24. List four common myths and then four facts about suicide. Myths Facts 1. People who talk about suicide 1 ...
Personality Disorder
... usually displays strange behavior and thinking • Histrionic Personality Disorder – the person engages in attentiongrabbing emotional outbursts and tries to gain other’s approval • Narcissistic Personality Disorder – the person is very self-absorbed and have delusions of grandeur • Borderline Persona ...
... usually displays strange behavior and thinking • Histrionic Personality Disorder – the person engages in attentiongrabbing emotional outbursts and tries to gain other’s approval • Narcissistic Personality Disorder – the person is very self-absorbed and have delusions of grandeur • Borderline Persona ...
Becoming familiar with the DSM 5
... • 91-100 Superior functioning in a wide range of activities, life’s problems never seem to get out of hand, is sought out by others because of his or her many positive qualities. No symptoms. • 81-90 Absent or minimal symptoms (e.g., mild anxiety before an exam), good functioning in all areas, inter ...
... • 91-100 Superior functioning in a wide range of activities, life’s problems never seem to get out of hand, is sought out by others because of his or her many positive qualities. No symptoms. • 81-90 Absent or minimal symptoms (e.g., mild anxiety before an exam), good functioning in all areas, inter ...