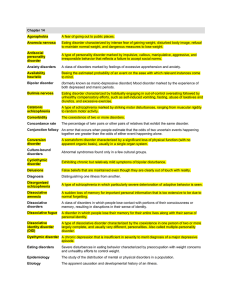
Chapter 10:Conversion and dissociation
... The predominant disturbance is one or more episodes of inability to recall important personal information, usually of a traumatic or stressful nature, that is too extensive to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness. The disturbance does not occur exclusively as a symptom of dissociative identity dis ...
... The predominant disturbance is one or more episodes of inability to recall important personal information, usually of a traumatic or stressful nature, that is too extensive to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness. The disturbance does not occur exclusively as a symptom of dissociative identity dis ...
Child and Adolescent Mental Health
... Other Psychiatric Disorders – Eliminations Disorders – Psychotic Disorders – Mood Disorders Depression Bipolar Disorder ...
... Other Psychiatric Disorders – Eliminations Disorders – Psychotic Disorders – Mood Disorders Depression Bipolar Disorder ...
Bipolar Disorder in Children and Adolescents National Institute of Mental Health
... Children with chronic, severe irritability and symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) may be misdiagnosed as having bipolar disorder. However, researchers believe that it is more appropriate to label these types of symptoms as severe mood dysregulation (SMD). Evidence suggests t ...
... Children with chronic, severe irritability and symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) may be misdiagnosed as having bipolar disorder. However, researchers believe that it is more appropriate to label these types of symptoms as severe mood dysregulation (SMD). Evidence suggests t ...
Psycho-flexed Hand Associated with Conversion Reaction: A Case
... depressed with little eye to eye contact. She was hostile and had evasive attitude combined with a pessimistic view about her future. She was talking about a car accident that had happend two years ago during which she had ...
... depressed with little eye to eye contact. She was hostile and had evasive attitude combined with a pessimistic view about her future. She was talking about a car accident that had happend two years ago during which she had ...
Impulse Control Disorders - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery
... disorder begins in early childhood; men > women. precipitating events are absent or disproportionately insignificant when compared with extent of aggressive behavioral outburst. attacks consist of kicking, scratching, biting, and shouting (including abusive and profane language); patient has c ...
... disorder begins in early childhood; men > women. precipitating events are absent or disproportionately insignificant when compared with extent of aggressive behavioral outburst. attacks consist of kicking, scratching, biting, and shouting (including abusive and profane language); patient has c ...
Cultural Barriers to Adequate Detection and Management of Major
... somatic symptoms, including insomnia, headaches, and fatigue. She labeled her problem “insomnia”.. When asked, patient replied that she had sort of heard of depression, but did not think she suffered from depression. We explained that in the West, depression refers to a cluster of symptoms including ...
... somatic symptoms, including insomnia, headaches, and fatigue. She labeled her problem “insomnia”.. When asked, patient replied that she had sort of heard of depression, but did not think she suffered from depression. We explained that in the West, depression refers to a cluster of symptoms including ...
PDF File
... Conversion disorder is closely associated with traumatic and stressful events, or impaired relationships. Occupational and social disability, absenteeism, poor productivity and unemployment are severe. A person with hypochondriasis has a poor quality of life, are socially isolated, depressed and at ...
... Conversion disorder is closely associated with traumatic and stressful events, or impaired relationships. Occupational and social disability, absenteeism, poor productivity and unemployment are severe. A person with hypochondriasis has a poor quality of life, are socially isolated, depressed and at ...
Glossary
... Eating disorder characterized by habitually engaging in out-of-control overeating followed by unhealthy compensatory efforts, such as self-induced vomiting, fasting, abuse of laxatives and diuretics, and excessive exercise. ...
... Eating disorder characterized by habitually engaging in out-of-control overeating followed by unhealthy compensatory efforts, such as self-induced vomiting, fasting, abuse of laxatives and diuretics, and excessive exercise. ...
Chapter 14 - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... A type of dissociative disorder characterized by the coexistence in one person of two or more largely complete, and usually very different, personalities. Also called multiple-personality disorder. ...
... A type of dissociative disorder characterized by the coexistence in one person of two or more largely complete, and usually very different, personalities. Also called multiple-personality disorder. ...
The PAS-ADD Clinical Interview
... Or at least two of the following: (a) persistent hallucinations in any modality, when occurring every day for at least I ...
... Or at least two of the following: (a) persistent hallucinations in any modality, when occurring every day for at least I ...
PDF
... teenage moodiness and irritability become intense, even debilitating, and invite a host of other problems, from difficulty concentrating to a chronic irritable state that can be overwhelming. Under Kastelic, however, the service has evolved tactics to provide patients with skills for managing such s ...
... teenage moodiness and irritability become intense, even debilitating, and invite a host of other problems, from difficulty concentrating to a chronic irritable state that can be overwhelming. Under Kastelic, however, the service has evolved tactics to provide patients with skills for managing such s ...
The following statements about porphyria are true, except Peripheral
... C. Narcissism D. * High frustration tolerance E. Absence of formal thought disorder 32.All of the following are true of institutional defense mechanisms except A. Splitting between staff B. Projection by staff onto patients C. * Oedipal in nature D. Can decrease anxiety in staff E. Can cause anxiet ...
... C. Narcissism D. * High frustration tolerance E. Absence of formal thought disorder 32.All of the following are true of institutional defense mechanisms except A. Splitting between staff B. Projection by staff onto patients C. * Oedipal in nature D. Can decrease anxiety in staff E. Can cause anxiet ...
Somatic Symptom Disorder - DSM-5
... changes better reflect the complex interface between mental and physical health. ...
... changes better reflect the complex interface between mental and physical health. ...
... additional fee for our Outreach Clinics. INSURANCE COVERAGE: PTC does not accept assignment or participate in Medicare, Medicaid, Tricare or any insurance plans. However, since we are committed to accurate and compliant coding of our services, the majority of our patients with insurance do typically ...
Mood Disorders
... Bipolar I disorder: involves periods of severe mood episodes from mania to depression. Bipolar II disorder: a milder form of mood elevation, involving milder episodes of hypomania that alternate with periods of severe depression. Cyclothymic disorder: periods of hypomania with brief periods of depre ...
... Bipolar I disorder: involves periods of severe mood episodes from mania to depression. Bipolar II disorder: a milder form of mood elevation, involving milder episodes of hypomania that alternate with periods of severe depression. Cyclothymic disorder: periods of hypomania with brief periods of depre ...
Specifiers of Mood Disorders
... marked social impairment). In a manic episode “severe” means the need for almost continual supervision to protect the individual from harm to self or others. “Moderate” in MD is simply defined as intermediate between mild and severe. In a manic episode, “moderate” means an extreme increase in activi ...
... marked social impairment). In a manic episode “severe” means the need for almost continual supervision to protect the individual from harm to self or others. “Moderate” in MD is simply defined as intermediate between mild and severe. In a manic episode, “moderate” means an extreme increase in activi ...
Abnormal and treatment
... Fatigue or loss of energy Feelings of worthlessness or unfounded guilt Reduced ability to concentrate or make decisions Recurrent thoughts of death or suicide Immediate attention - 15% eventual kill themselves (30,000 deaths in the US annually) More women attempt suicide but more men suc ...
... Fatigue or loss of energy Feelings of worthlessness or unfounded guilt Reduced ability to concentrate or make decisions Recurrent thoughts of death or suicide Immediate attention - 15% eventual kill themselves (30,000 deaths in the US annually) More women attempt suicide but more men suc ...
Substance-Related and Addictive Disorders
... dependence into a single disorder measured on a continuum from mild to severe. Each specific substance (other than caffeine, which cannot be diagnosed as a substance use disorder) is addressed as a separate use disorder (e.g., alcohol use disorder, stimulant use disorder, etc.), but nearly all subst ...
... dependence into a single disorder measured on a continuum from mild to severe. Each specific substance (other than caffeine, which cannot be diagnosed as a substance use disorder) is addressed as a separate use disorder (e.g., alcohol use disorder, stimulant use disorder, etc.), but nearly all subst ...
Chapter 8: Dissociative Disorders and Somatic-Symptom
... Somatic Symptom Disorder Dissociative Identity Disorder • Criteria Clarified • A. Disruption of identity characterized by two or more distinct personality states (alters) or an experience of possession, as evidenced by discontinuities in sense of self as reflected in altered cognition, behavior, af ...
... Somatic Symptom Disorder Dissociative Identity Disorder • Criteria Clarified • A. Disruption of identity characterized by two or more distinct personality states (alters) or an experience of possession, as evidenced by discontinuities in sense of self as reflected in altered cognition, behavior, af ...
Specify dissociative fugue subtype if the amnesia is
... Dissociative Identity Disorder • Criteria Clarified • A. Disruption of identity characterized by two or more distinct personality states (alters) or an experience of possession, as evidenced by discontinuities in sense of self as reflected in altered cognition, behavior, affect, perceptions, consci ...
... Dissociative Identity Disorder • Criteria Clarified • A. Disruption of identity characterized by two or more distinct personality states (alters) or an experience of possession, as evidenced by discontinuities in sense of self as reflected in altered cognition, behavior, affect, perceptions, consci ...
DSM-IV-TR Invalidities - Professionaltrainingresourcesinc.com
... ii. Being arrested more than once for disorderly conduct is also sufficient for diagnosis, therefore, one’s diagnostic status depends on the diligence of the local police force. d. As for the “hazardous use” criterion, it is clear that very large numbers of people drive under the influence of alcoho ...
... ii. Being arrested more than once for disorderly conduct is also sufficient for diagnosis, therefore, one’s diagnostic status depends on the diligence of the local police force. d. As for the “hazardous use” criterion, it is clear that very large numbers of people drive under the influence of alcoho ...
2 - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... Denmark, England, India, Nigeria, the Soviet Union, Taiwan, US; WHO, 1973, 1919, 1981) indicate that the prevalence of schizophrenia is similar across countries and has remained relatively constant across time. Across countries, males are more likely to develop ...
... Denmark, England, India, Nigeria, the Soviet Union, Taiwan, US; WHO, 1973, 1919, 1981) indicate that the prevalence of schizophrenia is similar across countries and has remained relatively constant across time. Across countries, males are more likely to develop ...
Somatoform and Sleep Disorders
... • physical symptoms suggesting medical disease but without a demonstrable organic pathological condition or a known pathophysiological mechanism to account for them. • Somatoform disorders are more common ...
... • physical symptoms suggesting medical disease but without a demonstrable organic pathological condition or a known pathophysiological mechanism to account for them. • Somatoform disorders are more common ...
Anxiety Disorders - Home
... – Develop anxiety, worry, or fear about another attack – Many develop agoraphobia • Prevalence of panic disorder – Affects about 2.7% (in a year) & 4.7% (in a lifetime) of the general population – Onset is often acute, median between 20 and 24 years of age – 75% of individuals with agoraphobia are f ...
... – Develop anxiety, worry, or fear about another attack – Many develop agoraphobia • Prevalence of panic disorder – Affects about 2.7% (in a year) & 4.7% (in a lifetime) of the general population – Onset is often acute, median between 20 and 24 years of age – 75% of individuals with agoraphobia are f ...
Panic Disorder
... primary care intervention. Studies suggest that virtually all placebo patients who sampled alcohol relapsed, while only half the naltrexone patients who sampled alcohol relapsed. ...
... primary care intervention. Studies suggest that virtually all placebo patients who sampled alcohol relapsed, while only half the naltrexone patients who sampled alcohol relapsed. ...