Bipolar Disorders - National Association of School Psychologists
... irritable and not elated) other symptoms. These symptoms include inflated self-esteem or grandiosity; decreased need for sleep; rapid, loud, or uninterruptible speech; racing thoughts; increased distractibility; increased goaldirected activity or psychomotor agitation; and excessive involvement in p ...
... irritable and not elated) other symptoms. These symptoms include inflated self-esteem or grandiosity; decreased need for sleep; rapid, loud, or uninterruptible speech; racing thoughts; increased distractibility; increased goaldirected activity or psychomotor agitation; and excessive involvement in p ...
Bipolar Disorder in Women
... B. The disturbance markedly interferes with work or school or with usual social activities and relationships with others (e.g., avoidance of social activities, decreased productivity and efficiency at work or school). C. The disturbance is not merely an exacerbation of the symptoms of another disord ...
... B. The disturbance markedly interferes with work or school or with usual social activities and relationships with others (e.g., avoidance of social activities, decreased productivity and efficiency at work or school). C. The disturbance is not merely an exacerbation of the symptoms of another disord ...
RECOGNISING BIPOLAR DISORDERS IN PRIMARY CARE
... paradox: anxiety, depression and fatigue are the commonest symptoms of Bipolar Disorder (Judd 2003, Judd 2002), but the diagnosis rests on the presence of mania or hypomania. This side of Bipolarity may only be apparent in retrospect, or via a third party, because individuals would be unlikely to se ...
... paradox: anxiety, depression and fatigue are the commonest symptoms of Bipolar Disorder (Judd 2003, Judd 2002), but the diagnosis rests on the presence of mania or hypomania. This side of Bipolarity may only be apparent in retrospect, or via a third party, because individuals would be unlikely to se ...
Mood Disorders
... Cyclothymic—mood disorder characterized by moderate but frequent mood swings that are not severe enough to qualify as bipolar disorder ...
... Cyclothymic—mood disorder characterized by moderate but frequent mood swings that are not severe enough to qualify as bipolar disorder ...
Mood Disorders
... Cyclothymic—mood disorder characterized by moderate but frequent mood swings that are not severe enough to qualify as bipolar disorder ...
... Cyclothymic—mood disorder characterized by moderate but frequent mood swings that are not severe enough to qualify as bipolar disorder ...
Overview of Mental Illness PowerPoint
... combination of psychosocial supports (e.g. family involvement, work or school support, psychotherapy and self-management strategies) and medications (to reduce symptom intensity). Unfortunately, fewer than one-third of adults and one-half of children with diagnosed mental health disorders receive ...
... combination of psychosocial supports (e.g. family involvement, work or school support, psychotherapy and self-management strategies) and medications (to reduce symptom intensity). Unfortunately, fewer than one-third of adults and one-half of children with diagnosed mental health disorders receive ...
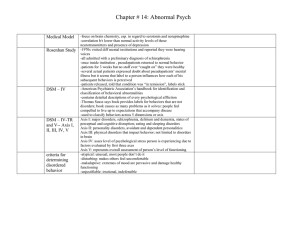
Medical Model - Biloxi Public Schools
... -fear triggered by specific thing or object -intense fear associated w/ public setting -fear of being in open spaces or public places or other places from which escape is perceived to be difficult -anxiety disorder -involuntary, persistent, undesirable obsessions one feels driven to carry out; repet ...
... -fear triggered by specific thing or object -intense fear associated w/ public setting -fear of being in open spaces or public places or other places from which escape is perceived to be difficult -anxiety disorder -involuntary, persistent, undesirable obsessions one feels driven to carry out; repet ...
Preparation for Lecture 13 (Chapter 14)
... In identifying a mental problem, DSM IV uses five different criteria for psychodiagnosis. We will discuss only four kinds of disorders here in terms of their symptoms, classifications, and etiologies. The anxiety disorders disrupt normal functioning either because of too high anxiety level or becaus ...
... In identifying a mental problem, DSM IV uses five different criteria for psychodiagnosis. We will discuss only four kinds of disorders here in terms of their symptoms, classifications, and etiologies. The anxiety disorders disrupt normal functioning either because of too high anxiety level or becaus ...
CHAPTER 11
... hallucinations combined with symptoms of depression or manic mood Delusional disorder – Less bizarre than schizophrenia delusions; usually related to a particular topic and have some foundation in real life. Shared psychotic disorder – Two or more people who share shame delusional belief; one origin ...
... hallucinations combined with symptoms of depression or manic mood Delusional disorder – Less bizarre than schizophrenia delusions; usually related to a particular topic and have some foundation in real life. Shared psychotic disorder – Two or more people who share shame delusional belief; one origin ...
practicle guidelines for treating mental disorders in
... Schizophrenia is the most common primary psychosis. It is a severe disorder that typically begins in late adolescence or early adulthood; it is found approximately equally in men and women, though the onset tends to be later in women, who also tend to have a better course and outcome of this disorde ...
... Schizophrenia is the most common primary psychosis. It is a severe disorder that typically begins in late adolescence or early adulthood; it is found approximately equally in men and women, though the onset tends to be later in women, who also tend to have a better course and outcome of this disorde ...
Bipolar Disorder - Psychiatry Lectures
... A. A distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood, lasting at least 1 week (or any duration if hospitalization is necessary). B. During the period of mood disturbance, three (or more) of the following symptoms have persisted (four if the mood is only irritabl ...
... A. A distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood, lasting at least 1 week (or any duration if hospitalization is necessary). B. During the period of mood disturbance, three (or more) of the following symptoms have persisted (four if the mood is only irritabl ...
Effectiveness of Simple Individual Psychoeducation for Bipolar II
... mood episodes consisting of at least one major depressive episode and at least one hypomanic episode [1]. It has been often considered a mild form of bipolar I disorder, perhaps based on the definition of hypomania, which is a less severe mood elevation compared to mania. However, some studies have ...
... mood episodes consisting of at least one major depressive episode and at least one hypomanic episode [1]. It has been often considered a mild form of bipolar I disorder, perhaps based on the definition of hypomania, which is a less severe mood elevation compared to mania. However, some studies have ...
Hyperaldosteronism and bipolar mixed episode: A case
... dysphoric mood, irritability, insomnia, decreased in appetite, talkativeness, anhedonia, hopelessness, worthlessness, recurrent thought of death, somatic symptoms, which include palpitation and sweating. Mental status examination revealed bipolar 1 disorder, single episode mixed, severe, without psy ...
... dysphoric mood, irritability, insomnia, decreased in appetite, talkativeness, anhedonia, hopelessness, worthlessness, recurrent thought of death, somatic symptoms, which include palpitation and sweating. Mental status examination revealed bipolar 1 disorder, single episode mixed, severe, without psy ...
Psychological Disorders notes
... The Diagnostic Statistical Manual (version 4) is the book that psychologists and psychiatrists use to define (list symptoms) of disorders. Insurance companies won’t cover treatment if not in the DSM. Version 1 said homosexuality was a disorder. Neurotic disorders - a psychological disorder that is u ...
... The Diagnostic Statistical Manual (version 4) is the book that psychologists and psychiatrists use to define (list symptoms) of disorders. Insurance companies won’t cover treatment if not in the DSM. Version 1 said homosexuality was a disorder. Neurotic disorders - a psychological disorder that is u ...
PSC 168 - Psychology
... A) “Avoid mood disorders, highly creative people have a lower than average incidence of them.” B) “Severe mania is related to long periods of high creativity.” C) “If you develop a mood disorder, don't get treated, or you'll lose your creative spark.” D) “Mild mood disorders are related to greater c ...
... A) “Avoid mood disorders, highly creative people have a lower than average incidence of them.” B) “Severe mania is related to long periods of high creativity.” C) “If you develop a mood disorder, don't get treated, or you'll lose your creative spark.” D) “Mild mood disorders are related to greater c ...
Adrian`s Powerpoint presentation here
... Dissociative Disorder Conversion disorder Are you comfortable with any of these? Are your patients? ...
... Dissociative Disorder Conversion disorder Are you comfortable with any of these? Are your patients? ...
Running Head: BIPOLAR DISORDER - People
... abnormally and persistently elevated and/or irritated mood with symptoms including inflated self-esteem, flight of ideas, decreased need for sleep, ease of distraction, and engagement in activities with potentially risky consequences. The episode must be severe enough to cause impairment in occupati ...
... abnormally and persistently elevated and/or irritated mood with symptoms including inflated self-esteem, flight of ideas, decreased need for sleep, ease of distraction, and engagement in activities with potentially risky consequences. The episode must be severe enough to cause impairment in occupati ...
I`m Bipolar, You`re Bipolar - Law Project for Psychiatric Rights
... particular moment by the pharmaceutical industry and thrust forcefully on the public with the help of the most sophisticated marketing and advertising techniques. ...
... particular moment by the pharmaceutical industry and thrust forcefully on the public with the help of the most sophisticated marketing and advertising techniques. ...
Lars and the Real Girl
... Little interest in having sexual experiences takes pleasure in few, if any, activities lacks close friends or confidants other than first-degree relatives appears indifferent to praise/criticism “Dependency and love are dangerous” ...
... Little interest in having sexual experiences takes pleasure in few, if any, activities lacks close friends or confidants other than first-degree relatives appears indifferent to praise/criticism “Dependency and love are dangerous” ...
Slide 1
... Mood Disorders Bipolar Disorder – once known as Manic Depression Two parts – manic – elevated mood – “high” and depression - Abrupt mood swings - Symptoms of manic episode include: inflated self-esteem, racing thoughts, no need for sleep, hyperactivity, feelings of invincibility, agitation, reckles ...
... Mood Disorders Bipolar Disorder – once known as Manic Depression Two parts – manic – elevated mood – “high” and depression - Abrupt mood swings - Symptoms of manic episode include: inflated self-esteem, racing thoughts, no need for sleep, hyperactivity, feelings of invincibility, agitation, reckles ...
CHS284 Sociocultural Aspects of Mental Health
... Major Depressive Disorder • 2+ weeks depressed mood • OR loss of interest or pleasure in nearly all activities. ...
... Major Depressive Disorder • 2+ weeks depressed mood • OR loss of interest or pleasure in nearly all activities. ...
Mental Health in Aging Powerpoint
... “But after my return to the dream-like delusional hypotheses in the later 60's I became a person of delusionally influenced thinking but of relatively moderate behavior and thus tended to avoid hospitalization and the direct attention of psychiatrists. Thus further time passed. Then gradually I bega ...
... “But after my return to the dream-like delusional hypotheses in the later 60's I became a person of delusionally influenced thinking but of relatively moderate behavior and thus tended to avoid hospitalization and the direct attention of psychiatrists. Thus further time passed. Then gradually I bega ...
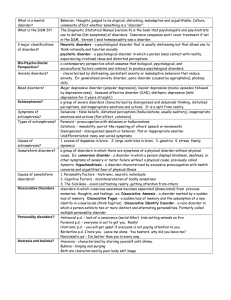
DSM-IV
... • Existence in one individual of two or more distinct identities or personality states that each has its own pattern of perceiving, relating to, and thinking about the environment and self. • At least 2 of the personalities take control of the person’s behavior in sequence, with gaps in recent & pas ...
... • Existence in one individual of two or more distinct identities or personality states that each has its own pattern of perceiving, relating to, and thinking about the environment and self. • At least 2 of the personalities take control of the person’s behavior in sequence, with gaps in recent & pas ...
Mood Disorders
... presence of a mood disorder so when the substance is not present the mood disorder is present. Seasonal Affective Disorder typically happens in the Winter and may result from the loss of hours of sunlight. ...
... presence of a mood disorder so when the substance is not present the mood disorder is present. Seasonal Affective Disorder typically happens in the Winter and may result from the loss of hours of sunlight. ...