OL Chapter 12 overview
... The difference between a blue mood after bad news and major depressive disorder is like the difference between gasping for breath after a hard run and having chronic asthma. We all feel depressed and sad (we have blue moods) in response to painful events and sometimes just to life in general. These ...
... The difference between a blue mood after bad news and major depressive disorder is like the difference between gasping for breath after a hard run and having chronic asthma. We all feel depressed and sad (we have blue moods) in response to painful events and sometimes just to life in general. These ...
Chapter 15 pt. 2: Mood Disorders, Dissociation, Schizophrenia, and
... Mood Disorders Illustrate Emotional Extremes Mood Disorders are characterized by emotional extremes and come in variety of forms: –1. Major Depressive Disorder –2. Dysthymic Disorder –3. Seasonal Affective Disorder –4. Bipolar Disorder ...
... Mood Disorders Illustrate Emotional Extremes Mood Disorders are characterized by emotional extremes and come in variety of forms: –1. Major Depressive Disorder –2. Dysthymic Disorder –3. Seasonal Affective Disorder –4. Bipolar Disorder ...
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors— Are We Missing Something?
... In fact, I worry that MAOIs may go out of production due to the paucity of their use. The reason to focus on MAOIs is that selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and related new-generation antidepressants (like bupropion) have shown limited efficacy. The STAR*D (Sequenced Treatment Alternat ...
... In fact, I worry that MAOIs may go out of production due to the paucity of their use. The reason to focus on MAOIs is that selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and related new-generation antidepressants (like bupropion) have shown limited efficacy. The STAR*D (Sequenced Treatment Alternat ...
Personality disorder
... Commonly adults (16 to 65 years old) with severe mental illness (e.g. schizophrenia, manic depressive disorders, severe depressive disorder) with an acute psychiatric crisis of such severity that, without the involvement of a crisis resolution/home treatment team, hospitalisation would be necessary. ...
... Commonly adults (16 to 65 years old) with severe mental illness (e.g. schizophrenia, manic depressive disorders, severe depressive disorder) with an acute psychiatric crisis of such severity that, without the involvement of a crisis resolution/home treatment team, hospitalisation would be necessary. ...
Overheads – Abnormal Psychology
... Issue: could they tell right from wrong of have ability to control their actions? Severely psychotic or severely mentally retarded ...
... Issue: could they tell right from wrong of have ability to control their actions? Severely psychotic or severely mentally retarded ...
Open Document
... 4.) Obsessive Compulsive Disorder ◦ Marked by persistent, uncontrollable intrusions of unwanted thoughts (obsessions) and urges to engage in senseless rituals (compulsions) ◦ Some common behaviors ...
... 4.) Obsessive Compulsive Disorder ◦ Marked by persistent, uncontrollable intrusions of unwanted thoughts (obsessions) and urges to engage in senseless rituals (compulsions) ◦ Some common behaviors ...
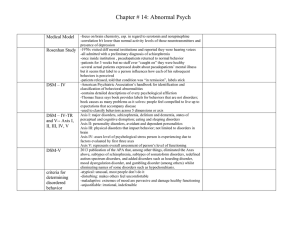
Appendix 7. Diagnostic criteria according to DSM-IV-TR
... (1) Depressed mood most of the day, nearly every day, as indicated by either subjective report or observation made by others. (2) Markedly diminished interest or pleasure in all, or almost all, activities most of the day, nearly every day. (3) Significant weight loss when not dieting or significant ...
... (1) Depressed mood most of the day, nearly every day, as indicated by either subjective report or observation made by others. (2) Markedly diminished interest or pleasure in all, or almost all, activities most of the day, nearly every day. (3) Significant weight loss when not dieting or significant ...
Chapter 27 SEVERE PSYCHIATRIC ILLNESS IN THE MILITARY
... but lasts for a lifetime) may be possible only after clinical observation. Often the clinician will need to wait to see if the symptoms persist over time; it is estimated that 25% of these cases will resolve.3 Unfortunately for many patients, both brief psychotic disorder and schizophreniform disord ...
... but lasts for a lifetime) may be possible only after clinical observation. Often the clinician will need to wait to see if the symptoms persist over time; it is estimated that 25% of these cases will resolve.3 Unfortunately for many patients, both brief psychotic disorder and schizophreniform disord ...
13 Mood Disorders
... • many symptoms do not obviously point to depression • stigma associated with diagnosis of depression ...
... • many symptoms do not obviously point to depression • stigma associated with diagnosis of depression ...
Chapter 16: Psychological disorders PowerPoint
... and increased activity in right – areas associated with the processing of emotions ...
... and increased activity in right – areas associated with the processing of emotions ...
The dilemma in the concept and the management of bipolar
... onset and offset, and seasonal depression, even without discernible hypomanic episodes [5]. Some bipolar disorder II features are more prevalent than bipolar disorder I in the community. It is frequently misdiagnosed as recurrent major depression (from 27 to 65% of patients with this diagnosis are r ...
... onset and offset, and seasonal depression, even without discernible hypomanic episodes [5]. Some bipolar disorder II features are more prevalent than bipolar disorder I in the community. It is frequently misdiagnosed as recurrent major depression (from 27 to 65% of patients with this diagnosis are r ...
Reactive Attachment Disorder (RAD) and Disinhibited Social
... Criterion B: One or more intrusion symptoms Criterion C: Persistent avoidance of stimuli Criterion D: Alterations in cognitive, arousal, mood, reactivity, etc. Duration in both is more than 1 month and causes clinically significant distress. Remaining criteria differ slightly for both groups. ...
... Criterion B: One or more intrusion symptoms Criterion C: Persistent avoidance of stimuli Criterion D: Alterations in cognitive, arousal, mood, reactivity, etc. Duration in both is more than 1 month and causes clinically significant distress. Remaining criteria differ slightly for both groups. ...
Mood Disorders
... Manic episode----Mania- mild-severe -severe with psychoses ----Hypomania Bipolar disorders-Bipolar I disorder -Bipolar II disorder Cyclothymia. Diagnostic criteria for manic episode (DSM IV): A. Elevated, expansive, or irritable mood for at least one week. B. During the mood disturbance, at least th ...
... Manic episode----Mania- mild-severe -severe with psychoses ----Hypomania Bipolar disorders-Bipolar I disorder -Bipolar II disorder Cyclothymia. Diagnostic criteria for manic episode (DSM IV): A. Elevated, expansive, or irritable mood for at least one week. B. During the mood disturbance, at least th ...
Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... Somatic Symptom Disorder (new!) Combined: Hypochondriasis, maybe Somatization Disorder Pain Disorder ...
... Somatic Symptom Disorder (new!) Combined: Hypochondriasis, maybe Somatization Disorder Pain Disorder ...
Notes_14 abnormal - Biloxi Public Schools
... -intense fear associated w/ public setting -fear of being in open spaces or public places or other places from which escape is perceived to be difficult -anxiety-based disorder; has it s own category in DSM V -involuntary, persistent, undesirable obsessions one feels driven to carry out; repetitive ...
... -intense fear associated w/ public setting -fear of being in open spaces or public places or other places from which escape is perceived to be difficult -anxiety-based disorder; has it s own category in DSM V -involuntary, persistent, undesirable obsessions one feels driven to carry out; repetitive ...
PDF - Research Review NZ
... Initial studies of quetiapine monotherapy, the well known BipOLar DEpRession (BOLDER) I and BOLDER II studies, indicated that quetiapine monotherapy was robustly antidepressant in the treatment of bipolar depression (see Figure 2).13,14 In the BOLDER I study, 542 patients with bipolar I (n = 360) or ...
... Initial studies of quetiapine monotherapy, the well known BipOLar DEpRession (BOLDER) I and BOLDER II studies, indicated that quetiapine monotherapy was robustly antidepressant in the treatment of bipolar depression (see Figure 2).13,14 In the BOLDER I study, 542 patients with bipolar I (n = 360) or ...
Part VII. Schizophrenia
... can provide circumstances under which a biological predisposition for illness can express itself. ...
... can provide circumstances under which a biological predisposition for illness can express itself. ...
Hypochondria: hypochondriasis
... The patient is help to interpret the symptoms properly rather than focusing on the intensity of the pain or where he’s felling it. If the patient is administer medication it must be limited and the time the PA will spend with him too. The PA must be careful of how he gives the reassurance and kee ...
... The patient is help to interpret the symptoms properly rather than focusing on the intensity of the pain or where he’s felling it. If the patient is administer medication it must be limited and the time the PA will spend with him too. The PA must be careful of how he gives the reassurance and kee ...
Abnormal Psychology - AP Psychology Community
... • Thinking that you are the center of the universe. ...
... • Thinking that you are the center of the universe. ...
View Publication
... Ultra-high risk of psychosis: Moderate but sub-threshold symptoms, with moderate neurocognitive changes and functional decline to caseness or chronic poor functioning (≥30% drop in SOFAS in previous 12 months OR <50 for previous 12 months) First episode of psychotic disorder: Full threshold disorder ...
... Ultra-high risk of psychosis: Moderate but sub-threshold symptoms, with moderate neurocognitive changes and functional decline to caseness or chronic poor functioning (≥30% drop in SOFAS in previous 12 months OR <50 for previous 12 months) First episode of psychotic disorder: Full threshold disorder ...
Continuing Education
... it is defined as a depressed mood and loss of interest in nearly all activities for the greater part of every day for at least a two-week period, plus at least four additional symptoms of depression. The mood change is so severe that it affects the patient’s ability to function on the job and in per ...
... it is defined as a depressed mood and loss of interest in nearly all activities for the greater part of every day for at least a two-week period, plus at least four additional symptoms of depression. The mood change is so severe that it affects the patient’s ability to function on the job and in per ...
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS
... signs of inattention:‘Daydreamers’ Often becoming easily distracted by irrelevant sights and sounds Often failing to pay attention to details and ...
... signs of inattention:‘Daydreamers’ Often becoming easily distracted by irrelevant sights and sounds Often failing to pay attention to details and ...