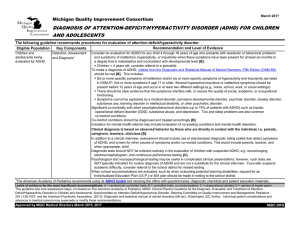
diagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (adhd)
... Consider an evaluation for ADHD for any child 4 through 18 years of age who presents with academic or behavioral problems and symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, or impulsivity when these symptoms have been present for at least six months to a degree that is maladaptive and inconsistent with dev ...
... Consider an evaluation for ADHD for any child 4 through 18 years of age who presents with academic or behavioral problems and symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, or impulsivity when these symptoms have been present for at least six months to a degree that is maladaptive and inconsistent with dev ...
學系別
... a) No correlation has been found between bipolar disorder and suicide b) Females usually commit suicide with more lethal methods c) Individuals usually commit suicide without disclosing obvious information about the suicide d) Pain and disability are the main reasons of suicide among elderly individ ...
... a) No correlation has been found between bipolar disorder and suicide b) Females usually commit suicide with more lethal methods c) Individuals usually commit suicide without disclosing obvious information about the suicide d) Pain and disability are the main reasons of suicide among elderly individ ...
Understanding Bipolar Disorder and Its Treatment
... try and find the drug that is most effective for them. Lithium has the longest history of being used for bipolar disorder, dating back to the 1940’s. It is usually the first course of medication given to a new patient who presents with symptoms of bipolar disorder. Lithium is a naturally occurring s ...
... try and find the drug that is most effective for them. Lithium has the longest history of being used for bipolar disorder, dating back to the 1940’s. It is usually the first course of medication given to a new patient who presents with symptoms of bipolar disorder. Lithium is a naturally occurring s ...
Abnormal Psychology - Bloomfield Central School
... • Thinking that you are the center of the universe. ...
... • Thinking that you are the center of the universe. ...
Mod 65: Introduction to Psychological Disorders
... Goal of classification system (DSM) is group symptoms for disorders to help correctly diagnosis disorder/syndrome Ex: schizophrenics can have unorganized speech, suffer hallucinations & delusions, be socially withdrawn & have inappropriate emotions Another goal is to also to describe the disorder a ...
... Goal of classification system (DSM) is group symptoms for disorders to help correctly diagnosis disorder/syndrome Ex: schizophrenics can have unorganized speech, suffer hallucinations & delusions, be socially withdrawn & have inappropriate emotions Another goal is to also to describe the disorder a ...
47.272 ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY Fall 2014 Quiz 5 For each
... c. Has the patient been experiencing actual physical symptoms that are significantly distressing and causing disruption in daily life? d. Is the patient preoccupied with or spending a lot of time thinking about his/her health? e. Does the patient seem unduly worried about his/her health even in the ...
... c. Has the patient been experiencing actual physical symptoms that are significantly distressing and causing disruption in daily life? d. Is the patient preoccupied with or spending a lot of time thinking about his/her health? e. Does the patient seem unduly worried about his/her health even in the ...
psychology - TeacherWeb
... – Causes: history of very traumatic experiences; childhood abuse – Dominant or stronger personality knows about the weaker, but not the other way around – Not considered schizophrenic because this disorder doesn’t have trouble thinking or communicating ...
... – Causes: history of very traumatic experiences; childhood abuse – Dominant or stronger personality knows about the weaker, but not the other way around – Not considered schizophrenic because this disorder doesn’t have trouble thinking or communicating ...
Signs & Symptoms of Mental Illness & Substance use Disorders
... by the World Health Organization, the World Bank and Harvard University, reported that mental illness is second only to cardiovascular disease in regard to societal burden, including years of life lost to premature death or disability. ...
... by the World Health Organization, the World Bank and Harvard University, reported that mental illness is second only to cardiovascular disease in regard to societal burden, including years of life lost to premature death or disability. ...
Personality disorder
... Commonly adults (16 to 65 years old) with severe mental illness (e.g. schizophrenia, manic depressive disorders, severe depressive disorder) with an acute psychiatric crisis of such severity that, without the involvement of a crisis resolution/home treatment team, hospitalisation would be necessary. ...
... Commonly adults (16 to 65 years old) with severe mental illness (e.g. schizophrenia, manic depressive disorders, severe depressive disorder) with an acute psychiatric crisis of such severity that, without the involvement of a crisis resolution/home treatment team, hospitalisation would be necessary. ...
Chapter 14: Psychological Disorders
... one week or any duration if hospitalization is required. Symptoms: inflated self-esteem or grandiosity, decreased need for sleep, being more talkative than usual, flight of ideas, distractibility, increase in goaloriented activity and excessive involvement in risky activities. ...
... one week or any duration if hospitalization is required. Symptoms: inflated self-esteem or grandiosity, decreased need for sleep, being more talkative than usual, flight of ideas, distractibility, increase in goaloriented activity and excessive involvement in risky activities. ...
E ncephalitis - School of Psychiatry
... slow relaxing reflexes in both upper limbs and lower limb oedema • Bloods reveal hypercholesterolaemia, hyponatraemia, hyperprolactinaemia, anaemia ...
... slow relaxing reflexes in both upper limbs and lower limb oedema • Bloods reveal hypercholesterolaemia, hyponatraemia, hyperprolactinaemia, anaemia ...
ho-2301-chap14powerpoint
... Explaining Schizophrenia • Genetic – Schizophrenia tends to cluster in certain families – The more closely related a person is to someone who has schizophrenia, the greater the risk that she will be diagnosed with schizophrenia at some point in her lifetime – If either biological parent of an adopt ...
... Explaining Schizophrenia • Genetic – Schizophrenia tends to cluster in certain families – The more closely related a person is to someone who has schizophrenia, the greater the risk that she will be diagnosed with schizophrenia at some point in her lifetime – If either biological parent of an adopt ...
Dysthymic Disorder in Males Over Age 50
... •Dysthmia most often presents in a primary MD’s office •Dysthymia is under diagnosed especially among the target population of males over the age of 50 •Dysthymia is most often treated with medication and therapy is seldom offered as an option. ...
... •Dysthmia most often presents in a primary MD’s office •Dysthymia is under diagnosed especially among the target population of males over the age of 50 •Dysthymia is most often treated with medication and therapy is seldom offered as an option. ...
Emotional Health
... Loss of interest in daily activities Weight loss or gain Sleep disturbances Fatigue/loss of energy nearly every day Diminished ability to concentrate Recurrent thoughts of death Not due to a chemical substance Extreme impairment in daily functioning ...
... Loss of interest in daily activities Weight loss or gain Sleep disturbances Fatigue/loss of energy nearly every day Diminished ability to concentrate Recurrent thoughts of death Not due to a chemical substance Extreme impairment in daily functioning ...
Vague Aches and pain - University of Michigan Depression Center
... There are at least two sides to the neurotransmitter story Functional domains of Serotonin and Norepinephrine1-4 ...
... There are at least two sides to the neurotransmitter story Functional domains of Serotonin and Norepinephrine1-4 ...
DSM-5 Condensed Training
... emotion regulation, or behavior that reflects a dysfunction in the psychological, biological, or developmental processes underlying mental functioning. MD's are usually associated with significant distress or disability in social, occupational, or other important activities. An expectable or cultura ...
... emotion regulation, or behavior that reflects a dysfunction in the psychological, biological, or developmental processes underlying mental functioning. MD's are usually associated with significant distress or disability in social, occupational, or other important activities. An expectable or cultura ...
DSM Powerpoint - Incoming Student Resources
... No exclusion criteria for people with autism spectrum disorder ...
... No exclusion criteria for people with autism spectrum disorder ...
Somatisation medical students
... pains and am frequently sick.’ ‘There’s a big question mark on the reason for this illness. I went through several medical exams but the doctors can’t quite seem to find a reason. I hit balls for half an hour and then have to stop because I’m just too tired.’ ...
... pains and am frequently sick.’ ‘There’s a big question mark on the reason for this illness. I went through several medical exams but the doctors can’t quite seem to find a reason. I hit balls for half an hour and then have to stop because I’m just too tired.’ ...
Recognizing and Treating Bipolar Disorder
... of bipolar spectrum disorders.2,6 In the past, bipolar disorder was thought to be relatively rare as compared to unipolar depression. It is well documented that major depression is a common condition, with a lifetime prevalence of 21.3% for females and 12.7% for males in the United States.12 The DSM ...
... of bipolar spectrum disorders.2,6 In the past, bipolar disorder was thought to be relatively rare as compared to unipolar depression. It is well documented that major depression is a common condition, with a lifetime prevalence of 21.3% for females and 12.7% for males in the United States.12 The DSM ...
SOMATOFORM DISORDERS - New York Medical College
... Exaggerations Simulations of the disease Self-induced disease ...
... Exaggerations Simulations of the disease Self-induced disease ...
L6_Disorders of Mood..
... either mania or depression, the easier it becomes to have another episode. There now is evidence that many psychiatric disorders, not just bipolar disorder, are subject to this phenomenon. The better the control of the illness and the fewer cycles an individual has, the better his or her quality of ...
... either mania or depression, the easier it becomes to have another episode. There now is evidence that many psychiatric disorders, not just bipolar disorder, are subject to this phenomenon. The better the control of the illness and the fewer cycles an individual has, the better his or her quality of ...
Child and Adolescent Mental Health
... Mood and Anxiety Disorders Attention Deficit and Disruptive Behavior Disorders Developmental Disorders: Autism ...
... Mood and Anxiety Disorders Attention Deficit and Disruptive Behavior Disorders Developmental Disorders: Autism ...
Multiple Personality Disorder
... People seem to most often confuse someone who is suffering from schizophrenia with someone who has dissociative identity disorder. While both are chronic, serious mental health concerns, the differences between these two disorders are stark. People with schizophrenia hear or see things that aren’t t ...
... People seem to most often confuse someone who is suffering from schizophrenia with someone who has dissociative identity disorder. While both are chronic, serious mental health concerns, the differences between these two disorders are stark. People with schizophrenia hear or see things that aren’t t ...























