031709.PHitchcock.CerebellumLecture
... We have reviewed this material in accordance with U.S. Copyright Law and have tried to maximize your ability to use, share, and adapt it. The citation key on the following slide provides information about how you may share and adapt this material. Copyright holders of content included in this materi ...
... We have reviewed this material in accordance with U.S. Copyright Law and have tried to maximize your ability to use, share, and adapt it. The citation key on the following slide provides information about how you may share and adapt this material. Copyright holders of content included in this materi ...
File
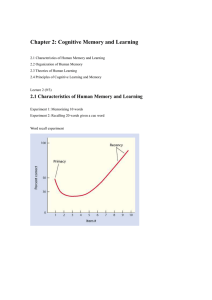
... and episodic memory (for facts and events) as already mentioned. When considered more closely case studies of amnesiacs suggest that both STM and LTM are far more complex than the multi-store model suggests, e.g. Clive Wearing has an intact memory for skills but a severely impaired memory of facts. ...
... and episodic memory (for facts and events) as already mentioned. When considered more closely case studies of amnesiacs suggest that both STM and LTM are far more complex than the multi-store model suggests, e.g. Clive Wearing has an intact memory for skills but a severely impaired memory of facts. ...
Mean - Fitchburg State University
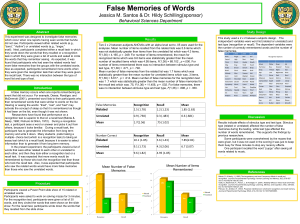
... recognition test is superior to that on a recall test (Balota & Neely ,1980; Petrusic & Dillon, 1972). During a recognition test, a participant sees a word or answer and picks it out from others, because it looks familiar. During a recall task, the participant has to generate the information from lo ...
... recognition test is superior to that on a recall test (Balota & Neely ,1980; Petrusic & Dillon, 1972). During a recognition test, a participant sees a word or answer and picks it out from others, because it looks familiar. During a recall task, the participant has to generate the information from lo ...
Document
... enhancement requires that we intervene in a highly complex system, the functioning of which is not fully understood. This complexity, combined with our lack of understanding of the risks associated with memory enhancement warrants that we precede with extreme caution. In addition to this, the drug s ...
... enhancement requires that we intervene in a highly complex system, the functioning of which is not fully understood. This complexity, combined with our lack of understanding of the risks associated with memory enhancement warrants that we precede with extreme caution. In addition to this, the drug s ...
Memory Intro - Walker Bioscience
... • Patients with Alzheimer's disease are unable to learn or remember ordinary facts (declarative memory) but are normal or nearly normal at learning and remembering how to do things (procedural memory). ...
... • Patients with Alzheimer's disease are unable to learn or remember ordinary facts (declarative memory) but are normal or nearly normal at learning and remembering how to do things (procedural memory). ...
Ch 12. Executive Functions and Frontal Lobes Introduction
... patients with prefrontal lesions. (TOP) In the item recognition task, only one object had appeared previously. (Bottom) ...
... patients with prefrontal lesions. (TOP) In the item recognition task, only one object had appeared previously. (Bottom) ...
Chapter 7: Long-term memory systems
... recognising a classmate’s photograph from 25 years earlier (Bahrick et al., 1975). Bahrick (1984) used the term “permastore” to describe these very long-term stable memories. Episodic memory can be assessed using tests for recognition and recall. Recognition memory test: Participants view a series ...
... recognising a classmate’s photograph from 25 years earlier (Bahrick et al., 1975). Bahrick (1984) used the term “permastore” to describe these very long-term stable memories. Episodic memory can be assessed using tests for recognition and recall. Recognition memory test: Participants view a series ...
Physiology Ch 57 p697-709 [4-25
... d. Area for Naming Objects – lateral area of ant occipital lobe and post temporal lobe is where naming objects takes place; learned through auditory input and physical natures are learned through visual input 2. Prefrontal Association Area – functions in association with motor cortex to plan comple ...
... d. Area for Naming Objects – lateral area of ant occipital lobe and post temporal lobe is where naming objects takes place; learned through auditory input and physical natures are learned through visual input 2. Prefrontal Association Area – functions in association with motor cortex to plan comple ...
Neural Basis of Memory: Systems Level
... and why it is meaningful to you, the more you actively integrate the new information with what you already know. Patients with prefrontal damage exhibit problems in organizing their thoughts and memories. These patients do not develop learning strategies or think deeply about what they need to learn ...
... and why it is meaningful to you, the more you actively integrate the new information with what you already know. Patients with prefrontal damage exhibit problems in organizing their thoughts and memories. These patients do not develop learning strategies or think deeply about what they need to learn ...
Chapter_3_ID2e_ekversion
... bookmarks, etc., – Major problem is deciding where and how to save them all, then remembering what they were called and where to find them again – Naming most common means of encoding them – Trying to remember a name of a file created some time back can be very difficult, especially when have 1000s ...
... bookmarks, etc., – Major problem is deciding where and how to save them all, then remembering what they were called and where to find them again – Naming most common means of encoding them – Trying to remember a name of a file created some time back can be very difficult, especially when have 1000s ...
concept of buddhi, mana and memory processes in
... The memory is the process in which information is encoded, stored, and retrieved. Encoding allows information that is from the outside world to reach our senses in the form of chemical and physical stimuli. The thinking and intellectual power of brain has an unlimited measureless capacity. Buddhi (i ...
... The memory is the process in which information is encoded, stored, and retrieved. Encoding allows information that is from the outside world to reach our senses in the form of chemical and physical stimuli. The thinking and intellectual power of brain has an unlimited measureless capacity. Buddhi (i ...
Chapter 14
... arose from subconscious beliefs isolated and forgotten, thus disassociated from consciousness. ...
... arose from subconscious beliefs isolated and forgotten, thus disassociated from consciousness. ...
Neuroscientists identify brain circuit necessary for memory formation
... memories are initially formed and stored in the comprehensive circuit mechanism for consolidation hippocampus only, before being gradually of memory," says Susumu Tonegawa, the Picower transferred to long-term storage in the neocortex Professor of Biology and Neuroscience, the and disappearing from ...
... memories are initially formed and stored in the comprehensive circuit mechanism for consolidation hippocampus only, before being gradually of memory," says Susumu Tonegawa, the Picower transferred to long-term storage in the neocortex Professor of Biology and Neuroscience, the and disappearing from ...
Chapter_3_ID2e_slides - Interaction Design
... bookmarks, etc., – Major problem is deciding where and how to save them all, then remembering what they were called and where to find them again – Naming most common means of encoding them – Trying to remember a name of a file created some time back can be very difficult, especially when have 1000s ...
... bookmarks, etc., – Major problem is deciding where and how to save them all, then remembering what they were called and where to find them again – Naming most common means of encoding them – Trying to remember a name of a file created some time back can be very difficult, especially when have 1000s ...
PDF
... Review findings on context effects on consumer expenditures Explore effects of different groupings Test hypotheses about groupings in laboratory and field Do field test to determine operational feasibility ...
... Review findings on context effects on consumer expenditures Explore effects of different groupings Test hypotheses about groupings in laboratory and field Do field test to determine operational feasibility ...
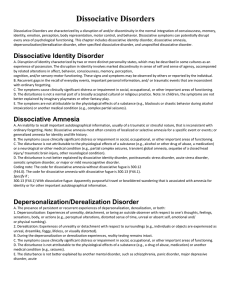
Dissociative Disorders
... A. Disruption of identity characterized by two or more distinct personality states, which may be described in some cultures as an experience of possession. The disruption in identity involves marked discontinuity in sense of self and sense of agency, accompanied by related alterations in affect, beh ...
... A. Disruption of identity characterized by two or more distinct personality states, which may be described in some cultures as an experience of possession. The disruption in identity involves marked discontinuity in sense of self and sense of agency, accompanied by related alterations in affect, beh ...
phys Learning Objectives Chapter 57 [10-31
... Rehearsal of the same information again and again in the mind accelerates and potentiates the degree of transfer of short-term memory into long-term memory. 41. How are new memories codified? New and old memories are compared for similarities and differences, and part of the storage process is to st ...
... Rehearsal of the same information again and again in the mind accelerates and potentiates the degree of transfer of short-term memory into long-term memory. 41. How are new memories codified? New and old memories are compared for similarities and differences, and part of the storage process is to st ...
Memory
... but no barn. 17% in the experimental group (the group asked the leading questions) reported seeing a barn. Only 3% in the control group (not asked leading questions) made this error. ...
... but no barn. 17% in the experimental group (the group asked the leading questions) reported seeing a barn. Only 3% in the control group (not asked leading questions) made this error. ...
Storing and Keeping Memories
... partly understood. Memories are fundamental for learning and being able to interact with our environment. There is a sequence of events that are involved in forming memories. These events include the acquisition and storage of something one wishes to remember and after retaining this information, be ...
... partly understood. Memories are fundamental for learning and being able to interact with our environment. There is a sequence of events that are involved in forming memories. These events include the acquisition and storage of something one wishes to remember and after retaining this information, be ...
Ch05x
... • Similar concept to short-term memory • Working memory (WM): limited capacity system for temporary storage and manipulation of information for complex tasks such as comprehension, learning, and reasoning ...
... • Similar concept to short-term memory • Working memory (WM): limited capacity system for temporary storage and manipulation of information for complex tasks such as comprehension, learning, and reasoning ...
Presentation 4: How memory works
... B6.1 How do organisms respond to changes in their environment? Coordination of responses to stimuli via the central nervous system. B6.4 How do humans develop more complex behaviour? Formation of neuron pathways and learning through repetition. B6.5 What do we know about the way in which the brain c ...
... B6.1 How do organisms respond to changes in their environment? Coordination of responses to stimuli via the central nervous system. B6.4 How do humans develop more complex behaviour? Formation of neuron pathways and learning through repetition. B6.5 What do we know about the way in which the brain c ...
Systems of Memory - Faculty Web Sites at the University of Virginia
... perform a word identification task in which a word is flashed very briefly on a computer monitor, and the patient must try to identify it. The patient will be better able to identify words read an hour ago than novel words. It is hypothesized that the representations supporting word identification a ...
... perform a word identification task in which a word is flashed very briefly on a computer monitor, and the patient must try to identify it. The patient will be better able to identify words read an hour ago than novel words. It is hypothesized that the representations supporting word identification a ...
McClelland226IntroCompLearnSys
... learning with dense (overlapping) patterns of activation. (Many aspects of semantic cognition and conceptual development are explained by this approach). • Rapid learning of new information in such systems leads to catastrophic interference. • The hippocampus (working with the cortex) can solve this ...
... learning with dense (overlapping) patterns of activation. (Many aspects of semantic cognition and conceptual development are explained by this approach). • Rapid learning of new information in such systems leads to catastrophic interference. • The hippocampus (working with the cortex) can solve this ...
Source amnesia

Source amnesia is the inability to remember where, when or how previously learned information has been acquired, while retaining the factual knowledge. This branch of amnesia is associated with the malfunctioning of one's explicit memory. It is likely that the disconnect between having the knowledge and remembering the context in which the knowledge was acquired is due to a dissociation between semantic and episodic memory – an individual retains the semantic knowledge (the fact), but lacks the episodic knowledge to indicate the context in which the knowledge was gained.Memory representations reflect the encoding processes during acquisition. Different types of acquisition processes (e.g.: reading, thinking, listening) and different types of events (e.g.: newspaper, thoughts, conversation) will produce mental depictions that perceptually differ from one another in the brain, making it harder to retrieve where information was learned when placed in a different context of retrieval. Source monitoring involves a systematic process of slow and deliberate thought of where information was originally learned. Source monitoring can be improved by using more retrieval cues, discovering and noting relations and extended reasoning.