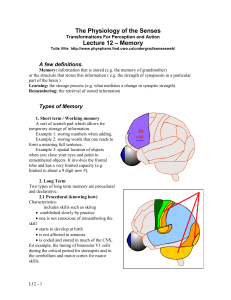
Types of Memory
... permanent changes in synaptic strength between assemblies of neurons. For example, rats raised in a rich environment have a thicker cortex with larger and more synapses. In the case of procedural memory, the changes are produced gradually by repeated exposure to the stimulus. ...
... permanent changes in synaptic strength between assemblies of neurons. For example, rats raised in a rich environment have a thicker cortex with larger and more synapses. In the case of procedural memory, the changes are produced gradually by repeated exposure to the stimulus. ...
Learning, remembering and forgetting in the mammalian brain
... Pavlovian conditioning. These studies have shown that learning and memory formation result from two forms of plasticity: synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis. Synaptic plasticity refers to changes in synaptic strength of connections in existing networks of neurons, by the process of LTP, and is init ...
... Pavlovian conditioning. These studies have shown that learning and memory formation result from two forms of plasticity: synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis. Synaptic plasticity refers to changes in synaptic strength of connections in existing networks of neurons, by the process of LTP, and is init ...
Memory
... but no barn. 17% in the experimental group (the group asked the leading questions) reported seeing a barn. Only 3% in the control group (not asked leading questions) made this error. ...
... but no barn. 17% in the experimental group (the group asked the leading questions) reported seeing a barn. Only 3% in the control group (not asked leading questions) made this error. ...
Lec 18 - Forgetting
... Forgetting (retention loss) refers to apparent loss of information already encoded and stored in an individual's long term memory. It is a spontaneous or gradual process in which oldmemories are unable to be recalled from memory storage. It is subject to delicately balanced optimization that ensures ...
... Forgetting (retention loss) refers to apparent loss of information already encoded and stored in an individual's long term memory. It is a spontaneous or gradual process in which oldmemories are unable to be recalled from memory storage. It is subject to delicately balanced optimization that ensures ...
No Slide Title
... • The ability to acquire new memories about facts, episodes of our lives, places that we have been, people that we know, etc. (declarative memories) is a function of the medial temporal lobe. • The medial temporal lobe is not required for immediate memory. • The medial temporal lobe is not the ultim ...
... • The ability to acquire new memories about facts, episodes of our lives, places that we have been, people that we know, etc. (declarative memories) is a function of the medial temporal lobe. • The medial temporal lobe is not required for immediate memory. • The medial temporal lobe is not the ultim ...
Is There a Connection Between the Brain and Learning?
... • Major functions of the higher levels of the nervous system are learning and memory – Learning is a neural mechanism by which the individual changes his or her behavior as the result of experience – Memory refers to the storage mechanism for what is learned ...
... • Major functions of the higher levels of the nervous system are learning and memory – Learning is a neural mechanism by which the individual changes his or her behavior as the result of experience – Memory refers to the storage mechanism for what is learned ...
Learning skills - Personal web pages for people of Metropolia
... navigates a path. When various rats paused on completion of a run, the place neurons fired in reverse order from the firing that had occurred during navigation. This reverse replay occurred more frequently after walking through new mazes than familiar ones, implying that the technique plays a role i ...
... navigates a path. When various rats paused on completion of a run, the place neurons fired in reverse order from the firing that had occurred during navigation. This reverse replay occurred more frequently after walking through new mazes than familiar ones, implying that the technique plays a role i ...
Silva & White - Walker Bioscience
... remembered how to read complex words in a mirror as well as normal control subjects • Were unable to recall the training session or the fact that they had acquired this skill. ...
... remembered how to read complex words in a mirror as well as normal control subjects • Were unable to recall the training session or the fact that they had acquired this skill. ...
Document
... • They support generalization on the basis of similarity • They can support micro-inferences based on consistent relationships between participating units ...
... • They support generalization on the basis of similarity • They can support micro-inferences based on consistent relationships between participating units ...
Memory
... Episodic memory is about happenings at particular places at particular times: - what - where - when Episodic memory develops late Not found in children younger than 4 years old (Give example from self) ...
... Episodic memory is about happenings at particular places at particular times: - what - where - when Episodic memory develops late Not found in children younger than 4 years old (Give example from self) ...
Cognitive
... Semantic Memory - This is information that has lost its time reference. That is, we know the information, facts, and concepts, but we cannot remember where or when the information was acquired. This is our generic knowledge of the world. Episodic Memory - These memories are associated with a specifi ...
... Semantic Memory - This is information that has lost its time reference. That is, we know the information, facts, and concepts, but we cannot remember where or when the information was acquired. This is our generic knowledge of the world. Episodic Memory - These memories are associated with a specifi ...
Biology of Learning and Memory
... them all correct & remembered what she did on each day! • Typical college student knows about 50,000 words + rules of language, familiar phrases. • Learning a language requires about 100,000 items of knowledge!! ...
... them all correct & remembered what she did on each day! • Typical college student knows about 50,000 words + rules of language, familiar phrases. • Learning a language requires about 100,000 items of knowledge!! ...
long-term memory
... H. M. and his amnesia II H.M.’s case ushered in the modern era of research on memory systems came from the four aspects of his mental capacity that remained intact. 1.Formal testing identified that cognitive abilities other than memory were intact → Memory could be separated from perception and inte ...
... H. M. and his amnesia II H.M.’s case ushered in the modern era of research on memory systems came from the four aspects of his mental capacity that remained intact. 1.Formal testing identified that cognitive abilities other than memory were intact → Memory could be separated from perception and inte ...
Working memory
... • Test 2 (non-word repetition task): – the experimenter read aloud non-word syllables (e.g., “mashpole,” “woop” “kintent.” ) to children. Then, children were asked to repeat the syllables. – Children’s ability to repeat the syllables was scored. ...
... • Test 2 (non-word repetition task): – the experimenter read aloud non-word syllables (e.g., “mashpole,” “woop” “kintent.” ) to children. Then, children were asked to repeat the syllables. – Children’s ability to repeat the syllables was scored. ...
Instructor`s Answer Key
... the acquisition of new information about facts and events, and for the consolidation of shortterm memory, which is stored in the cerebral cortex. People with head trauma, and those treated with electroconvulsive shock therapy, lose their memory of recent events but retain their older memories. Peopl ...
... the acquisition of new information about facts and events, and for the consolidation of shortterm memory, which is stored in the cerebral cortex. People with head trauma, and those treated with electroconvulsive shock therapy, lose their memory of recent events but retain their older memories. Peopl ...
Unit VII: Cognition - Rapid City Area Schools
... 3. Which of the following is an example of the flashbulb memory? a. Barry remembers an especially bright sunrise because he was by the ocean and the sunlight reflected off of the water. b. Robert remembers that correlation does not prove an cause-effect relationship because his teacher emphasized th ...
... 3. Which of the following is an example of the flashbulb memory? a. Barry remembers an especially bright sunrise because he was by the ocean and the sunlight reflected off of the water. b. Robert remembers that correlation does not prove an cause-effect relationship because his teacher emphasized th ...
1 - UCL
... from zero. Strong oscillations in the theta range were seen in each of the significantly phase locked neurons. For intelligible results to be computed the STA was equalised for number of spikes; this was how differences in phase locking were computed. The group found that the power of LFP when the s ...
... from zero. Strong oscillations in the theta range were seen in each of the significantly phase locked neurons. For intelligible results to be computed the STA was equalised for number of spikes; this was how differences in phase locking were computed. The group found that the power of LFP when the s ...
Memory - My Haiku
... Unit 3: Memory (Cognition) Essential Task 3-1: Describe the information processing model of memory with specific attention to the following steps: - Encoding: external stimuli, sensory registers, selective attention, reticular formation, short-term memory - Storage: long-term memory, explicit memory ...
... Unit 3: Memory (Cognition) Essential Task 3-1: Describe the information processing model of memory with specific attention to the following steps: - Encoding: external stimuli, sensory registers, selective attention, reticular formation, short-term memory - Storage: long-term memory, explicit memory ...
Limbic System - WELCOME to the future website of
... • Declarative (explicit) memory: facts, and knowledge that can be recalled into consciousness • Short term memory: may be forgotten or push into long term memory • Procedural memory (implicit) memory: learned skills • The hippocampus and its connections are necessary for new and short form memories. ...
... • Declarative (explicit) memory: facts, and knowledge that can be recalled into consciousness • Short term memory: may be forgotten or push into long term memory • Procedural memory (implicit) memory: learned skills • The hippocampus and its connections are necessary for new and short form memories. ...
Neuroscientists identify brain circuit necessary for memory formation
... memories fade completely from hippocampal cells or if some traces remain. Right now, the researchers can only monitor engram cells for about two weeks, but they are working on adapting their technology to work for a longer period. Kitamura says he believes that some trace of memory may stay in the h ...
... memories fade completely from hippocampal cells or if some traces remain. Right now, the researchers can only monitor engram cells for about two weeks, but they are working on adapting their technology to work for a longer period. Kitamura says he believes that some trace of memory may stay in the h ...
Answers to Test Your Knowledge questions for
... Categorization, classification and definition forms a very important aspect of the study of memory. This is particularly so when attempts are made to link memory to biological structures. The ability of humans to recall consciously and to articulate verbally what they recall reveals an important cla ...
... Categorization, classification and definition forms a very important aspect of the study of memory. This is particularly so when attempts are made to link memory to biological structures. The ability of humans to recall consciously and to articulate verbally what they recall reveals an important cla ...