Conventional septic tank/drain field - The Urban Rancher
... Educational programs of the Texas Agricultural Extension Service are open to all people without regard to race, color, sex, disability, religion, age or national origin. Issued in furtherance of Cooperative Extension Work in Agriculture and Home Economics, Acts of Congress of May 8, 1914, as amended ...
... Educational programs of the Texas Agricultural Extension Service are open to all people without regard to race, color, sex, disability, religion, age or national origin. Issued in furtherance of Cooperative Extension Work in Agriculture and Home Economics, Acts of Congress of May 8, 1914, as amended ...
Digestive and Urinary
... o Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) are stored in body; excessive intake leads to toxic effects, liver damage. o Water-soluble vitamins (C, B) not readily toxic; excess excreted. • Minerals o Iron, Calcium, Magnesium, Potassium, Selenium, Zinc, Manganese, Copper, Chromium, Iodine, Silicon, Vanadium, ...
... o Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) are stored in body; excessive intake leads to toxic effects, liver damage. o Water-soluble vitamins (C, B) not readily toxic; excess excreted. • Minerals o Iron, Calcium, Magnesium, Potassium, Selenium, Zinc, Manganese, Copper, Chromium, Iodine, Silicon, Vanadium, ...
Chapter 8 – Your Body Systems Lesson 4 – The Digestive System
... • the large intestine absorbs water and salts from the remaining food material • the parts of the food the body can’t use becomes waste • the waste passes through the large intestine and leaves through the anus Non-digestive Waste Removal ...
... • the large intestine absorbs water and salts from the remaining food material • the parts of the food the body can’t use becomes waste • the waste passes through the large intestine and leaves through the anus Non-digestive Waste Removal ...
Digestive - Puschuspeake
... Essential Question: How do the organs in the digestive system work together to process food and get the nutrients our body needs to stay healthy? ...
... Essential Question: How do the organs in the digestive system work together to process food and get the nutrients our body needs to stay healthy? ...
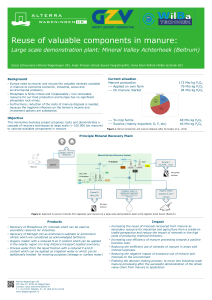
Poster Reuse of valuable components in manure
... Oscar Schoumans (Alterra Wageningen UR), Arjan Prinsen (Groot-Zevert Vergisting BV), Hans Klein Willink (Wilba techniek BV) ...
... Oscar Schoumans (Alterra Wageningen UR), Arjan Prinsen (Groot-Zevert Vergisting BV), Hans Klein Willink (Wilba techniek BV) ...
eutrophication - Upplandsstiftelsen
... ploughing. Leaching of fertilizers can also be avoided by planting winter vegetation on fields, which prevents the leaching of nutrients with spring time snowmelt. Landscapes that are continuously covered with grass have practically no erosion, thus pollution of the Baltic Sea can also be reduced th ...
... ploughing. Leaching of fertilizers can also be avoided by planting winter vegetation on fields, which prevents the leaching of nutrients with spring time snowmelt. Landscapes that are continuously covered with grass have practically no erosion, thus pollution of the Baltic Sea can also be reduced th ...
ANITA™Mox - Veolia Water Technologies
... ANITA™Mox solutions are especially suited to: • Bring into compliance wastewater treatment plants with existing sludge digestion and facing a significant rise in the nitrogen content of their raw water. • Wastewater treatment plants wishing to add sludge digestion that may or may not be combined w ...
... ANITA™Mox solutions are especially suited to: • Bring into compliance wastewater treatment plants with existing sludge digestion and facing a significant rise in the nitrogen content of their raw water. • Wastewater treatment plants wishing to add sludge digestion that may or may not be combined w ...
Nutrition - Uniservity CLC
... intestine into the bodies’ tissues and blood. The process of absorption happens in the villi that line the small intestine. These finger-like projections provide a large surface area for absorption to take place. ...
... intestine into the bodies’ tissues and blood. The process of absorption happens in the villi that line the small intestine. These finger-like projections provide a large surface area for absorption to take place. ...
Substituted Urine Debate
... and 1.002 before consuming the 1,868 ml of water. Whether or not that is her normal state or she purposely over hydrated prior to the study is not known. We do not have a preloading value for either creatinine or specific gravity in Joan Goodwin’s case. In neither of these cases so we find the kind ...
... and 1.002 before consuming the 1,868 ml of water. Whether or not that is her normal state or she purposely over hydrated prior to the study is not known. We do not have a preloading value for either creatinine or specific gravity in Joan Goodwin’s case. In neither of these cases so we find the kind ...
Water pollution control methods in agriculture
... About a million people, some 20% of the population of Finland, live in houses that are not connected to centralised sewarage systems. This means that about 350,000 permanent residences and a further 450,000 holiday homes must treat their own wastewater treated 'on site'. The treatment systems in ver ...
... About a million people, some 20% of the population of Finland, live in houses that are not connected to centralised sewarage systems. This means that about 350,000 permanent residences and a further 450,000 holiday homes must treat their own wastewater treated 'on site'. The treatment systems in ver ...
Penrith Wastewater Treatment Plant
... to a wider range of flows, including significant wet weather flows. They are also much simpler to construct than the various stages of the four stage biological reactor. The IDAL cycle usually takes about three hours. The difference between the IDAL and the biological reactor is that aeration, settl ...
... to a wider range of flows, including significant wet weather flows. They are also much simpler to construct than the various stages of the four stage biological reactor. The IDAL cycle usually takes about three hours. The difference between the IDAL and the biological reactor is that aeration, settl ...
Excretory System Notes
... System of the body that collects wastes produced by cells and removes the wastes from the body. Excretion- what the removal process is called. The structures of the excretory system that eliminate urea, water, and other wastes include the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra ...
... System of the body that collects wastes produced by cells and removes the wastes from the body. Excretion- what the removal process is called. The structures of the excretory system that eliminate urea, water, and other wastes include the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra ...
Chapter 18: Review
... Absorption: end products of digestion are transferred to blood and lymph (nutrients go into the blood from the small intestines) Villi: fingerlike projections in the lining of small intestines (do absorption) Define excretion: ...
... Absorption: end products of digestion are transferred to blood and lymph (nutrients go into the blood from the small intestines) Villi: fingerlike projections in the lining of small intestines (do absorption) Define excretion: ...
ppt - WordPress.com
... Diabetes- glucose in urine can be caused when the body does not produce enough insulin and the excess blood sugar is excreted Hyperuricosuria- too much uric acid in urine would produce a pH less than 7. This could be a sign of gout, ...
... Diabetes- glucose in urine can be caused when the body does not produce enough insulin and the excess blood sugar is excreted Hyperuricosuria- too much uric acid in urine would produce a pH less than 7. This could be a sign of gout, ...
Semester 1 Final Review
... Capillary Bleeding - Most common type of bleeding, oozes when injured, bright red. Shock - Occurs when to little oxygen and nutrients reach the body’s cells, tissue, and organs. ...
... Capillary Bleeding - Most common type of bleeding, oozes when injured, bright red. Shock - Occurs when to little oxygen and nutrients reach the body’s cells, tissue, and organs. ...
Document
... The flap of skin that covers your trachea when you swallow so that food doesn’t go into your lungs. ...
... The flap of skin that covers your trachea when you swallow so that food doesn’t go into your lungs. ...
Environmental Technology 1
... If residence time is excessive (> 2hr) the risk in secondary clarifier is that denitrification takes place, generating N2 microbubbles which can float sludge flocs. What we obviously want to avoid is sludge loss into the receiving water body we actually wanted to protect in the first place. On site ...
... If residence time is excessive (> 2hr) the risk in secondary clarifier is that denitrification takes place, generating N2 microbubbles which can float sludge flocs. What we obviously want to avoid is sludge loss into the receiving water body we actually wanted to protect in the first place. On site ...
Digestive System Digestive System- a series of organs that work
... 4. Epiglottis- small flap of tissue that closes the windpipe as food is swallowed. 5. Stomach- a muscular organ that mixes and churns food with acid and enzymes to further break down food. (Chyme) 6. Small Intestine- a coiled tube about 20 feet long, where most of the digestive process takes place. ...
... 4. Epiglottis- small flap of tissue that closes the windpipe as food is swallowed. 5. Stomach- a muscular organ that mixes and churns food with acid and enzymes to further break down food. (Chyme) 6. Small Intestine- a coiled tube about 20 feet long, where most of the digestive process takes place. ...
ACTIVATED SLUDGE What is it and where did it start? Activated
... in suspension by aeration and mixing. The activated sludge process was discovered (Fowler, Adren & Lockett) in 1913 in Britain. Their experimentation on treating sewage in a draw-and-fill reactor produced highly treated effluent. They aerated the wastewater continuously for about a month and were ab ...
... in suspension by aeration and mixing. The activated sludge process was discovered (Fowler, Adren & Lockett) in 1913 in Britain. Their experimentation on treating sewage in a draw-and-fill reactor produced highly treated effluent. They aerated the wastewater continuously for about a month and were ab ...
Reuse of excreta

Reuse of excreta (alternative spelling: re-use) refers to the safe, beneficial use of animal or human excreta, i.e. feces (or faeces in British English) and urine. Such beneficial use can be as a soil conditioner or fertilizer in agriculture, gardening, aquaculture or ornamental activities. Other possible uses include use as building material, fuel source or protein production. An alternative term is also ""use of excreta"" rather than ""reuse"" as strictly speaking it is the first use of excreta, not the second time that it is used.Reuse of excreta is one example of resource recovery of the resources contained in excreta, mainly the plant-available nutrients nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium as well as micronutrients such as sulphur and organic matter. These resources which are contained in wastewater, excreta and greywater have traditionally been reused in agriculture in many countries and are still being reused in agriculture to this day, but the practice is often carried out in an unregulated and unsafe manner for example in many developing countries (e.g. Mexico, India, Bangladesh, Ghana). The WHO Guidelines from 2006 have set up a framework how this reuse can be done safely by following a multiple barrier approach.Excreta-based fertilisers vary in their general properties and fertilising characteristics and include the following types: urine, dried feces, composted feces, faecal sludge (septage), municipal wastewater, sewage sludge and animal manure. Reuse of sanitised excreta in agriculture has also been called a ""closing the loop"" approach for sanitation and agriculture and is central to the ecological sanitation approach.Reuse of excreta is the final step of the sanitation chain which starts with collection of excreta (by use of toilets) and continues with transport and treatment (wastewater treatment is one example) all the way to either disposal or reuse.