Purification and Partial Characterization of a Latent Serine Protease
... During purification of proteases Mi and Fa, we fortuitously isolated a new, additional serine protease (LSP) in E. coli. From 8 g of the crude extract, approximately 1 flg of the purified LSP was obtained. However, the final yield as well as -·the specific activity could not be calculated until the ...
... During purification of proteases Mi and Fa, we fortuitously isolated a new, additional serine protease (LSP) in E. coli. From 8 g of the crude extract, approximately 1 flg of the purified LSP was obtained. However, the final yield as well as -·the specific activity could not be calculated until the ...
(a) (b)
... enzyme-catalyzed steps to two molecules of 3-carbon pyruvate. 1930s, Most of the details of this pathway were worked out by Otto Warburg, Gustav Embden, and Otto Meyerhof (German). This pathway is often referred to as the Embden–Meyerhof Pathway (EMP). Why is glycolysis so important to organisms? Fo ...
... enzyme-catalyzed steps to two molecules of 3-carbon pyruvate. 1930s, Most of the details of this pathway were worked out by Otto Warburg, Gustav Embden, and Otto Meyerhof (German). This pathway is often referred to as the Embden–Meyerhof Pathway (EMP). Why is glycolysis so important to organisms? Fo ...
CHAPTER 20 - AMINO ACID METABOLISM Introduction Amino acid
... Amino acid degradation also occurs as a result of normal protein turnover (see Table 201 for half-lives of some enzymes). Proteins, for example, can be damaged and must be replace. Also, controlling the levels (as well as the activities) of enzymes constitutes an important regulatory mechanism. Acco ...
... Amino acid degradation also occurs as a result of normal protein turnover (see Table 201 for half-lives of some enzymes). Proteins, for example, can be damaged and must be replace. Also, controlling the levels (as well as the activities) of enzymes constitutes an important regulatory mechanism. Acco ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules • Carbohydrates can be broken down to provide energy for cells. • Some carbohydrates are part of cell structure. Polymer (starch) Starch is a polymer of glucose monomers that often has a branched structure. ...
... 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules • Carbohydrates can be broken down to provide energy for cells. • Some carbohydrates are part of cell structure. Polymer (starch) Starch is a polymer of glucose monomers that often has a branched structure. ...
Biological Molecules: Water and Carbohydrates
... Globular proteins usually have a spherical shape caused by tightly folded polypeptide chains. The chains are usually folded so that hydrophobic groups are on the inside, while the hydrophilic groups are on the outside. This makes many globular proteins soluble in water. ...
... Globular proteins usually have a spherical shape caused by tightly folded polypeptide chains. The chains are usually folded so that hydrophobic groups are on the inside, while the hydrophilic groups are on the outside. This makes many globular proteins soluble in water. ...
c) acidic amino acids
... So 3 ATPs are required for the transportation of each amino acid. The key enzyme of the gamma-glutamyl cycle is gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase which is found in high levels in the kidneys ...
... So 3 ATPs are required for the transportation of each amino acid. The key enzyme of the gamma-glutamyl cycle is gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase which is found in high levels in the kidneys ...
BCHEM 254 – METABOLISM IN HEALTH AND DISEASES II Lecture
... nucleoside names end in -idine. The convention is to number the ring atoms of the base normally and to use l', etc. to distinguish the ring atoms of the sugar. Unless otherwise specified, the sugar is assumed to be ribose. To indicate that the sugar is 2'-deoxyribose, a d- is placed before the name. ...
... nucleoside names end in -idine. The convention is to number the ring atoms of the base normally and to use l', etc. to distinguish the ring atoms of the sugar. Unless otherwise specified, the sugar is assumed to be ribose. To indicate that the sugar is 2'-deoxyribose, a d- is placed before the name. ...
Design of Tight-Binding Human Immunodeficiency
... the death of many humans and infected patients have little chance to become healthy. In the beginning, people become exposed to HIV mainly by unsafe sex with HIV positive person of the same sex. But the situation has changed. Transmission can occur by many ways such as unsafe sex with either sex, sh ...
... the death of many humans and infected patients have little chance to become healthy. In the beginning, people become exposed to HIV mainly by unsafe sex with HIV positive person of the same sex. But the situation has changed. Transmission can occur by many ways such as unsafe sex with either sex, sh ...
Are You Getting It??
... Are You Getting It?? ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ Which events can occur during or after translation in E. coli? (multiple answers) a) Multiple ribosomes can bind to one mRNA. b) Translation can begin only after transcript ...
... Are You Getting It?? ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ Which events can occur during or after translation in E. coli? (multiple answers) a) Multiple ribosomes can bind to one mRNA. b) Translation can begin only after transcript ...
DOC
... can recognize identical DNA code and cuts at those positions with identical DNA code. Briefly, DNA fragments are generated from bacteria experimentally; and these DNA fragments are tagged fluorescently at one end. Finally, restriction enzyme is applied to cut DNA fragments; only fragment end is fluo ...
... can recognize identical DNA code and cuts at those positions with identical DNA code. Briefly, DNA fragments are generated from bacteria experimentally; and these DNA fragments are tagged fluorescently at one end. Finally, restriction enzyme is applied to cut DNA fragments; only fragment end is fluo ...
Document
... a. Acetyl CoA combines with bicarbonate to form malonyl CoA, which reacts with ACP to form malonyl ACP. Acetyl CoA + HCO3− + ATP → malonyl CoA + ADP + Pi + H+ Malonyl CoA + HS—ACP → malonyl ACP + HS—CoA b. The enzyme for the first reaction is acetyl CoA carboxylase. The enzyme for the second reactio ...
... a. Acetyl CoA combines with bicarbonate to form malonyl CoA, which reacts with ACP to form malonyl ACP. Acetyl CoA + HCO3− + ATP → malonyl CoA + ADP + Pi + H+ Malonyl CoA + HS—ACP → malonyl ACP + HS—CoA b. The enzyme for the first reaction is acetyl CoA carboxylase. The enzyme for the second reactio ...
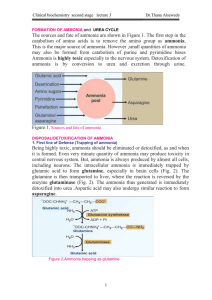
FORMATION OF AMMONIA
... results in a deficiency of one of the enzymes in the urea cycle. These enzymes are responsible for removing ammonia from the blood stream. Severe deficiency or total absence of activity of any of the first four enzymes (CPS1, OTC, ASS, ASL) in the urea cycle or the cofactor producer (NAGS) results i ...
... results in a deficiency of one of the enzymes in the urea cycle. These enzymes are responsible for removing ammonia from the blood stream. Severe deficiency or total absence of activity of any of the first four enzymes (CPS1, OTC, ASS, ASL) in the urea cycle or the cofactor producer (NAGS) results i ...
Example of Research Proposal
... catalysis, termed the peptidyl transferase center (PTC). The reaction substrates include a peptidyltRNA, charged with the growing peptide chain bound to a tRNA binding site on the ribosome, termed the P-site, and an aminoacyl-tRNA, charged with a single amino acid bound to a second location on the r ...
... catalysis, termed the peptidyl transferase center (PTC). The reaction substrates include a peptidyltRNA, charged with the growing peptide chain bound to a tRNA binding site on the ribosome, termed the P-site, and an aminoacyl-tRNA, charged with a single amino acid bound to a second location on the r ...
Bioorganic chemistry-a scientific endeavour in continuous
... showed comparable activity as coenzymes in a representative number of enzyme conversions (3). The lack of "visibility" of 3-iso-ATP as a probe was corrected by rendering ATP fluorescent by reaction with chloroacetaldehyde, with the formation of l , N b ethenoadenosine S'-triphosphate, E-ATP, a fluor ...
... showed comparable activity as coenzymes in a representative number of enzyme conversions (3). The lack of "visibility" of 3-iso-ATP as a probe was corrected by rendering ATP fluorescent by reaction with chloroacetaldehyde, with the formation of l , N b ethenoadenosine S'-triphosphate, E-ATP, a fluor ...
characteristics and stabilization of dnaase
... It has been assumed for many years that in protein synthesis the base sequence of DNA specifies the base sequence of RNA and that RNA in turn cont’rols the In accord with this notion, several groups recently amino acid sequence of protein. have observed an inhibition of amino acid incorporation into ...
... It has been assumed for many years that in protein synthesis the base sequence of DNA specifies the base sequence of RNA and that RNA in turn cont’rols the In accord with this notion, several groups recently amino acid sequence of protein. have observed an inhibition of amino acid incorporation into ...
Metabolism of BCAAs
... of which is a redox-sensitive CXXC center that plays a major role in catalytic reactions. In this case, the C’s represent the amino acid cysteine, while the X’s can be any amino acid. Both isozymes of BCAT are reversible, and it is this redox center that permits this reversibility. In most cells, BC ...
... of which is a redox-sensitive CXXC center that plays a major role in catalytic reactions. In this case, the C’s represent the amino acid cysteine, while the X’s can be any amino acid. Both isozymes of BCAT are reversible, and it is this redox center that permits this reversibility. In most cells, BC ...
Electron Transport Chain, Oxidative phosphorylation and Pentose
... Please solve this problem at home and check with Dr. Pandey during office hour. 24. List the three experiments that show that oxidation reactions in the intact mitochondrial membrane are coupled to the phosphorylation of ADP (leading to the ATP generation). 1. Oxygen consumption (oxidation) and ATP ...
... Please solve this problem at home and check with Dr. Pandey during office hour. 24. List the three experiments that show that oxidation reactions in the intact mitochondrial membrane are coupled to the phosphorylation of ADP (leading to the ATP generation). 1. Oxygen consumption (oxidation) and ATP ...
Supplementary Figure 1
... To obtain a more quantitative perspective on the sequence relationships between ubiquitin variants of different species, we used this phylogram to compare the protein sequences of UbS27a with the ribosomal S27a domain and with homologs to the ubiquitinlike modifier SUMO1 as a reference. The UPGMA al ...
... To obtain a more quantitative perspective on the sequence relationships between ubiquitin variants of different species, we used this phylogram to compare the protein sequences of UbS27a with the ribosomal S27a domain and with homologs to the ubiquitinlike modifier SUMO1 as a reference. The UPGMA al ...
12-Glycolysis2016-11-15 13:225.6 MB
... Regulation by: allosteric effectors. When ATP and Citrate are abundant (more than enough) they inhibit the reaction N.B they are not involved in the chemical reaction they have allosteric effect ...
... Regulation by: allosteric effectors. When ATP and Citrate are abundant (more than enough) they inhibit the reaction N.B they are not involved in the chemical reaction they have allosteric effect ...
Ch20.2 Amino-acids-degradation and synthesis
... It is possible to incorporate carbon units at each of these oxidation states, except methane, into other organic compounds. These single carbon units can be transferred from carrier compounds such as tetrahydrofolic acid and Sadenosylmethionine to specific structures that are being synthesized o ...
... It is possible to incorporate carbon units at each of these oxidation states, except methane, into other organic compounds. These single carbon units can be transferred from carrier compounds such as tetrahydrofolic acid and Sadenosylmethionine to specific structures that are being synthesized o ...
Biochemistry Final
... interactions with the environment. For example, alpha-helices that have amino acids with hydrophobic side groups tend to be found in hydrophobic environments, such as the plasma membrane. These helices tend to be part of transmembrane proteins, where the transmembrane domain is made of hydrophobic ...
... interactions with the environment. For example, alpha-helices that have amino acids with hydrophobic side groups tend to be found in hydrophobic environments, such as the plasma membrane. These helices tend to be part of transmembrane proteins, where the transmembrane domain is made of hydrophobic ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.