NAD+-dependent formate dehydrogenase. From a model enzyme to
... from various sectors of life sciences community ranging from quantum chemists to biotechnologists as NAD+-dependent formate dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.2; FDH). First discovered in 1950-1951 [1,2] it has not attracted much interest until the middle of seventies of the last century when a problem of cofa ...
... from various sectors of life sciences community ranging from quantum chemists to biotechnologists as NAD+-dependent formate dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.2; FDH). First discovered in 1950-1951 [1,2] it has not attracted much interest until the middle of seventies of the last century when a problem of cofa ...
Course Outline - KSU Faculty Member websites
... For practical, each main group (A&B) will be subdivided into 3 subgroups to allow a relatively small group at each practical class. A practical handout will be given to the student at the beginning of the year including all the practical classes to be given. It is beneficial for the student to read ...
... For practical, each main group (A&B) will be subdivided into 3 subgroups to allow a relatively small group at each practical class. A practical handout will be given to the student at the beginning of the year including all the practical classes to be given. It is beneficial for the student to read ...
Muscle as the Primary Site of Urea Cycle Enzyme Activity in an
... localized (Table I). In addition, the GSase in liver is localized in the cytosol (Table II), analogous to largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) where the liver mitochondrial glutamine-dependent CPSase III appears to have little or no function (13). Since GSase biosynthetic activity is '5% of the t ...
... localized (Table I). In addition, the GSase in liver is localized in the cytosol (Table II), analogous to largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) where the liver mitochondrial glutamine-dependent CPSase III appears to have little or no function (13). Since GSase biosynthetic activity is '5% of the t ...
Glycogen Metabolism Gluconeogenesis
... binding site, holding GDP in the inactive form, and is the “warhead” of the G protein. At least 20 different forms of Ga exist in mammalian cells. • Binding of the extracellular signal by the GPCR causes it to undergo an intracellular conformational change; this causes an allosteric effect on Gα. Th ...
... binding site, holding GDP in the inactive form, and is the “warhead” of the G protein. At least 20 different forms of Ga exist in mammalian cells. • Binding of the extracellular signal by the GPCR causes it to undergo an intracellular conformational change; this causes an allosteric effect on Gα. Th ...
1 - We can offer most test bank and solution manual you need.
... 23. NAD+ and FAD are often referred to as a. redox proteins. b. polymers. c. reduced dinucleotides. d. electron-carrying coenzymes. Ans: d ...
... 23. NAD+ and FAD are often referred to as a. redox proteins. b. polymers. c. reduced dinucleotides. d. electron-carrying coenzymes. Ans: d ...
An Organometallic Inhibitor for Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3
... hydrophobic interactions. In contrast, inorganic compounds find applications in medicinal chemistry predominately for their reactivity and imaging properties.1 We started a research program that aims in exploring the versatility of organometallic and inorganic compounds as structural scaffolds for t ...
... hydrophobic interactions. In contrast, inorganic compounds find applications in medicinal chemistry predominately for their reactivity and imaging properties.1 We started a research program that aims in exploring the versatility of organometallic and inorganic compounds as structural scaffolds for t ...
1 - GET Test Bank
... asymmetry around the carbon. Proteins consist of the L form of amino acids, and as these stereoisomers possess distinct biological properties and are not readily interconverted, you should choose the form that is normally utilized by cells. 28. Cysteine often plays an important role in stabilizing ...
... asymmetry around the carbon. Proteins consist of the L form of amino acids, and as these stereoisomers possess distinct biological properties and are not readily interconverted, you should choose the form that is normally utilized by cells. 28. Cysteine often plays an important role in stabilizing ...
Slide 1
... The repressor prevents gene transcription by binding to the operator and blocking RNA polymerase ...
... The repressor prevents gene transcription by binding to the operator and blocking RNA polymerase ...
THE EXTRACTION OF PAPAIN FROM PAPAYA LEAVES NUR
... Enzyme is known for its powerful attribute in catalyzing reactions. It is present in animal, plant and bacteria. You may find up to 4000 different kind of enzymes in an animal cell. It performs by lowering the activation energy of a given reaction, helps in speeding up the reaction identical to the ...
... Enzyme is known for its powerful attribute in catalyzing reactions. It is present in animal, plant and bacteria. You may find up to 4000 different kind of enzymes in an animal cell. It performs by lowering the activation energy of a given reaction, helps in speeding up the reaction identical to the ...
Promega Enzyme Resource Guide, Cloning Enzymes , BR075B
... bacteriophage’s tail fibers to its base plate during bacteriophage assembly (2). However, its activity as a ligase has been used effectively in various molecular biology applications. Both DNA and RNA ligases catalyze the formation of a phosphodiester bond between adjacent nucleotides with the concom ...
... bacteriophage’s tail fibers to its base plate during bacteriophage assembly (2). However, its activity as a ligase has been used effectively in various molecular biology applications. Both DNA and RNA ligases catalyze the formation of a phosphodiester bond between adjacent nucleotides with the concom ...
Journal of Phycology 44
... ammonium concentrations. As shown in Figure 1A, at initial ammonium concentration of 3 or 6 mg Æ L)1, combined immobilization enhanced the growth of C. vulgaris with A. brasilense Cd. However, the larger population did not yield higher protein content in the system (Fig. 1C) or in greater absorption ...
... ammonium concentrations. As shown in Figure 1A, at initial ammonium concentration of 3 or 6 mg Æ L)1, combined immobilization enhanced the growth of C. vulgaris with A. brasilense Cd. However, the larger population did not yield higher protein content in the system (Fig. 1C) or in greater absorption ...
Amino Acid Metabolism 1 Key Concepts
... into intestinal epithelial cells and then exported to the blood. The complete degradation of dietary proteins by these digestive proteases results from the distinct substrate specificities of the enzymes. Another source of free amino acids in the body comes from Figure 14. degradation of cellular pr ...
... into intestinal epithelial cells and then exported to the blood. The complete degradation of dietary proteins by these digestive proteases results from the distinct substrate specificities of the enzymes. Another source of free amino acids in the body comes from Figure 14. degradation of cellular pr ...
Building Triketide α-Pyrone-Producing Yeast Platform Using
... trimethylsilyl ether (C16); 4, 9-octadecenoic acid methyl ether (C18:1); 4-1, 9-octadecenoic acid trimethylsilyl ether (C18:1); 5, octadecanoic acid methyl ether (C18); 5-1, octadecanoic acid trimethylsilyl ether (C18); and 6, 9-hexanedioic acid 2,3-bis ester. ...
... trimethylsilyl ether (C16); 4, 9-octadecenoic acid methyl ether (C18:1); 4-1, 9-octadecenoic acid trimethylsilyl ether (C18:1); 5, octadecanoic acid methyl ether (C18); 5-1, octadecanoic acid trimethylsilyl ether (C18); and 6, 9-hexanedioic acid 2,3-bis ester. ...
Exam Procedures: this isBMB 514 Exam #2 10/8/12 this is form A
... During gluconeogenesis malate is moving into the cytoplasm It transports NADH from the cytosol to the matrix It is essentially irreversible It uses an α-ketoglutarate-aspartate cotransporter to maintains carbon balance It maintain glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase activity under anaerobic ...
... During gluconeogenesis malate is moving into the cytoplasm It transports NADH from the cytosol to the matrix It is essentially irreversible It uses an α-ketoglutarate-aspartate cotransporter to maintains carbon balance It maintain glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase activity under anaerobic ...
Classification and substrate head-group specificity of membrane
... desaturases (Δ4SPs) [44]. The different clusters include multiple sequences from different evolutionary kingdoms as well as a range of different substrate preferences (Fig. 2). This coarse separation of the clusters is consistent with the previously proposed membrane FAD classification, which was bas ...
... desaturases (Δ4SPs) [44]. The different clusters include multiple sequences from different evolutionary kingdoms as well as a range of different substrate preferences (Fig. 2). This coarse separation of the clusters is consistent with the previously proposed membrane FAD classification, which was bas ...
Word
... During gluconeogenesis malate is moving into the cytoplasm It transports NADH from the cytosol to the matrix It is essentially irreversible It uses an -ketoglutarate-aspartate cotransporter to maintains carbon balance It maintain glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase activity under anaerobic ...
... During gluconeogenesis malate is moving into the cytoplasm It transports NADH from the cytosol to the matrix It is essentially irreversible It uses an -ketoglutarate-aspartate cotransporter to maintains carbon balance It maintain glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase activity under anaerobic ...
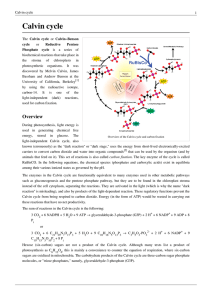
Calvin cycle
... 2. The enzyme G3P dehydrogenase catalyses the reduction of 1,3BPGA by NADPH (which is another product of the light-dependent stage). Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (also G3P, GP, TP, PGAL) is produced, and the NADPH itself was oxidized and becomes NADP+. Again, two NADPH are utilized per CO2 fixed. (Sim ...
... 2. The enzyme G3P dehydrogenase catalyses the reduction of 1,3BPGA by NADPH (which is another product of the light-dependent stage). Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (also G3P, GP, TP, PGAL) is produced, and the NADPH itself was oxidized and becomes NADP+. Again, two NADPH are utilized per CO2 fixed. (Sim ...
Click 1
... Rennin or chymosin is a pepsin-like protease (EC 3.4.23.4) that is produced as an inactive precursor, prorennin, in the stomachs of all nursing mammals. It is converted to active rennin (30.7 kDa) by the action of pepsin or by its autocatalysis. It is used extensively in the dairy industry to produ ...
... Rennin or chymosin is a pepsin-like protease (EC 3.4.23.4) that is produced as an inactive precursor, prorennin, in the stomachs of all nursing mammals. It is converted to active rennin (30.7 kDa) by the action of pepsin or by its autocatalysis. It is used extensively in the dairy industry to produ ...
Purification and Characterization of a Novel Pumpkin Short
... on a PhastGel gradient of 10% to 15% following ion-exchange chromatography. Peak fractions (nos. 19–25) following a chromatography on a Mono-S column were subjected to SDS-PAGE and transferred onto a PVDF membrane. Approximately 1 L from each fraction was loaded per lane. Molecular mass marker posi ...
... on a PhastGel gradient of 10% to 15% following ion-exchange chromatography. Peak fractions (nos. 19–25) following a chromatography on a Mono-S column were subjected to SDS-PAGE and transferred onto a PVDF membrane. Approximately 1 L from each fraction was loaded per lane. Molecular mass marker posi ...
Alkaptonuria and Aspergillus nidulans
... particularly nose bleeds. Jaundice may or may not be prominent. Despite vigorous therapy, death from hepatic failure frequently occurs between three and nine months of age unless a liver transplantation is performed. ...
... particularly nose bleeds. Jaundice may or may not be prominent. Despite vigorous therapy, death from hepatic failure frequently occurs between three and nine months of age unless a liver transplantation is performed. ...
Slide 1
... 2. No mammal can synthesize B vitamins but rumen bacteria do. 3. Some function as vitamins after undergoing a chemical change: Provitamins (e.g., β-carotene to vitamin A). ...
... 2. No mammal can synthesize B vitamins but rumen bacteria do. 3. Some function as vitamins after undergoing a chemical change: Provitamins (e.g., β-carotene to vitamin A). ...
Exam2_2012 final key - (canvas.brown.edu).
... E) All of the above are correct. Circle the correct answer 9. [2 points] In the reoxidation of QH2 by purified ubiquinone-cytochrome c reductase (Complex III) from heart muscle, the overall stoichiometry of the reaction requires 2 mol of cytochrome c per mole of QH2 because: A) cytochrome c is a one ...
... E) All of the above are correct. Circle the correct answer 9. [2 points] In the reoxidation of QH2 by purified ubiquinone-cytochrome c reductase (Complex III) from heart muscle, the overall stoichiometry of the reaction requires 2 mol of cytochrome c per mole of QH2 because: A) cytochrome c is a one ...
Enter Legible BANNER ID: B 0 0 __ __ __ __ __ __ DO NOT WRITE
... E) All of the above are correct. Circle the correct answer 9. [2 points] In the reoxidation of QH2 by purified ubiquinone-cytochrome c reductase (Complex III) from heart muscle, the overall stoichiometry of the reaction requires 2 mol of cytochrome c per mole of QH2 because: A) cytochrome c is a one ...
... E) All of the above are correct. Circle the correct answer 9. [2 points] In the reoxidation of QH2 by purified ubiquinone-cytochrome c reductase (Complex III) from heart muscle, the overall stoichiometry of the reaction requires 2 mol of cytochrome c per mole of QH2 because: A) cytochrome c is a one ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.