Carbohydrate Metabolism
... A. This enzyme is produced by salivary glands. Its optimum pH is 6.7. B. It is activated by chloride ions (cl-). C. It acts on cooked starch and glycogen breaking α 1-4 bonds, converting them into maltose [a disaccharide containing two glucose molecules attached by α 1-4 linkage]. This bond is not a ...
... A. This enzyme is produced by salivary glands. Its optimum pH is 6.7. B. It is activated by chloride ions (cl-). C. It acts on cooked starch and glycogen breaking α 1-4 bonds, converting them into maltose [a disaccharide containing two glucose molecules attached by α 1-4 linkage]. This bond is not a ...
LP - Columbia University
... 53 kcal/mole released, TOO high. Too much energy released: if it were used in one fell swoop of the usual coupled reaction, we would get only a single ATP's worth, 7 kcal/mole, from this 53 kcal/mole, and we'd release a LOT of heat besides. It would be better if we could break up this -53 kcal/mole ...
... 53 kcal/mole released, TOO high. Too much energy released: if it were used in one fell swoop of the usual coupled reaction, we would get only a single ATP's worth, 7 kcal/mole, from this 53 kcal/mole, and we'd release a LOT of heat besides. It would be better if we could break up this -53 kcal/mole ...
GIBBERELLIN BIOSYNTHESIS: Enzymes, Genes and Their
... of this must await the availability of pure enzyme because a regulatory function for Lh cannot be excluded. The Tan-ginbozu mutant of rice (dx) is probably also deficient in ent-kaurene oxidase activity (89). Application of uniconazole, an ent-kaurene oxidase inhibitor, mimics the phenotype of Tan-g ...
... of this must await the availability of pure enzyme because a regulatory function for Lh cannot be excluded. The Tan-ginbozu mutant of rice (dx) is probably also deficient in ent-kaurene oxidase activity (89). Application of uniconazole, an ent-kaurene oxidase inhibitor, mimics the phenotype of Tan-g ...
Fatty acid and phospholipid metabolism in prokaryotes
... coli is relatively facile. Mutants in many specific enzymes were generated by employing mutagens in combination with a battery of clever selection and screening techniques [7]. Such mutations generally fall into one of two classes. Firstly, they may confer an auxotrophy on a strain, such as a requir ...
... coli is relatively facile. Mutants in many specific enzymes were generated by employing mutagens in combination with a battery of clever selection and screening techniques [7]. Such mutations generally fall into one of two classes. Firstly, they may confer an auxotrophy on a strain, such as a requir ...
DEPARTMENT OF BIOCHEMISTRY UNIVERSITY OF KERALA
... AIM: The purpose of this course is to familiarize students with operation of all biochemical equipments and methods of statistical analysis of biological data. COURSE DESCRIPTION: The objectives of this course are to: • Train students on laboratory ethics and the use of some laboratory equipments. ...
... AIM: The purpose of this course is to familiarize students with operation of all biochemical equipments and methods of statistical analysis of biological data. COURSE DESCRIPTION: The objectives of this course are to: • Train students on laboratory ethics and the use of some laboratory equipments. ...
Rubisco Synthesis, Assembly, Mechanism, and Regulation
... to a more efficient form I enzyme, particularly under conditions in which low CC>2 prevails. Form I Rubisco is composed of two different-sized subunits. In addition to eight L-subunits, the enzyme requires an equivalent number of S-subunits to be fully active. Although the quaternary structures of t ...
... to a more efficient form I enzyme, particularly under conditions in which low CC>2 prevails. Form I Rubisco is composed of two different-sized subunits. In addition to eight L-subunits, the enzyme requires an equivalent number of S-subunits to be fully active. Although the quaternary structures of t ...
Microbial degradation of chloroaromatics Mars, Astrid E.
... Muconate cycloisomerase was measured by determining the decrease in substrate concentration at 260 nm. Reaction mixtures contained (in 1 ml) 30 mmol of Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 1 mmol of MnCl2, and 0.1 mmol of cis,cis-muconic acid. The reaction was started by adding crude extract (0.02 to 0.2 mg of protei ...
... Muconate cycloisomerase was measured by determining the decrease in substrate concentration at 260 nm. Reaction mixtures contained (in 1 ml) 30 mmol of Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 1 mmol of MnCl2, and 0.1 mmol of cis,cis-muconic acid. The reaction was started by adding crude extract (0.02 to 0.2 mg of protei ...
The serC-aroA operon of Escherichia coli
... Messing, 1983). The coding region of the aroA gene was identified by comparison of the translated DNA sequence with the N-terminal protein sequence of EPSP synthase. The start point of the aroA coding region is an ATG codon approx. 700 bp to the right of the Clal site and the gene runs left to right ...
... Messing, 1983). The coding region of the aroA gene was identified by comparison of the translated DNA sequence with the N-terminal protein sequence of EPSP synthase. The start point of the aroA coding region is an ATG codon approx. 700 bp to the right of the Clal site and the gene runs left to right ...
mineralization of chlorobenzene. of the meta
... Enzymes used in the degradation of monoaromatic compounds. To investigate which degradation pathway is used by P. putida GJ31 for growth on aromatic compounds, the presence of enzymes involved in the meta-, ortho-, and modified ortho-cleavage pathways was determined in crude extracts prepared from c ...
... Enzymes used in the degradation of monoaromatic compounds. To investigate which degradation pathway is used by P. putida GJ31 for growth on aromatic compounds, the presence of enzymes involved in the meta-, ortho-, and modified ortho-cleavage pathways was determined in crude extracts prepared from c ...
Chapter 3
... Coupled reactions – Liberation of energy in an exergonic reaction drives an endergonic reaction • “Harnessed energy to accomplish a task” ...
... Coupled reactions – Liberation of energy in an exergonic reaction drives an endergonic reaction • “Harnessed energy to accomplish a task” ...
1. Introduction to Natural Products Chemistry
... 6. The production of secondary metabolites depends on genetic and environmental factors. That is, secondary metabolites may be present in the organism in various amounts depending on the time of day or season, at particular stages of the organism’s life, or in response to certain environmental stimu ...
... 6. The production of secondary metabolites depends on genetic and environmental factors. That is, secondary metabolites may be present in the organism in various amounts depending on the time of day or season, at particular stages of the organism’s life, or in response to certain environmental stimu ...
Inherited Propionyl
... impaired when mixed with A. G.'s extracts, there is no evidence for either an unusual cofactor requirement or for an intracellular inhibitor causing defective propionylCoA carboxylation in A. G.'s cells. Therefore, we conclude that her cells either fail to synthesize propionylCoA carboxylase, or, al ...
... impaired when mixed with A. G.'s extracts, there is no evidence for either an unusual cofactor requirement or for an intracellular inhibitor causing defective propionylCoA carboxylation in A. G.'s cells. Therefore, we conclude that her cells either fail to synthesize propionylCoA carboxylase, or, al ...
A: _____/18
... The transition state is a high energy intermediate in the reaction. By reducing the energy of the transition state, enzyme will increase the concentration of the transition state, thus increasing the rate of the reaction (6 pts). The reduction in energy of the transition state can be due to two fact ...
... The transition state is a high energy intermediate in the reaction. By reducing the energy of the transition state, enzyme will increase the concentration of the transition state, thus increasing the rate of the reaction (6 pts). The reduction in energy of the transition state can be due to two fact ...
Molecular Docking Studies of Isorhamnetin from Corchorus olitorius
... Diabetes is the 7th leading cause of mortality in the United States, with over 68,071 death certificates registering it as a major cause of death [1]. The approximate estimation of diabetes in Africa is 1% in rural areas, and varies from 5% to 7% in urban sub-Saharan [8]. Type II diabetes (T2DM) is ...
... Diabetes is the 7th leading cause of mortality in the United States, with over 68,071 death certificates registering it as a major cause of death [1]. The approximate estimation of diabetes in Africa is 1% in rural areas, and varies from 5% to 7% in urban sub-Saharan [8]. Type II diabetes (T2DM) is ...
03. Metabolism of lipids
... • Lipids are water-insoluble organic biomolecules that can be extracted from cells and tissues by nonpolar solvents, e.g., chloroform, ether, or benzene. ...
... • Lipids are water-insoluble organic biomolecules that can be extracted from cells and tissues by nonpolar solvents, e.g., chloroform, ether, or benzene. ...
Turnover-based in vitro selection and evolution of biocatalysts from
... 105-fold faster than the uncatalyzed reaction. The system is thus capable of identifying both highly efficient and poorly active catalysts18. Covalent trapping of phages displaying catalytic scFv fragments We sought to identify catalysts from the highly diverse HuCAL-scFv library by covalent binding ...
... 105-fold faster than the uncatalyzed reaction. The system is thus capable of identifying both highly efficient and poorly active catalysts18. Covalent trapping of phages displaying catalytic scFv fragments We sought to identify catalysts from the highly diverse HuCAL-scFv library by covalent binding ...
Caspaar Bijleveld and Math JH Geelen
... carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to form malonyl-CoA. This reaction is the first committed step leading to de novo synthesis of long-chain fatty acids. A number of studies have identified acetyl-CoA carboxylase as the rate-limiting enzyme in the pathway and it is believed to be one of the key control poi ...
... carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to form malonyl-CoA. This reaction is the first committed step leading to de novo synthesis of long-chain fatty acids. A number of studies have identified acetyl-CoA carboxylase as the rate-limiting enzyme in the pathway and it is believed to be one of the key control poi ...
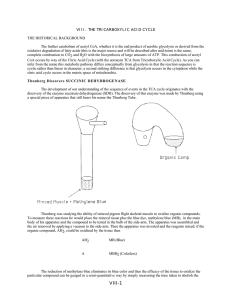
Chapter 8
... At this point all of the reactions that result in reduction in carbon chain length are complete, 2 CO2 have been eliminated 2 NADH and 1 ATP have been made and we are back with a 4-carbon acid. However the acid is succinate, whereas to start a new cycle we need oxalacetate. This requires the oxidati ...
... At this point all of the reactions that result in reduction in carbon chain length are complete, 2 CO2 have been eliminated 2 NADH and 1 ATP have been made and we are back with a 4-carbon acid. However the acid is succinate, whereas to start a new cycle we need oxalacetate. This requires the oxidati ...
The nature of mycelial lipolytic enzymes in filamentous fungi
... liberated is indicative of the positional specificity of the hydrolysis. According to the data of Kuksis and Marai [3], a ratio of up to 8 would imply phospholipase A1 attack whereas A2 attack would be indicated by a ratio as low as 0.02. A ratio approximating to unity would be obtained following ph ...
... liberated is indicative of the positional specificity of the hydrolysis. According to the data of Kuksis and Marai [3], a ratio of up to 8 would imply phospholipase A1 attack whereas A2 attack would be indicated by a ratio as low as 0.02. A ratio approximating to unity would be obtained following ph ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.