Micro 2 transcripts to be made into flashcards
... lid on your agar plate next lab period, and put one drop of H2O2 onto the colony. A positive test will show the oxygen bubbles rising up from the plate. That means the organism has the enzyme, so it is catalase +. NOTE: do not get catalase mixed up with oxidase. Catalase breaks down into oxygen, but ...
... lid on your agar plate next lab period, and put one drop of H2O2 onto the colony. A positive test will show the oxygen bubbles rising up from the plate. That means the organism has the enzyme, so it is catalase +. NOTE: do not get catalase mixed up with oxidase. Catalase breaks down into oxygen, but ...
CHAPTER-IV LIPID METABOLISM BETA
... broken down in mitochondria and/or peroxisomes to generate acetyl-CoA, the entry molecule for the citric acid cycle. The beta oxidation of fatty acids involve three stages: 1. Activation of fatty acids in the cytosol 2. Transport of activated fatty acids into mitochondria (carnitine shuttle) 3. Beta ...
... broken down in mitochondria and/or peroxisomes to generate acetyl-CoA, the entry molecule for the citric acid cycle. The beta oxidation of fatty acids involve three stages: 1. Activation of fatty acids in the cytosol 2. Transport of activated fatty acids into mitochondria (carnitine shuttle) 3. Beta ...
Comparative Estimation of Total Protein Content and Enzymatic
... problems in many regions of the world [2]. Furthermore, it is also common in Iraq [1]. E. multilocularis, causing alveolar echinococcosis (AE) is more widely distributed in the northern hemisphere, and represents a considerable public health burden as it’s the most virulent species and infection wit ...
... problems in many regions of the world [2]. Furthermore, it is also common in Iraq [1]. E. multilocularis, causing alveolar echinococcosis (AE) is more widely distributed in the northern hemisphere, and represents a considerable public health burden as it’s the most virulent species and infection wit ...
(De)regulation of key enzyme steps in the shikimate pathway and
... Prephenate dehydratase (PDT), chorismate mutase (CM) and 3-deoxy-D-arabino-7-heptulosonate 7-phosphate (DAHP) synthase are key regulatory enzymes in aromatic amino acid biosynthesis in the actinomycete Amycolatopsis methanolica. Deregulated, feedback-control-resistant mutants were isolated by incuba ...
... Prephenate dehydratase (PDT), chorismate mutase (CM) and 3-deoxy-D-arabino-7-heptulosonate 7-phosphate (DAHP) synthase are key regulatory enzymes in aromatic amino acid biosynthesis in the actinomycete Amycolatopsis methanolica. Deregulated, feedback-control-resistant mutants were isolated by incuba ...
Haem biosynthesis and excretion of porphyrins
... substrate molecules at the catalytic site and directing the condensation of PBG to form the tetrapyrrole. Uroporphyrinogen III cosynthase then rapidly converts the intermediate into uroporphyrinogen III, a cyclic tetrapyrrole with eight carboxyl side-chains. In the absence of this ring-closing and s ...
... substrate molecules at the catalytic site and directing the condensation of PBG to form the tetrapyrrole. Uroporphyrinogen III cosynthase then rapidly converts the intermediate into uroporphyrinogen III, a cyclic tetrapyrrole with eight carboxyl side-chains. In the absence of this ring-closing and s ...
Are there errors in glycogen biosynthesis and is laforin a repair
... The most important constituent of glycogen is glucose which of course underlies its metabolic function. Since the 1980s, however, it has been recognized that glycogen contains trace amounts of phosphate [16–18], 1 phosphate per 500 to 1500 glucoses in muscle glycogen [2,3]. In mice, this level of ph ...
... The most important constituent of glycogen is glucose which of course underlies its metabolic function. Since the 1980s, however, it has been recognized that glycogen contains trace amounts of phosphate [16–18], 1 phosphate per 500 to 1500 glucoses in muscle glycogen [2,3]. In mice, this level of ph ...
Uric acid estimation in plasma
... Describe the principle of uric acid estimation in serum and its clinical importance ...
... Describe the principle of uric acid estimation in serum and its clinical importance ...
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (TCA), Krebs Cycle
... pyr dehydrogenase complex is composed of three enzymes – pyr decarboxylase (E1) - dihydrolipoyl transacylase (E2) - dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (E3) Each catalyzed a part of the overall reaction In addition to two regulatory enzymes protein kinase and phosphoprotein phosphatase. ...
... pyr dehydrogenase complex is composed of three enzymes – pyr decarboxylase (E1) - dihydrolipoyl transacylase (E2) - dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (E3) Each catalyzed a part of the overall reaction In addition to two regulatory enzymes protein kinase and phosphoprotein phosphatase. ...
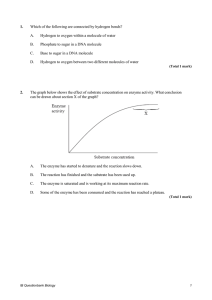
1. Which of the following are connected by hydrogen bonds? A
... Escherichia coli is a unicellular organism, so each cell must carry out all of the processes required for life. Outline the functions of each of the structures in the cells of Escherichia coli. ...
... Escherichia coli is a unicellular organism, so each cell must carry out all of the processes required for life. Outline the functions of each of the structures in the cells of Escherichia coli. ...
medical chemistry and biochemistry
... Outline the four principal mechanisms by which enzymes achieve catalysis. Describe how an “induced fit” facilitates substrate recognition and catalysis. Indicate whether ΔG, the overall free energy change in a reaction, is dependent on the reaction mechanism. Indicate whether ΔG is a function of the ...
... Outline the four principal mechanisms by which enzymes achieve catalysis. Describe how an “induced fit” facilitates substrate recognition and catalysis. Indicate whether ΔG, the overall free energy change in a reaction, is dependent on the reaction mechanism. Indicate whether ΔG is a function of the ...
Aerobic respiration - Wesleyan
... substrate-level phosphorylation. Two molecules of pyruvate form at this last reaction step. 6 Summing up, glycolysis yields two NADH, two ATP (net), ...
... substrate-level phosphorylation. Two molecules of pyruvate form at this last reaction step. 6 Summing up, glycolysis yields two NADH, two ATP (net), ...
Partial Purification and Characterization of the Maize Mitochondrial
... that of pea. This may explain why the maize complex, unlike the pea complex (Miernyk and Randall, 1987), required exogenous TPP for activity. The Ki for NADH was 5-fold lower than the Km for NAD1, whereas the Ki for acetyl-CoA was much higher than the Km for CoA, suggesting that NADH could be a more ...
... that of pea. This may explain why the maize complex, unlike the pea complex (Miernyk and Randall, 1987), required exogenous TPP for activity. The Ki for NADH was 5-fold lower than the Km for NAD1, whereas the Ki for acetyl-CoA was much higher than the Km for CoA, suggesting that NADH could be a more ...
Caffeoylquinic acids as inhibitors for HIV-I protease and HIV
... Three types of docking were used on this study. In rigid docking, the possible binding conformations of a ligand (small molecule) in a specific area of the receptor are evaluated by rotating its bonds and translating the molecule. Flexible docking is similar to rigid docking in the sense that the se ...
... Three types of docking were used on this study. In rigid docking, the possible binding conformations of a ligand (small molecule) in a specific area of the receptor are evaluated by rotating its bonds and translating the molecule. Flexible docking is similar to rigid docking in the sense that the se ...
Untitled
... must be linked together during the course of translation. The first step towards ensuring translational accuracy depends on the tRNA synthetase which is responsible for linking the correct amino acid to each tRNA. Most synthetases select the correct amino acid by a two-step mechanism that involves t ...
... must be linked together during the course of translation. The first step towards ensuring translational accuracy depends on the tRNA synthetase which is responsible for linking the correct amino acid to each tRNA. Most synthetases select the correct amino acid by a two-step mechanism that involves t ...
Caffeoylquinic acids as inhibitors for HIV-I protease and HIV
... Three types of docking were used on this study. In rigid docking, the possible binding conformations of a ligand (small molecule) in a specific area of the receptor are evaluated by rotating its bonds and translating the molecule. Flexible docking is similar to rigid docking in the sense that the se ...
... Three types of docking were used on this study. In rigid docking, the possible binding conformations of a ligand (small molecule) in a specific area of the receptor are evaluated by rotating its bonds and translating the molecule. Flexible docking is similar to rigid docking in the sense that the se ...
Untitled
... must be linked together during the course of translation. The first step towards ensuring translational accuracy depends on the tRNA synthetase which is responsible for linking the correct amino acid to each tRNA. Most synthetases select the correct amino acid by a two-step mechanism that involves t ...
... must be linked together during the course of translation. The first step towards ensuring translational accuracy depends on the tRNA synthetase which is responsible for linking the correct amino acid to each tRNA. Most synthetases select the correct amino acid by a two-step mechanism that involves t ...
Biology 6 Test 1 Study Guide
... i. Biosynthesis – production of chemicals through a series of reactions ii. Movement – cell movement, internal movement, membrane transport iii. Bioluminescence - glowing B. Enzymes a. Enzymes are catalysts that speed up reactions by lowering activation energy (Fig. 5.2) i. Reactions must be spontan ...
... i. Biosynthesis – production of chemicals through a series of reactions ii. Movement – cell movement, internal movement, membrane transport iii. Bioluminescence - glowing B. Enzymes a. Enzymes are catalysts that speed up reactions by lowering activation energy (Fig. 5.2) i. Reactions must be spontan ...
Dynamic Modeling of Lactic Acid Fermentation Metabolism with
... biotechnology-produced PLA can become an alternate material of fossil fuel-based chemicals, the amount of CO2 emissions can be significantly reduced to step towards the goal of sustainable development. For these kinds of studies, systems biotechnology is an essential tool for the prediction and anal ...
... biotechnology-produced PLA can become an alternate material of fossil fuel-based chemicals, the amount of CO2 emissions can be significantly reduced to step towards the goal of sustainable development. For these kinds of studies, systems biotechnology is an essential tool for the prediction and anal ...
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA FOR DUPLICATED SACCHAROMYCES
... glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) homologues. MCK1 is involved in control of chromosome segregation and regulation of entry into meiosis ([9-11]; for review see [12]). MCK1 down-regulates pyruvate kinase [13] that involves inhibition of a cAMPdependent protein kinase [14]. MCK1 also has a role in r ...
... glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) homologues. MCK1 is involved in control of chromosome segregation and regulation of entry into meiosis ([9-11]; for review see [12]). MCK1 down-regulates pyruvate kinase [13] that involves inhibition of a cAMPdependent protein kinase [14]. MCK1 also has a role in r ...
Amino Acid
... Explain why an enzyme can catalyze a chemical reaction involving just one enantiomer of a compound ...
... Explain why an enzyme can catalyze a chemical reaction involving just one enantiomer of a compound ...
Reactivation of Creatine Kinase by Dithiothreitol Prior to Use
... CK might be critical for the generation of cell extracts for in vitro translation. Indeed, we have previously shown that the addition of sucrose during the preparation and storage of cell extracts could to some extent prevent the loss of the biological activity of the creatine kinase (Favre and Trep ...
... CK might be critical for the generation of cell extracts for in vitro translation. Indeed, we have previously shown that the addition of sucrose during the preparation and storage of cell extracts could to some extent prevent the loss of the biological activity of the creatine kinase (Favre and Trep ...
Crystal structure of ATP sulfurylase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... by hydrogen bonds and salt bridges. Contacts between the residues of helix H3 and the coiled region preceding H11 of the interdomain show a more hydrophobic character. Domain II (residues 168±327) comprises the active site and the substrate binding pocket. It shows a typical righthanded a/b-fold in ...
... by hydrogen bonds and salt bridges. Contacts between the residues of helix H3 and the coiled region preceding H11 of the interdomain show a more hydrophobic character. Domain II (residues 168±327) comprises the active site and the substrate binding pocket. It shows a typical righthanded a/b-fold in ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.