DNA Restriction and mechanism
... • The mammalian enzymes methylate the cytosine in mainly CG sequences to 5-methylcytosine (5-meC), but they do it efficiently only if the cytosine in the opposite strand already bears a methyl residue. The result is that CG sequences that are methylated perpetuate their methylated state following DN ...
... • The mammalian enzymes methylate the cytosine in mainly CG sequences to 5-methylcytosine (5-meC), but they do it efficiently only if the cytosine in the opposite strand already bears a methyl residue. The result is that CG sequences that are methylated perpetuate their methylated state following DN ...
1 Biochemistry 462a – Enzyme Mechanisms Reading
... enzyme somehow caused the substrate to become distorted toward the transition state. Transition state stabilization is a more modern concept, which states that it is not the substrate that is distorted but rather that the transition state makes better contacts with the enzyme than the substrate does ...
... enzyme somehow caused the substrate to become distorted toward the transition state. Transition state stabilization is a more modern concept, which states that it is not the substrate that is distorted but rather that the transition state makes better contacts with the enzyme than the substrate does ...
Chymotrypsin
... o The binding of NAM4 in the chair conformation is unfavorable. o But the binding of residue 4 in the half-chair conformation is favorable (preferential transition state binding). o Hydrolysis involves acid-base catalysis (Glu35 serves as a proton donor to the oxygen of the leaving alcohol. The resu ...
... o The binding of NAM4 in the chair conformation is unfavorable. o But the binding of residue 4 in the half-chair conformation is favorable (preferential transition state binding). o Hydrolysis involves acid-base catalysis (Glu35 serves as a proton donor to the oxygen of the leaving alcohol. The resu ...
1 Biology - Organic Chemistry Notes Name Date Organic Chemistry
... proteins. Protein molecules are long, usually folded chains made from 20 different kinds of amino acids in a specific sequence. This sequence influences the shape of the protein. The shape of the protein, in tern determines its function. -------------------------------------------------------------- ...
... proteins. Protein molecules are long, usually folded chains made from 20 different kinds of amino acids in a specific sequence. This sequence influences the shape of the protein. The shape of the protein, in tern determines its function. -------------------------------------------------------------- ...
Chapter 3. Enzymes
... of at least a million, but not change the equilibrium; b) enzymes are highly specific for their reactants which are so called “substrates”; ...
... of at least a million, but not change the equilibrium; b) enzymes are highly specific for their reactants which are so called “substrates”; ...
8 Introduction to Metabolism Notes
... on substrate concentrations. At low substrate concentrations, an increase in substrate concentration speeds binding to available active sites. However, there is a limit to how fast a reaction can occur. At high substrate concentrations, the active sites on all enzymes are engaged. We say the enzyme ...
... on substrate concentrations. At low substrate concentrations, an increase in substrate concentration speeds binding to available active sites. However, there is a limit to how fast a reaction can occur. At high substrate concentrations, the active sites on all enzymes are engaged. We say the enzyme ...
Introduction to Metabolism Notes
... on substrate concentrations. At low substrate concentrations, an increase in substrate concentration speeds binding to available active sites. However, there is a limit to how fast a reaction can occur. At high substrate concentrations, the active sites on all enzymes are engaged. We say the enzyme ...
... on substrate concentrations. At low substrate concentrations, an increase in substrate concentration speeds binding to available active sites. However, there is a limit to how fast a reaction can occur. At high substrate concentrations, the active sites on all enzymes are engaged. We say the enzyme ...
ch3a FA11 - Cal State LA
... How to lower EA • Mechanism: form an Enzyme-Substrate (ES) complex at active site – Enhance substrate reactivity • Enhance polarity of bonds via interaction with amino acid functional groups • Possibly form covalent bonded intermediates with amino acid side chains ...
... How to lower EA • Mechanism: form an Enzyme-Substrate (ES) complex at active site – Enhance substrate reactivity • Enhance polarity of bonds via interaction with amino acid functional groups • Possibly form covalent bonded intermediates with amino acid side chains ...
Enzyme
... - The molecular structure corresponding to this maximum potential energy point is referred to as the “ transition state”—in the physical sense, the transition state can be envisioned as a transient pseudointermediate in the reaction with the maximum potential energy - Transition state (TS) theory po ...
... - The molecular structure corresponding to this maximum potential energy point is referred to as the “ transition state”—in the physical sense, the transition state can be envisioned as a transient pseudointermediate in the reaction with the maximum potential energy - Transition state (TS) theory po ...
October 12 AP Biology - John D. O`Bryant School of Math & Science
... C) Enzymes are used up in chemical reactions. D) Enzymes emerge unchanged from the reactions they ...
... C) Enzymes are used up in chemical reactions. D) Enzymes emerge unchanged from the reactions they ...
Biology 20
... 3. After you have broken down your breakfast items into simpler products. The chemical reactions that result in the building of more complex molecules are referred to as reactions. a) anabolic; b) catabolic; c) dehydration; d) none of these. 4. Three or four of the following statements concerning en ...
... 3. After you have broken down your breakfast items into simpler products. The chemical reactions that result in the building of more complex molecules are referred to as reactions. a) anabolic; b) catabolic; c) dehydration; d) none of these. 4. Three or four of the following statements concerning en ...
fats and oils into fatty acids and glycerol
... The system is adapted to break down and absorb food. Physical digestion breaks the food down into smaller pieces and chemical digestion breaks these pieces into smaller molecules. Various enzymes and other substances, such as hydrochloric acid and bile, are involved in this process. ...
... The system is adapted to break down and absorb food. Physical digestion breaks the food down into smaller pieces and chemical digestion breaks these pieces into smaller molecules. Various enzymes and other substances, such as hydrochloric acid and bile, are involved in this process. ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
... The system is adapted to break down and absorb food. Physical digestion breaks the food down into smaller pieces and chemical digestion breaks these pieces into smaller molecules. Various enzymes and other substances, such as hydrochloric acid and bile, are involved in this process. ...
... The system is adapted to break down and absorb food. Physical digestion breaks the food down into smaller pieces and chemical digestion breaks these pieces into smaller molecules. Various enzymes and other substances, such as hydrochloric acid and bile, are involved in this process. ...
ppt - 3.LF UK 2015
... The figure is found at: http://fig.cox.miami.edu/~cmallery/255/255enz/enzymology.htm (December 2006) ...
... The figure is found at: http://fig.cox.miami.edu/~cmallery/255/255enz/enzymology.htm (December 2006) ...
Outline 19.1 Catalysis by Enzymes
... The enzyme lactate dehydrogenase catalyzes the removal of hydrogen from L-lactate but not from D-lactate. ...
... The enzyme lactate dehydrogenase catalyzes the removal of hydrogen from L-lactate but not from D-lactate. ...
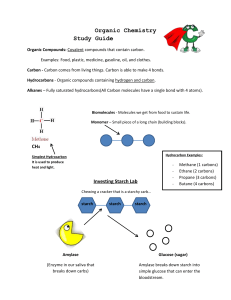
Organic Chemistry Study Guide Organic Compounds: Covalent
... essential for all known forms of life. Nucleic acids, which include DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid), are made from monomers known as nucleotides. ...
... essential for all known forms of life. Nucleic acids, which include DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid), are made from monomers known as nucleotides. ...
Whittier Union High School District
... 20. What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Eukaryotic Cells have a nucleus and many organelles, prokaryotic cells do not. 21. Give an example of a prokaryotic cell: Bacteria 22. Give at least two examples of eukaryotic cells: Plant cells and animal cells 23. What is a virus ...
... 20. What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Eukaryotic Cells have a nucleus and many organelles, prokaryotic cells do not. 21. Give an example of a prokaryotic cell: Bacteria 22. Give at least two examples of eukaryotic cells: Plant cells and animal cells 23. What is a virus ...
Enzymes Problem Set 1 A) What concentration of the substrate
... reaction in which the reaction product, DHAP, is subsequently converted into glycerol 3phosphate by the presence of the enzyme glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, which uses NADH as a co-substrate. Glycerol is added to the assay to prevent glycerol kinase interference. ,-dipyridyl is added to the ...
... reaction in which the reaction product, DHAP, is subsequently converted into glycerol 3phosphate by the presence of the enzyme glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, which uses NADH as a co-substrate. Glycerol is added to the assay to prevent glycerol kinase interference. ,-dipyridyl is added to the ...
G5. Strategies for Stabilization of Enzymes in Organic
... important biocatalysts are hydrolases, particularly lipases, since they are able to convert wide variety of substances. They have many favourable properties; stability at extreme temperatures, high chemo-, regio-, and enantioselectivity, and no need for cofactors. Biocatalysts as such have evolved t ...
... important biocatalysts are hydrolases, particularly lipases, since they are able to convert wide variety of substances. They have many favourable properties; stability at extreme temperatures, high chemo-, regio-, and enantioselectivity, and no need for cofactors. Biocatalysts as such have evolved t ...
Enzymes
... The reaction catalyzed by lysozyme is the hydrolysis of the glycosidic bond of the (NAM-NAG)n heteropolymer that is the backbone of the bacterial cell wall. The enzyme is specific for NAMNAG glycosidic bonds (β-1,4 conformation). ...
... The reaction catalyzed by lysozyme is the hydrolysis of the glycosidic bond of the (NAM-NAG)n heteropolymer that is the backbone of the bacterial cell wall. The enzyme is specific for NAMNAG glycosidic bonds (β-1,4 conformation). ...
Enzyme Complete ppt
... Factors affecting enzyme function • pH • changes in pH • adds or remove H+ • disrupts bonds, disrupts 3D shape • disrupts attractions between charged amino acids • affect 2° & 3° structure • denatures protein ...
... Factors affecting enzyme function • pH • changes in pH • adds or remove H+ • disrupts bonds, disrupts 3D shape • disrupts attractions between charged amino acids • affect 2° & 3° structure • denatures protein ...
SBI3C – Unit 1 Test
... 9. How many amino acids are there? 10. What is the difference between essential and non-essential amino acids? 11. Humans make 12 amino acids. The other 8 amino acids… how do we obtain them? Enzymes (Definition: They are biological molecules that speed up chemical reactions without being destroyed i ...
... 9. How many amino acids are there? 10. What is the difference between essential and non-essential amino acids? 11. Humans make 12 amino acids. The other 8 amino acids… how do we obtain them? Enzymes (Definition: They are biological molecules that speed up chemical reactions without being destroyed i ...
Chemical Basis of Life packet #2
... 5. A scientist observes that, when the pH of the environment surrounding an enzyme is changed, the rate the enzyme catalyzes a reaction greatly decreases. Which statement best describes how a change in pH can affect an enzyme? A. A pH change can cause the enzyme to change its shape. B. A pH change c ...
... 5. A scientist observes that, when the pH of the environment surrounding an enzyme is changed, the rate the enzyme catalyzes a reaction greatly decreases. Which statement best describes how a change in pH can affect an enzyme? A. A pH change can cause the enzyme to change its shape. B. A pH change c ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.