Restriction Enzymes
... unaffected when exposed to phages • Luria hypothesized that these bacteria had some type of primitive immune system that restricted phage growth • Luria’s hypothesis was later confirmed by several teams of researchers when they discovered restriction enzymes which cut up phage DNA when it is injecte ...
... unaffected when exposed to phages • Luria hypothesized that these bacteria had some type of primitive immune system that restricted phage growth • Luria’s hypothesis was later confirmed by several teams of researchers when they discovered restriction enzymes which cut up phage DNA when it is injecte ...
Zhan-3-Enzyme
... are competitive (which increases the apparent Km) and noncompetitive (which decreases the Vmax). In contrast, the multi-subunit allosteric enzymes frequently show a sigmoidal curve similar in shape to the oxygen dissociation curve of hemoglobin. They are frequently found catalyzing the committed (ra ...
... are competitive (which increases the apparent Km) and noncompetitive (which decreases the Vmax). In contrast, the multi-subunit allosteric enzymes frequently show a sigmoidal curve similar in shape to the oxygen dissociation curve of hemoglobin. They are frequently found catalyzing the committed (ra ...
enzymes - Yengage
... Catalytic sites of enzymes contain sites for binding cofactors or coenzymes exists d/t tertiary structure of protein loss of native enzyme structure derangement of active site loss of function ...
... Catalytic sites of enzymes contain sites for binding cofactors or coenzymes exists d/t tertiary structure of protein loss of native enzyme structure derangement of active site loss of function ...
Ch1_2
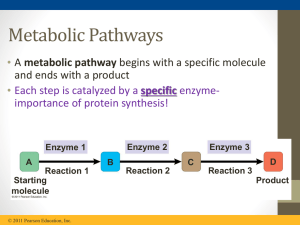
... Introduction • A B C D E F Products • Whenever the overall chemical process of a metabolic pathway has to be reversed, the reverse pathway is not exactly the same as the forward pathway-some of the reactions are different in the two directions. ...
... Introduction • A B C D E F Products • Whenever the overall chemical process of a metabolic pathway has to be reversed, the reverse pathway is not exactly the same as the forward pathway-some of the reactions are different in the two directions. ...
Molecules and Enzymes - Northeast High School
... Use the letters to indentify the organic molecule the statement is referencing. Some statements may be associated with more than one molecule. C- carbohydrate; L – lipids; P – proteins; N – nucleic acids 1. _________ building block is amino acids 2. _________ main source of energy for cells 3. _____ ...
... Use the letters to indentify the organic molecule the statement is referencing. Some statements may be associated with more than one molecule. C- carbohydrate; L – lipids; P – proteins; N – nucleic acids 1. _________ building block is amino acids 2. _________ main source of energy for cells 3. _____ ...
Chapter 1 Review Understanding Concepts
... Amylose and amylopectin are similar in that they are polymers of α-glucose and contain α 1–4 glycosidic linkages; however, amylopectin also contains α 1–6 glycosidic linkages. α-glucose has a hydroxyl group at carbon-1 that is below the plane of the ring, while β-glucose has a hydroxyl group at carb ...
... Amylose and amylopectin are similar in that they are polymers of α-glucose and contain α 1–4 glycosidic linkages; however, amylopectin also contains α 1–6 glycosidic linkages. α-glucose has a hydroxyl group at carbon-1 that is below the plane of the ring, while β-glucose has a hydroxyl group at carb ...
Document
... • Enzymes act by providing an alternate, easier pathway for a reaction. • Same reactants, products and equilibrium. • Increase reaction rates by having a lower activation energy barrier. Some enzymes require an additional component to function properly - cofactor. This can be an organic or organomet ...
... • Enzymes act by providing an alternate, easier pathway for a reaction. • Same reactants, products and equilibrium. • Increase reaction rates by having a lower activation energy barrier. Some enzymes require an additional component to function properly - cofactor. This can be an organic or organomet ...
499 Med Chem Chap 3 problems
... 07) Which of the following descriptions best describes a coenzyme? a. A non-protein substance that is required by an enzyme if it is to catalyse a reaction. b. A non-protein organic molecule that is required by some enzymes in order to catalyse a reaction on a substrate. c. A non-protein organic mol ...
... 07) Which of the following descriptions best describes a coenzyme? a. A non-protein substance that is required by an enzyme if it is to catalyse a reaction. b. A non-protein organic molecule that is required by some enzymes in order to catalyse a reaction on a substrate. c. A non-protein organic mol ...
Describe how cells are used in the production of
... • (enzymes are) composed of proteins • (enzymes aree) catalysts/speed up reactions/lower activation energy required for a reaction to take place. • (enzymes) can be reused/(enzymes) are unchanged in the reaction • They have an active site • Specific substrate fits into enzyme/enzyme substrate comple ...
... • (enzymes are) composed of proteins • (enzymes aree) catalysts/speed up reactions/lower activation energy required for a reaction to take place. • (enzymes) can be reused/(enzymes) are unchanged in the reaction • They have an active site • Specific substrate fits into enzyme/enzyme substrate comple ...
(a) (b)
... the cycloxygenase-2 (COX-2) enzyme. High substrate concentrations reduce the efficacy of inhibition by these drugs. These drugs are ...
... the cycloxygenase-2 (COX-2) enzyme. High substrate concentrations reduce the efficacy of inhibition by these drugs. These drugs are ...
Insulin is a relatively small protein that in its final form consists of two
... 1. Insulin is a relatively small protein that in its final form consists of two polypeptide chains. The smaller of these two polypeptides consists of 21 amino acids and the larger consists of 30 amino acids. This is how insulin forms: In the beta cells within islets of Langerhans of the pancreas, in ...
... 1. Insulin is a relatively small protein that in its final form consists of two polypeptide chains. The smaller of these two polypeptides consists of 21 amino acids and the larger consists of 30 amino acids. This is how insulin forms: In the beta cells within islets of Langerhans of the pancreas, in ...
Translation Series No. 568
... shows a remarkably high heat-lability (PARTMANN ). Experiments for applying a heat-denaturation to the purification of cathepsin from cod musculature were unsuccessful, (SIEBERT and v. MALORTIE 2 ). Codfish, "Gadus callarias ...
... shows a remarkably high heat-lability (PARTMANN ). Experiments for applying a heat-denaturation to the purification of cathepsin from cod musculature were unsuccessful, (SIEBERT and v. MALORTIE 2 ). Codfish, "Gadus callarias ...
Chapter 6 Energy Flow in the life of a Cell
... catalyze (speed up) chemical reactions in cells Catalysts speed up the rate of a chemical reaction without themselves being used up Catalysts speed up spontaneous reactions by reducing activation energy ...
... catalyze (speed up) chemical reactions in cells Catalysts speed up the rate of a chemical reaction without themselves being used up Catalysts speed up spontaneous reactions by reducing activation energy ...
2-7 Active-Site Geometry
... molecule may rearrange during the reaction), then in a simple reaction in which two molecules combine, both of them must collide reactive side-to-reactive side. Any other orientation and the collision will be non-productive. Thus, if both molecules first bind to an enzyme active site, and do so in s ...
... molecule may rearrange during the reaction), then in a simple reaction in which two molecules combine, both of them must collide reactive side-to-reactive side. Any other orientation and the collision will be non-productive. Thus, if both molecules first bind to an enzyme active site, and do so in s ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 06. Native gel is used to isolate enzymes. 07. Starch is a homopoloysaccharide. 08. The dipeptide contains one peptide bond. 09. Saturated fatty acids contain double bond. 10. IUB refers to International Union of Biochemistry. III. Complete the following ...
... 06. Native gel is used to isolate enzymes. 07. Starch is a homopoloysaccharide. 08. The dipeptide contains one peptide bond. 09. Saturated fatty acids contain double bond. 10. IUB refers to International Union of Biochemistry. III. Complete the following ...
Document
... oxygen) • Anabolic pathways consume energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones (synthesis of protein from amino acids) ...
... oxygen) • Anabolic pathways consume energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones (synthesis of protein from amino acids) ...
Overview of Metaboli.. - Frozen Crocus Productions
... ETC: electrons from TCA cycle & glycolysis are “joined” to oxygen to make water & the production of ATP Pentose Phosphate Pathway: production of ribose and NADPH for nucleotide and other synthesis processes ...
... ETC: electrons from TCA cycle & glycolysis are “joined” to oxygen to make water & the production of ATP Pentose Phosphate Pathway: production of ribose and NADPH for nucleotide and other synthesis processes ...
2008 CELL BIOLOGY – TRAINING HANDOUT
... Surface of Cell: Cell Wall – commonly found in plants cells – protection & support Plasma Membrane – control of substances coming in and out Cilia - sweep materials across the cell surface Flagellum - enables a cell to propel and move in different directions Cytoplasm – between plasma membra ...
... Surface of Cell: Cell Wall – commonly found in plants cells – protection & support Plasma Membrane – control of substances coming in and out Cilia - sweep materials across the cell surface Flagellum - enables a cell to propel and move in different directions Cytoplasm – between plasma membra ...
Biology Study Guide for Section (Macromolecules) Test
... Monosaccharide- A simple sugar like glucose. Carbohydrate- A type of macromolecule that is produced by plants during photosynthesis. Glycogen- Animal cells store excess sugar as molecules of this. Polysaccharide- Monosaccharides may bond together to form these molecules. Energy-The main function of ...
... Monosaccharide- A simple sugar like glucose. Carbohydrate- A type of macromolecule that is produced by plants during photosynthesis. Glycogen- Animal cells store excess sugar as molecules of this. Polysaccharide- Monosaccharides may bond together to form these molecules. Energy-The main function of ...
BIOLOGY 311C - Brand Spring 2007 NAME (printed very legibly
... d. quaternary structure. 4. The binding domain for a regulatory molecule of a regulatory enzyme is called a(an): a. allosteric site. b. active site. c. signal receptor. d. membrane receptor. 5. The half-reaction shown at right can be described as a(n): a. oxidation. b. reduction. c. de-protonation. ...
... d. quaternary structure. 4. The binding domain for a regulatory molecule of a regulatory enzyme is called a(an): a. allosteric site. b. active site. c. signal receptor. d. membrane receptor. 5. The half-reaction shown at right can be described as a(n): a. oxidation. b. reduction. c. de-protonation. ...
Biology: Exploring Life Resource Pro
... Concept 5.4 Proteins perform most functions in cells. (pp. 100–102) A protein is a polymer made from a set of 20 kinds of monomers called amino acids. An amino acid has a central carbon atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a side group. The side group is different fo ...
... Concept 5.4 Proteins perform most functions in cells. (pp. 100–102) A protein is a polymer made from a set of 20 kinds of monomers called amino acids. An amino acid has a central carbon atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a side group. The side group is different fo ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.