Unit 2 Study Guide: Carbon Compounds
... 3. I can use the periodic table to determine and depict atomic structure of various elements (including valence electrons)…use N, O, S, P, K, and Ca as examples to demonstrate your understanding! ...
... 3. I can use the periodic table to determine and depict atomic structure of various elements (including valence electrons)…use N, O, S, P, K, and Ca as examples to demonstrate your understanding! ...
Assessment Statement
... IB says: Originally, it was assumed that one gene would invariably code for one polypeptide, but many exceptions have been discovered. ...
... IB says: Originally, it was assumed that one gene would invariably code for one polypeptide, but many exceptions have been discovered. ...
1 - contentextra
... © Pearson Education Ltd 2011. For more information about the Pearson Baccalaureate series please visit www.pearsonbacc.com ...
... © Pearson Education Ltd 2011. For more information about the Pearson Baccalaureate series please visit www.pearsonbacc.com ...
1) From
... Km and Vmax • The activity of enzymes can be discussed in terms of their Km, a measure of the affinity of the enzyme for its substrate, and the Vmax, which is the maximal velocity of the enzymatic reaction. • Km has two meanings: 1) the concentration of substrate at which 1/2 the active sites on an ...
... Km and Vmax • The activity of enzymes can be discussed in terms of their Km, a measure of the affinity of the enzyme for its substrate, and the Vmax, which is the maximal velocity of the enzymatic reaction. • Km has two meanings: 1) the concentration of substrate at which 1/2 the active sites on an ...
Enzymes - Best Friends of Flours The Miller`s Little Helpers
... in the production of pan (toast) bread, where a soft dough that precisely fills the tin is required. Proteases are also very useful in the production of cracker, biscuit or wafer flours where elasticity of the gluten is not desirable. Enzymes for biscuits, crackers and wafers Whereas a high protein ...
... in the production of pan (toast) bread, where a soft dough that precisely fills the tin is required. Proteases are also very useful in the production of cracker, biscuit or wafer flours where elasticity of the gluten is not desirable. Enzymes for biscuits, crackers and wafers Whereas a high protein ...
Unit 3 Biochemistry Chp 2 The Chemistry of Life Notes
... Electrons are grouped into different levels (energy shells). The levels closest to the nucleus have less energy than the levels farther from the nucleus. Each level can hold a limited number of electrons. The outer electron levels of H and He can hold up to two electrons. All other atoms have outer ...
... Electrons are grouped into different levels (energy shells). The levels closest to the nucleus have less energy than the levels farther from the nucleus. Each level can hold a limited number of electrons. The outer electron levels of H and He can hold up to two electrons. All other atoms have outer ...
chemistryandmacromolecules3
... fatty acids and glycerol backbones. • Contain hydrocarbons (composed of C and H atoms); they are insoluble in water because of many nonpolar covalent bonds. • When close together, weak but additive van der Waals interactions hold them together. Store energy in C—C and C—H bonds • Play structural rol ...
... fatty acids and glycerol backbones. • Contain hydrocarbons (composed of C and H atoms); they are insoluble in water because of many nonpolar covalent bonds. • When close together, weak but additive van der Waals interactions hold them together. Store energy in C—C and C—H bonds • Play structural rol ...
Биологическая химия
... of certain enzymes, called proteinases (proteases, peptidases). This yields a mixture of peptides and amino acids. • Study of the products of partial and complete hydrolysis of peptides and proteins play is important for the understanding of their structure. ...
... of certain enzymes, called proteinases (proteases, peptidases). This yields a mixture of peptides and amino acids. • Study of the products of partial and complete hydrolysis of peptides and proteins play is important for the understanding of their structure. ...
Active Learning Exercise 3
... c.) Explain why the rate of the enzymecatalyzed reaction decreases at temperatures above the optimum temperature. Explain in terms of the role of the tertiary structure in enzyme function, the relevant bonds within the tertiary structure that are affected, E-S complex formation, Ea lowering, etc. ...
... c.) Explain why the rate of the enzymecatalyzed reaction decreases at temperatures above the optimum temperature. Explain in terms of the role of the tertiary structure in enzyme function, the relevant bonds within the tertiary structure that are affected, E-S complex formation, Ea lowering, etc. ...
SOME Important Points About Cellular Energetics by Dr. Ty C.M.
... The citric acid cycle receives acetyl (a two-‐carbon compound) and combines it with oxaloacetate (a four-‐carbon compound) to produce citrate (a six-‐ carbon compound). This six carbon compound is then broken ...
... The citric acid cycle receives acetyl (a two-‐carbon compound) and combines it with oxaloacetate (a four-‐carbon compound) to produce citrate (a six-‐ carbon compound). This six carbon compound is then broken ...
travel cards B4
... an enzyme called salivary amylase. The enzyme breaks down starch into glucose, and is present in saliva in the human mouth. Alex eats chicken and chips for her lunch. She wonders which parts of her lunch will start to be digested by salivary amylase in her mouth. She knows that chicken meat is made ...
... an enzyme called salivary amylase. The enzyme breaks down starch into glucose, and is present in saliva in the human mouth. Alex eats chicken and chips for her lunch. She wonders which parts of her lunch will start to be digested by salivary amylase in her mouth. She knows that chicken meat is made ...
Genes and Enzymes in Man
... It is now generally believed that genes exert their effects by enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, and this, of course, is only 1 directing the synthesis of enzymes and other proteins. There example out of many. A few cases are also known where a are, of course, a very large number of different enzyme ...
... It is now generally believed that genes exert their effects by enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, and this, of course, is only 1 directing the synthesis of enzymes and other proteins. There example out of many. A few cases are also known where a are, of course, a very large number of different enzyme ...
03 - summer worksheet
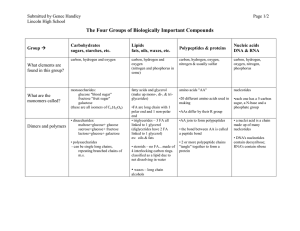
... compounds suggested in the “types” column (choose from car4bohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids). ...
... compounds suggested in the “types” column (choose from car4bohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids). ...
gil, virginia
... One strand of Dna can serve as a template for the formation of the other. Themes: I. The continuity of life is based on heritable information obtained through DNA. DNA’s complex double helix structure allows it to carry vital information of all living things. II. Cells are the basic unit of structur ...
... One strand of Dna can serve as a template for the formation of the other. Themes: I. The continuity of life is based on heritable information obtained through DNA. DNA’s complex double helix structure allows it to carry vital information of all living things. II. Cells are the basic unit of structur ...
Modern Biotechnology. Connecting Innovations in Microbiology and Biochemistry to Engineering Fundamentals
... A unique resource for the next generation of biotech innovators Enabling everything from the deciphering of the human genome to environmentally friendly biofuels to lifesaving new pharmaceuticals, biotechnology has blossomed as an area of discovery and opportunity. Modern Biotechnology provides a mu ...
... A unique resource for the next generation of biotech innovators Enabling everything from the deciphering of the human genome to environmentally friendly biofuels to lifesaving new pharmaceuticals, biotechnology has blossomed as an area of discovery and opportunity. Modern Biotechnology provides a mu ...
File
... • Enzymes—proteins that function as biological catalysts – Permit reactions to occur rapidly at normal body temperature ...
... • Enzymes—proteins that function as biological catalysts – Permit reactions to occur rapidly at normal body temperature ...
A) chemical bonds between carbon atoms are formed during
... 24. Which statement explains the importance of maintaining a constant internal environment to ensure proper enzyme functioning? A) Changes in pH and temperature will cause the enzyme reaction rate to be too fast. B) Temperature and pH determine amino acid sequences in enzymes. C) Changes in pH will ...
... 24. Which statement explains the importance of maintaining a constant internal environment to ensure proper enzyme functioning? A) Changes in pH and temperature will cause the enzyme reaction rate to be too fast. B) Temperature and pH determine amino acid sequences in enzymes. C) Changes in pH will ...
Lecture: Biochemistry
... i. albumin - acid & base buffer in blood d. Hormonal Function i. insulin - regulates blood glucose level ii. growth hormone - regulates human growth e. Neurotransmitter i. enkephalins - regulate pain in spinal cord f. Immunity i. antibodies - attach to foreign molecules ii. complement proteins - enh ...
... i. albumin - acid & base buffer in blood d. Hormonal Function i. insulin - regulates blood glucose level ii. growth hormone - regulates human growth e. Neurotransmitter i. enkephalins - regulate pain in spinal cord f. Immunity i. antibodies - attach to foreign molecules ii. complement proteins - enh ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.