rational drug design
... Cone shells produce many toxins. The drug Professor Livett’s team are interested in is an alphaconotoxin. Some alpha conotoxins kill and some don’t. It is important to test the drugs stringently prior to starting clinical trials. Killer conotoxins: We now know that the killer drugs have a loop of ...
... Cone shells produce many toxins. The drug Professor Livett’s team are interested in is an alphaconotoxin. Some alpha conotoxins kill and some don’t. It is important to test the drugs stringently prior to starting clinical trials. Killer conotoxins: We now know that the killer drugs have a loop of ...
Exam 3
... Section 3. Problems. 4 questions 10 points each. 31. (10pts) A molecule of glucose stored in glycogen can be catabolized to two molecules of lactate under anaerobic conditions in muscle. Fill in each box with the name or structure of the intermediates along this pathway. Then indicate every step th ...
... Section 3. Problems. 4 questions 10 points each. 31. (10pts) A molecule of glucose stored in glycogen can be catabolized to two molecules of lactate under anaerobic conditions in muscle. Fill in each box with the name or structure of the intermediates along this pathway. Then indicate every step th ...
9) Several oxygen saturation curves are shown in the figure below
... Which of the following vitamin coenzymes is most likely to participate in this reaction? A) thiamine pyrophosphate B) coenzyme A C) tetrahydrofolate D) cobalamin E) biotin 29) You are seeing a 65 year old woman who recently had gastric bypass surgery and who has developed symptoms of fatigue and wea ...
... Which of the following vitamin coenzymes is most likely to participate in this reaction? A) thiamine pyrophosphate B) coenzyme A C) tetrahydrofolate D) cobalamin E) biotin 29) You are seeing a 65 year old woman who recently had gastric bypass surgery and who has developed symptoms of fatigue and wea ...
Lecture 1 - Doolittle Lab
... UUX, UXU or XUU, it was thought, X being one of the other three bases (A, G or T). ...
... UUX, UXU or XUU, it was thought, X being one of the other three bases (A, G or T). ...
CHANNELING OF SUBSTRATES AND INTERMEDIATES IN
... phosphate synthetase, glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase, and asparagine synthetase have revealed the relative locations of multiple active sites within these proteins. In all of these polyfunctional enzymes, a product formed from the catalytic reaction at one active site is a su ...
... phosphate synthetase, glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase, and asparagine synthetase have revealed the relative locations of multiple active sites within these proteins. In all of these polyfunctional enzymes, a product formed from the catalytic reaction at one active site is a su ...
Amino acid sequence alignment of a `small` citrate synthase from
... Although the existence of two CS genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is well documented [3], evidence has now been provided suggesting the presence of two CS genes in Escherichia coli [4] and Bacillus subtilis [S], organisms considered for many years to contain a single molecular form of CS. There is ...
... Although the existence of two CS genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is well documented [3], evidence has now been provided suggesting the presence of two CS genes in Escherichia coli [4] and Bacillus subtilis [S], organisms considered for many years to contain a single molecular form of CS. There is ...
IMD and NBS 170314
... • T.bilirubin generally <200 umol/L (unless preterm) • Conj. generally <20 umol/L • Levels peak around 3-4 days and return to normal by day 7-10 ...
... • T.bilirubin generally <200 umol/L (unless preterm) • Conj. generally <20 umol/L • Levels peak around 3-4 days and return to normal by day 7-10 ...
Respiration - Orange Coast College
... • You are free to use, modify, and distribute these slides according to the terms of the Creative Commons license (e.g., you must attribute the slides, no commercial uses are allowed, and future distributions must be licensed under a similar license). • Attribution should be given to Marc C. Perkins ...
... • You are free to use, modify, and distribute these slides according to the terms of the Creative Commons license (e.g., you must attribute the slides, no commercial uses are allowed, and future distributions must be licensed under a similar license). • Attribution should be given to Marc C. Perkins ...
Word doc
... because of the indicators we have already discussed. Differential media contain a substrate that can be used by an organism only if it produces the enzymes required to catalyze that particular biochemical reaction. Sometimes the indicator is already present in the medium, sometimes the indicator may ...
... because of the indicators we have already discussed. Differential media contain a substrate that can be used by an organism only if it produces the enzymes required to catalyze that particular biochemical reaction. Sometimes the indicator is already present in the medium, sometimes the indicator may ...
WYSE – “Academic Challenge” - Worldwide Youth in Science and
... Which of the following functional groups is in every amino acid? ...
... Which of the following functional groups is in every amino acid? ...
Circadian Rhythm of Intestinal SucraseActivity in Rats
... equivalence point was reached, (0.15 U), at which time sucrase activity in the supernate increased secondary to antigen excess. The equivalence points were the same in both groups of animals, indicating that enzyme activity per unit of immunologically identified protein was not significantly differe ...
... equivalence point was reached, (0.15 U), at which time sucrase activity in the supernate increased secondary to antigen excess. The equivalence points were the same in both groups of animals, indicating that enzyme activity per unit of immunologically identified protein was not significantly differe ...
Preferentially biotinylate N-terminal α
... groups (-NH2), which exist in the side chain of lysine residues and at the N-terminus of each polypeptide. With large proteins, labeling of several lysine residues and the N-terminus does not usually harm protein function or binding properties. With short peptides, however, the random biotinylation ...
... groups (-NH2), which exist in the side chain of lysine residues and at the N-terminus of each polypeptide. With large proteins, labeling of several lysine residues and the N-terminus does not usually harm protein function or binding properties. With short peptides, however, the random biotinylation ...
Manipulating and Analyzing DNA
... DNA and gel electrophoresis. You will use two different websites to understand both topics. By the end of today you should be able answer the flooring questions: What are restriction enzymes? How and why are they used in biotechnology? How do restriction enzymes play a role in recombinant DNA? How d ...
... DNA and gel electrophoresis. You will use two different websites to understand both topics. By the end of today you should be able answer the flooring questions: What are restriction enzymes? How and why are they used in biotechnology? How do restriction enzymes play a role in recombinant DNA? How d ...
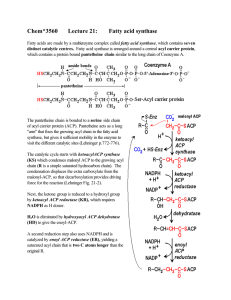
Chem*3560 Lecture 21: Fatty acid synthase
... acetyl-CoA + 7 malonyl-CoA + 14 NADPH → palmitate + 7 CO2 + 8 HSCoA + 14 NADP+ + 14 H+ + 6 H2 O Overall cost of synthesis in bacteria includes 7 ATP as the energy cost of making 7 malonyl-CoA: acetyl CoA carboxylase 7 acetyl-CoA + 7 ATP + 7 CO2 + 7 H2 O → 7 malonyl-CoA + 7 H+ + 7 ADP + 7 Pi Overall ...
... acetyl-CoA + 7 malonyl-CoA + 14 NADPH → palmitate + 7 CO2 + 8 HSCoA + 14 NADP+ + 14 H+ + 6 H2 O Overall cost of synthesis in bacteria includes 7 ATP as the energy cost of making 7 malonyl-CoA: acetyl CoA carboxylase 7 acetyl-CoA + 7 ATP + 7 CO2 + 7 H2 O → 7 malonyl-CoA + 7 H+ + 7 ADP + 7 Pi Overall ...
Ch.24Pt.7_000
... Bilirubin transported to liver. Becomes more water soluble with attachment of glucoronide sugars to propionate side chains. (Glucose + COO- group attached to 6th C) ...
... Bilirubin transported to liver. Becomes more water soluble with attachment of glucoronide sugars to propionate side chains. (Glucose + COO- group attached to 6th C) ...
biology i standard assessment a
... 1. Where in the cell does transcription take place? Why does it occur here? 2. Translation allows for amino acids to be bonded together. What type of molecule is formed when this occurs? Where does this occur? 3. An enzyme represents a molecule that is formed by translation. Describe 3 characteristi ...
... 1. Where in the cell does transcription take place? Why does it occur here? 2. Translation allows for amino acids to be bonded together. What type of molecule is formed when this occurs? Where does this occur? 3. An enzyme represents a molecule that is formed by translation. Describe 3 characteristi ...
biochemistry of fish - Central Institute of Fisheries Technology
... feed industry is complicated by variable availability of raw material and expensive production process because of the comparatively low enzyme concentration. In future, some of these enzymes may be produced more profitably by recombinant DNA or gene technology. Another approach to enzyme engineering ...
... feed industry is complicated by variable availability of raw material and expensive production process because of the comparatively low enzyme concentration. In future, some of these enzymes may be produced more profitably by recombinant DNA or gene technology. Another approach to enzyme engineering ...
document
... – Ranges in color from brown to bright red – White poultry meat has low myoglobin – Dark meat has high myoglobin content – Veal and pork have less myoglobin than beef Myoglobin and hemoglobin without iron are colorless Myoglobin and hemoglobin with iron are pink to red Cooking meat dissociates heme ...
... – Ranges in color from brown to bright red – White poultry meat has low myoglobin – Dark meat has high myoglobin content – Veal and pork have less myoglobin than beef Myoglobin and hemoglobin without iron are colorless Myoglobin and hemoglobin with iron are pink to red Cooking meat dissociates heme ...
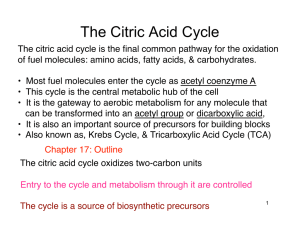
The Citric Acid Cycle
... The Citric Acid Cycle The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules: amino acids, fatty acids, & carbohydrates. • Most fuel molecules enter the cycle as acetyl coenzyme A • This cycle is the central metabolic hub of the cell • It is the gateway to aerobic ...
... The Citric Acid Cycle The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules: amino acids, fatty acids, & carbohydrates. • Most fuel molecules enter the cycle as acetyl coenzyme A • This cycle is the central metabolic hub of the cell • It is the gateway to aerobic ...
Cell Respiration State that oxidation involves the loss of electrons
... In the Krebs cycle and glycolysis, pairs of hydrogen atoms are removed from the respiratory substrates. Oxidised NAD is converted into reduced NAD, except in the Krebs cycle, where FAD is reduced instead. Hydrogen atoms or their electrons are transported along a series of carriers in the final stage ...
... In the Krebs cycle and glycolysis, pairs of hydrogen atoms are removed from the respiratory substrates. Oxidised NAD is converted into reduced NAD, except in the Krebs cycle, where FAD is reduced instead. Hydrogen atoms or their electrons are transported along a series of carriers in the final stage ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.