DNA Technology – Mapping a plasmid A first step in working with
... A first step in working with DNA is mapping the DNA molecule. One way to do this is to use restriction enzymes (restriction endonucleases) that are naturally found in bacteria to cut the DNA molecule into fragments, and then perform a gel electrophoresis on the treated DNA. The fragments of DNA can ...
... A first step in working with DNA is mapping the DNA molecule. One way to do this is to use restriction enzymes (restriction endonucleases) that are naturally found in bacteria to cut the DNA molecule into fragments, and then perform a gel electrophoresis on the treated DNA. The fragments of DNA can ...
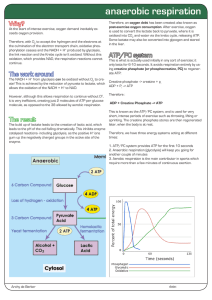
anaerobic respiration
... The NADH + H+ from glycolysis can be oxidized without O2 to create! This is achieved by the reduction of pyruvate to lactate, which allows the oxidation of the NADH + H+ to NAD. However, although this allows respiration to continue without O2, it is very inefficient, creating just 2 molecules of ATP ...
... The NADH + H+ from glycolysis can be oxidized without O2 to create! This is achieved by the reduction of pyruvate to lactate, which allows the oxidation of the NADH + H+ to NAD. However, although this allows respiration to continue without O2, it is very inefficient, creating just 2 molecules of ATP ...
EXAM OF SCIENTIFIC CULTURE CHEMISTRY PROBLEM 1
... 3.1.2 This step can be decomposed into three reactions: (a) enolisation of acetylS-CoA, (b) condensation of the formed enol onto oxaloacetate and (c) hydrolysis of the thioester function. Propose a mechanism for each reaction under acidic catalysis conditions. Actually, an X-ray diffraction study of ...
... 3.1.2 This step can be decomposed into three reactions: (a) enolisation of acetylS-CoA, (b) condensation of the formed enol onto oxaloacetate and (c) hydrolysis of the thioester function. Propose a mechanism for each reaction under acidic catalysis conditions. Actually, an X-ray diffraction study of ...
Slide 1
... Urine in an infant's diaper may darken and can turn almost black after several hours. However, many persons with this condition may not know they have it until midadulthood (around age 40), when joint and other problems occur. Other symptoms: Arthritis that worsens over time, Darkening of ear, Dar ...
... Urine in an infant's diaper may darken and can turn almost black after several hours. However, many persons with this condition may not know they have it until midadulthood (around age 40), when joint and other problems occur. Other symptoms: Arthritis that worsens over time, Darkening of ear, Dar ...
Glycolysis is the major oxidative pathway for glucose
... phosphoglycerate kinase. There is formation of 1 ATP molecule. This is a substrate-level phosphorylation. Because 2 molecules of 1,3-BPG are formed from each glucose molecule, there is formation of 2 ATP molecule in this step. 8. Shift of P group from carbon 3 to carbon 2 by phosphoglycerate ...
... phosphoglycerate kinase. There is formation of 1 ATP molecule. This is a substrate-level phosphorylation. Because 2 molecules of 1,3-BPG are formed from each glucose molecule, there is formation of 2 ATP molecule in this step. 8. Shift of P group from carbon 3 to carbon 2 by phosphoglycerate ...
The Citric Acid Cycle
... • Sensory nerve cells pass the perception of a threat, or stress, from the environment to the hypothalamus in the brain, where neurosecretory cells transmit a signal to the pituitary gland inciting cells there to release a chemical messenger ACTH into the bloodstream. • Simultaneously, the hypothala ...
... • Sensory nerve cells pass the perception of a threat, or stress, from the environment to the hypothalamus in the brain, where neurosecretory cells transmit a signal to the pituitary gland inciting cells there to release a chemical messenger ACTH into the bloodstream. • Simultaneously, the hypothala ...
Carbohydrates
... • Isomers are molecules that have the same formula, but a different physical structure. • Glucose (C6H12O6) and galactose (C6H12O6) and fructose (C6H12O6) are examples of isomers. ...
... • Isomers are molecules that have the same formula, but a different physical structure. • Glucose (C6H12O6) and galactose (C6H12O6) and fructose (C6H12O6) are examples of isomers. ...
Krebs cycle
... Very similar to PDC but has no intrinsic protein kinases & phosphatases. Otherwise has ~ the same regulation ...
... Very similar to PDC but has no intrinsic protein kinases & phosphatases. Otherwise has ~ the same regulation ...
Chapter summaries
... 10. Analysis yields several important parameters; Vmax the maximal velocity that occurs when all of the enzyme is found as ES complex, Km the substrate concentration at which the reaction velocity is half maximal and kcat/Km a second order rate constant that represents the catalytic efficiency of en ...
... 10. Analysis yields several important parameters; Vmax the maximal velocity that occurs when all of the enzyme is found as ES complex, Km the substrate concentration at which the reaction velocity is half maximal and kcat/Km a second order rate constant that represents the catalytic efficiency of en ...
Metabolism Review - Brookings School District
... attaches so that it binds more snugly INDUCED FIT is called _____________ Essential knowledge 4.B.1: b. The shape of enzymes, active sites and interaction with specific molecules are essential for basic functioning of the enzyme. Essential knowledge 4.B.1: b 1. For an enzyme-mediated chemical reacti ...
... attaches so that it binds more snugly INDUCED FIT is called _____________ Essential knowledge 4.B.1: b. The shape of enzymes, active sites and interaction with specific molecules are essential for basic functioning of the enzyme. Essential knowledge 4.B.1: b 1. For an enzyme-mediated chemical reacti ...
Cellular Respiration Overview
... down NADH and FADH2 by pumping H+ into the outer compartment of the mitochondria Where: The mitochondria A gradient is created to produce ATP • Electrons continue down the energy gradient ...
... down NADH and FADH2 by pumping H+ into the outer compartment of the mitochondria Where: The mitochondria A gradient is created to produce ATP • Electrons continue down the energy gradient ...
ap® biology 2008 scoring guidelines - AP Central
... AP® BIOLOGY 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 1. The physical structure of a protein often reflects and affects its function. (a) Describe THREE types of chemical bonds/interactions found in proteins. For each type, describe its role in determining protein structure. (6 points; 1 point for bond/int ...
... AP® BIOLOGY 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 1. The physical structure of a protein often reflects and affects its function. (a) Describe THREE types of chemical bonds/interactions found in proteins. For each type, describe its role in determining protein structure. (6 points; 1 point for bond/int ...
Induction of reverse mutations with plate test in T26 and... Table 2.
... 1985, Neurospora Newsl. 32:9-10). The spontaneous reversion rate of inl mutant strain 89601 is 10^-8-10^-9 (N.H. Giles, 1956, Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology XVI:283-313). In this study, we characterized the MIPS activity and antigen content (CRM) of an inl^+ (483-7) strain showi ...
... 1985, Neurospora Newsl. 32:9-10). The spontaneous reversion rate of inl mutant strain 89601 is 10^-8-10^-9 (N.H. Giles, 1956, Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology XVI:283-313). In this study, we characterized the MIPS activity and antigen content (CRM) of an inl^+ (483-7) strain showi ...
Answer Key (up to 3/21)
... b. dNTPs contain a triphosphate, however, the phosphodiester bonds formed in the DNA helix require only one of these phosphates. Therefore, two of the phosphates are cleaved off. Keep in mind that, similar to ATP, these phosphates have repulsion caused by the (-) charges of the phosphates, which are ...
... b. dNTPs contain a triphosphate, however, the phosphodiester bonds formed in the DNA helix require only one of these phosphates. Therefore, two of the phosphates are cleaved off. Keep in mind that, similar to ATP, these phosphates have repulsion caused by the (-) charges of the phosphates, which are ...
Enzymatic properties of the N- and C
... permanent rather than a transient fusion partner, one should remember that many proteins require an intact N-terminus for their biochemical activity (24). Previous studies showed that the first 11 N-terminal amino acids of HK I are very hydrophobic and may influence the kinetic properties of the enz ...
... permanent rather than a transient fusion partner, one should remember that many proteins require an intact N-terminus for their biochemical activity (24). Previous studies showed that the first 11 N-terminal amino acids of HK I are very hydrophobic and may influence the kinetic properties of the enz ...
RFLP Lab Report
... Genetic abnormalities that are associated with diseases such as cystic fibrosis can be identified by using restriction length polymorphisms (RFLP). Restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA and electrophoretic analysis is used to find base pair lengths. Restriction enzymes are endonucleases that are c ...
... Genetic abnormalities that are associated with diseases such as cystic fibrosis can be identified by using restriction length polymorphisms (RFLP). Restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA and electrophoretic analysis is used to find base pair lengths. Restriction enzymes are endonucleases that are c ...
Bacterial digestive enzyme activity in the stomach and hepatopancreas of Meganyctiphanes norvegica (M. Sars, 1857)
... Whitney, 1968; Lewis, 1980; Mayasich & Smucker, 1987), however, has been comparatively overlooked. A particularly high digestive potential is shown by crustaceans, and they can utilise a wide range of organic substrates. The euphausiid Meganyctiphanes norvegica for example is mainly carnivorous, but ...
... Whitney, 1968; Lewis, 1980; Mayasich & Smucker, 1987), however, has been comparatively overlooked. A particularly high digestive potential is shown by crustaceans, and they can utilise a wide range of organic substrates. The euphausiid Meganyctiphanes norvegica for example is mainly carnivorous, but ...
the molecular mechanism of photosynthetic glyceraldehyde
... different isoforms with either A4 or AnBn stochiometry, the latter being more abundant and displaying sophisticated regulatory properties. Photosynthetic GAPDH can use both NADPH and NADH as electron donors, but only the NADPH-dependent activity is regulated. Thirty amino acids at the Cterminus of G ...
... different isoforms with either A4 or AnBn stochiometry, the latter being more abundant and displaying sophisticated regulatory properties. Photosynthetic GAPDH can use both NADPH and NADH as electron donors, but only the NADPH-dependent activity is regulated. Thirty amino acids at the Cterminus of G ...
UDP-sugar pyrophosphorylase controls the activity of proceeding
... The synthesis of plant cell wall polymers requires a number of different nucleotide sugars as building blocks. A complex enzymatic network is providing the different GDP- and UDP-sugars to polymer synthases in the Golgi apparatus.1 Mutants in nucleotide sugar interconverting enzymes from Arabidopsis ...
... The synthesis of plant cell wall polymers requires a number of different nucleotide sugars as building blocks. A complex enzymatic network is providing the different GDP- and UDP-sugars to polymer synthases in the Golgi apparatus.1 Mutants in nucleotide sugar interconverting enzymes from Arabidopsis ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.