Protein Synthesis
... CIS Biology Team The amino acids in the chain are held together by peptide bonds. As such, a chain of amino acids is called a polypeptide chain. This will be further discussed in the amino acid structure ...
... CIS Biology Team The amino acids in the chain are held together by peptide bonds. As such, a chain of amino acids is called a polypeptide chain. This will be further discussed in the amino acid structure ...
mb_ch03
... • Condensation reactions join monomers (small simple molecules) to form polymers. A condensation reaction releases water as a by-product. • In a hydrolysis reaction, water is used to split polymers into monomers. ...
... • Condensation reactions join monomers (small simple molecules) to form polymers. A condensation reaction releases water as a by-product. • In a hydrolysis reaction, water is used to split polymers into monomers. ...
Ch 3 Notes
... • Condensation reactions join monomers (small simple molecules) to form polymers. A condensation reaction releases water as a by-product. • In a hydrolysis reaction, water is used to split polymers into monomers. ...
... • Condensation reactions join monomers (small simple molecules) to form polymers. A condensation reaction releases water as a by-product. • In a hydrolysis reaction, water is used to split polymers into monomers. ...
Autotrophic growth on methanol by bacteria isolated from activated
... utilized by many different microorganisms. The pathway of carbon assimilation from methanol has been studied extensively, particularly with respect to the question whether C rcompounds are assimilated as CO2 or at a more reduced level. Three cyclic mechanisms for the assimilation of Cl-compounds are ...
... utilized by many different microorganisms. The pathway of carbon assimilation from methanol has been studied extensively, particularly with respect to the question whether C rcompounds are assimilated as CO2 or at a more reduced level. Three cyclic mechanisms for the assimilation of Cl-compounds are ...
sg 13
... Describe how bacteria can be induced to produce eukaryotic gene products. List and describe four complementary approaches used to map the human genome. Describe how recombinant DNA technology can have medical applications such as diagnosis of genetic disease, development of gene therapy, vacci ...
... Describe how bacteria can be induced to produce eukaryotic gene products. List and describe four complementary approaches used to map the human genome. Describe how recombinant DNA technology can have medical applications such as diagnosis of genetic disease, development of gene therapy, vacci ...
Evolution of Enzymatic Activity in the Enolase Superfamily
... The OSBS-catalyzed reaction occurs in the biosynthesis of menaquinone, which is required for anaerobic growth by many eubacteria and some archeae (4). As a result, genes encoding OSBSs have been identified in the genomes of more than 70 microorganisms (5). Curiously, the pairwise sequence identities ...
... The OSBS-catalyzed reaction occurs in the biosynthesis of menaquinone, which is required for anaerobic growth by many eubacteria and some archeae (4). As a result, genes encoding OSBSs have been identified in the genomes of more than 70 microorganisms (5). Curiously, the pairwise sequence identities ...
Biology Chp 7 Notes
... 1. Cellular Respiration: complex chemical process in which cells make ATP by breaking down organic compounds. a. cells use the energy from the ATP to do work b. all auto and heterotorphs carry out respiration 2. Overview of Cellular Respiration a. Go over diagram of Respiration/Photosynthesis b. Cel ...
... 1. Cellular Respiration: complex chemical process in which cells make ATP by breaking down organic compounds. a. cells use the energy from the ATP to do work b. all auto and heterotorphs carry out respiration 2. Overview of Cellular Respiration a. Go over diagram of Respiration/Photosynthesis b. Cel ...
Practice Test for BIO 311C
... D) The O2 released during photosynthesis comes from water. E) RuBP is produced during cyclic electron flow in the light reactions of photosynthesis. 76) The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event? A) the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA B) the c ...
... D) The O2 released during photosynthesis comes from water. E) RuBP is produced during cyclic electron flow in the light reactions of photosynthesis. 76) The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event? A) the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA B) the c ...
Chapter 13
... What is the Nu:, electrophile and leaving group for this reaction? (hint: consider phosphoglycerate kinase) ...
... What is the Nu:, electrophile and leaving group for this reaction? (hint: consider phosphoglycerate kinase) ...
A Mechanistic Analysis of Enzymatic Degradation - J
... atom from the substrates. Enzymes that catalyze the conversion of organohalogen compounds to other organohalogen compounds are also known. These are useful in environmental technology to decontaminate ...
... atom from the substrates. Enzymes that catalyze the conversion of organohalogen compounds to other organohalogen compounds are also known. These are useful in environmental technology to decontaminate ...
anmol publications pvt. ltd.
... paper on the synthesis of urea, proving that organic compounds can be created artificially. The dawn of biochemistry may have been the discovery of the first enzyme, diastase (today called amylase), in 1833 by Anselme Payen. Eduard Buchner contributed the first demonstration of a complex biochemical ...
... paper on the synthesis of urea, proving that organic compounds can be created artificially. The dawn of biochemistry may have been the discovery of the first enzyme, diastase (today called amylase), in 1833 by Anselme Payen. Eduard Buchner contributed the first demonstration of a complex biochemical ...
The Chemistry of Life
... Enzyme-Substrate Complex • For chemical reactions to occur, reactants must collide with enough energy so that existing bonds are broken and new bonds will be formed. • If reactants do not have enough energy, they will not be changed after the collision • Enzymes provide a site where reactants can co ...
... Enzyme-Substrate Complex • For chemical reactions to occur, reactants must collide with enough energy so that existing bonds are broken and new bonds will be formed. • If reactants do not have enough energy, they will not be changed after the collision • Enzymes provide a site where reactants can co ...
Energy - Moodle NTOU
... • Some enzymes act as structural components of membranes • In eukaryotic cells, some enzymes reside in specific organelles; for example, enzymes for cellular respiration are located in mitochondria ...
... • Some enzymes act as structural components of membranes • In eukaryotic cells, some enzymes reside in specific organelles; for example, enzymes for cellular respiration are located in mitochondria ...
ADP-ribosyltransferases: plastic tools for inactivating protein and
... bacterial toxins and metabolic regulators. ADPRTs catalyze the transfer of the ADP-ribose moiety from NAD+ onto specific substrates including proteins. ADP-ribosylation usually inactivates the function of the target. ADPRTs have become adapted to function in extra- and intracellular settings. Regula ...
... bacterial toxins and metabolic regulators. ADPRTs catalyze the transfer of the ADP-ribose moiety from NAD+ onto specific substrates including proteins. ADP-ribosylation usually inactivates the function of the target. ADPRTs have become adapted to function in extra- and intracellular settings. Regula ...
Bio 226: Cell and Molecular Biology
... •Insensitive to Cyanide, Azide or CO •Sensitive to SHAM (salicylhydroxamic acid,) •Also found in fungi, trypanosomes & Plasmodium ...
... •Insensitive to Cyanide, Azide or CO •Sensitive to SHAM (salicylhydroxamic acid,) •Also found in fungi, trypanosomes & Plasmodium ...
Exam 2 Key
... 3· (8 pts) The 6 events listed below occur during photosynthesis. List the order of events (#1 first-#6last) ...
... 3· (8 pts) The 6 events listed below occur during photosynthesis. List the order of events (#1 first-#6last) ...
Metabolism Review - Local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... attaches so that it binds more snugly INDUCED FIT is called _____________ Essential knowledge 4.B.1: b. The shape of enzymes, active sites and interaction with specific molecules are essential for basic functioning of the enzyme. Essential knowledge 4.B.1: b 1. For an enzyme-mediated chemical reacti ...
... attaches so that it binds more snugly INDUCED FIT is called _____________ Essential knowledge 4.B.1: b. The shape of enzymes, active sites and interaction with specific molecules are essential for basic functioning of the enzyme. Essential knowledge 4.B.1: b 1. For an enzyme-mediated chemical reacti ...
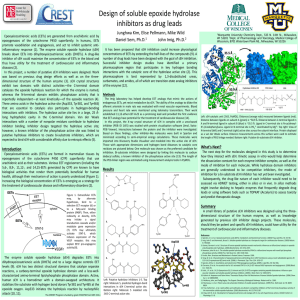
Poster
... diseases (2). In this project, a number of putative sEH inhibitors were designed. Work was based on previous drug design efforts as well as on the threedimensional structure of the human enzyme (3). sEH crystal structures exhibit two domains with distinct activities—the C-terminal domain catalyzes t ...
... diseases (2). In this project, a number of putative sEH inhibitors were designed. Work was based on previous drug design efforts as well as on the threedimensional structure of the human enzyme (3). sEH crystal structures exhibit two domains with distinct activities—the C-terminal domain catalyzes t ...
HiPer®Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) Teaching
... Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) method in molecular biology was evolved for detecting variation at the DNA sequence level of various biological samples. The principle of this method is based upon the comparison of restriction enzyme cleavage profiles following the existence of a poly ...
... Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) method in molecular biology was evolved for detecting variation at the DNA sequence level of various biological samples. The principle of this method is based upon the comparison of restriction enzyme cleavage profiles following the existence of a poly ...
Metabolism Part II: The tricarboxylic acid (TCA), citric acid, or Krebs
... fact a cycle of reactions that was responsible for the aerobic oxidation of fuel molecules. Concern over whether citric acid (or more accurately the citrate ion) was the first product of this cycle led Krebs to propose calling this sequence of enzyme-catalyzed reactions the tricarboxylic acid cycle. ...
... fact a cycle of reactions that was responsible for the aerobic oxidation of fuel molecules. Concern over whether citric acid (or more accurately the citrate ion) was the first product of this cycle led Krebs to propose calling this sequence of enzyme-catalyzed reactions the tricarboxylic acid cycle. ...
Decarboxylation Reactions Major concepts Decarboxylation
... 8. Pyruvate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that converts pyruvate to acetyl CoA through a series of chemical reactions. Although this is a simplified scheme, the pathway generally follows this path: O ...
... 8. Pyruvate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that converts pyruvate to acetyl CoA through a series of chemical reactions. Although this is a simplified scheme, the pathway generally follows this path: O ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.