C12P
... In some of these cases, the chemical part or aspect brings with it a non-chemical one, even though purely mechanical, because this latter aspect either is essential to the operation or treatment or constitutes an important element thereof. It has seemed, in fact, more logical not to dissociate the d ...
... In some of these cases, the chemical part or aspect brings with it a non-chemical one, even though purely mechanical, because this latter aspect either is essential to the operation or treatment or constitutes an important element thereof. It has seemed, in fact, more logical not to dissociate the d ...
PART 2 – CHEMISTRY
... Matter, anything that has mass and occupies space, consists not only of things you can see and touch but also of such things as air, which you cannot see. Matter exists in three phases: solids, liquids, and gases. A solid is matter with a rigid shape and a fixed volume that does not change much with ...
... Matter, anything that has mass and occupies space, consists not only of things you can see and touch but also of such things as air, which you cannot see. Matter exists in three phases: solids, liquids, and gases. A solid is matter with a rigid shape and a fixed volume that does not change much with ...
Chromatography Method Measures Protein
... Chem. 2014, DOI: 10.1021/ac503391c). Researchers could use the approach to rank potential drug candidates by their ability to form stable complexes with a target protein, the method’s developers say. The stability of a protein-small molecule complex is determined by how quickly the two molecules ass ...
... Chem. 2014, DOI: 10.1021/ac503391c). Researchers could use the approach to rank potential drug candidates by their ability to form stable complexes with a target protein, the method’s developers say. The stability of a protein-small molecule complex is determined by how quickly the two molecules ass ...
STUDY GUIDE: GLYCOLYSIS, FERMENTATION AND ANAEROBIC
... chemi - = chemical (chemiosmosis: the production of ATP using the enrgy of hydrogen ion gradients across membranes to phophorylate ADP) glyco - = sweet; - lysis = split (glycolysis: the splitting of glucose into pyruvate) ...
... chemi - = chemical (chemiosmosis: the production of ATP using the enrgy of hydrogen ion gradients across membranes to phophorylate ADP) glyco - = sweet; - lysis = split (glycolysis: the splitting of glucose into pyruvate) ...
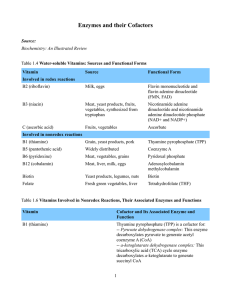
Enzymes and their Cofactors Source: Biochemistry: An Illustrated
... source of methyl groups, which are transferred to various molecules. Methyl-THF is used in the biosynthesis of the purine nucleotides and thymidylate. ...
... source of methyl groups, which are transferred to various molecules. Methyl-THF is used in the biosynthesis of the purine nucleotides and thymidylate. ...
01 Intro Chemistry
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
02Ch02chemistry2005
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
Biology Chp 7 Notes
... 1. Cellular Respiration: complex chemical process in which cells make ATP by breaking down organic compounds. a. cells use the energy from the ATP to do work b. all auto and heterotorphs carry out respiration 2. Overview of Cellular Respiration a. Go over diagram of Respiration/Photosynthesis b. Cel ...
... 1. Cellular Respiration: complex chemical process in which cells make ATP by breaking down organic compounds. a. cells use the energy from the ATP to do work b. all auto and heterotorphs carry out respiration 2. Overview of Cellular Respiration a. Go over diagram of Respiration/Photosynthesis b. Cel ...
The Pharmacology Of Ginexin – F
... 6) Free O2 radicals interact with various amino acids containing unsaturated carbons e.g Tryptophan, histidine ….etc. and those containing S groups e.g Cysteine to result in protein damages (Denaturation). 7) The – . OH Radical but not other radicals interact with Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) at the ...
... 6) Free O2 radicals interact with various amino acids containing unsaturated carbons e.g Tryptophan, histidine ….etc. and those containing S groups e.g Cysteine to result in protein damages (Denaturation). 7) The – . OH Radical but not other radicals interact with Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) at the ...
Document
... to the equation in Scheme (1), and the reaction was practically complete ( 95 per cent yield) in four days. In the winter there action may take as long as two weeks [11] ...
... to the equation in Scheme (1), and the reaction was practically complete ( 95 per cent yield) in four days. In the winter there action may take as long as two weeks [11] ...
Cell Respiration Notes (Honors)
... These new molecules are broken down to form ATP and CO2. One ATP per cycle is produced, two cycles occur per glucose molecule – therefore 2 ATP’s are produced by Krebs Cycle. *Also generates high energy electrons carried by NADH and FADH2. ...
... These new molecules are broken down to form ATP and CO2. One ATP per cycle is produced, two cycles occur per glucose molecule – therefore 2 ATP’s are produced by Krebs Cycle. *Also generates high energy electrons carried by NADH and FADH2. ...
Lesson Objective: Vocabulary: Lesson Question: Focus Question
... b) Glycolysis Glcolysis is a biochemical pathway in which one six-carbon molecule of glucose is oxidized to produce 2 three carbon molecules of pyruvic acid. Series of chemical reactions catalyzed by specific enzymes. All reactions take place in the cytosol and occur in 4 main steps: (1) Step ...
... b) Glycolysis Glcolysis is a biochemical pathway in which one six-carbon molecule of glucose is oxidized to produce 2 three carbon molecules of pyruvic acid. Series of chemical reactions catalyzed by specific enzymes. All reactions take place in the cytosol and occur in 4 main steps: (1) Step ...
Lecture 5 – Chemical Reactions
... Decomposition reactions involve the breakdown of a single reactant to produce two or more products. ...
... Decomposition reactions involve the breakdown of a single reactant to produce two or more products. ...
CHAPTER 2 The Chemistry of Living Things
... involved in generating isoleucine from threonine • Why regulate this? • How could one regulate this, most efficiently? • Also see fig 3.39 e5 ...
... involved in generating isoleucine from threonine • Why regulate this? • How could one regulate this, most efficiently? • Also see fig 3.39 e5 ...
Name - rwebbchem
... with AgNO3, Pb(NO3)2, and BaCl2. Precipitates form in all three cases. Which of the following could be the anion of the unknown salt: Br-, CO32-, or NO3-? ...
... with AgNO3, Pb(NO3)2, and BaCl2. Precipitates form in all three cases. Which of the following could be the anion of the unknown salt: Br-, CO32-, or NO3-? ...
Key concepts of chemistry from high school chemistry
... agree: It’s easy to skip classes since attendance is not required or even recorded in most classes; It’s easy to put off reading the book before or after class because most classes do not have ...
... agree: It’s easy to skip classes since attendance is not required or even recorded in most classes; It’s easy to put off reading the book before or after class because most classes do not have ...
Where It Starts: Photosynthesis
... Enzymes of glycolysis use two ATP to convert one molecule of glucose to two molecules of three-carbon pyruvate Reactions transfer electrons and hydrogen atoms to two NAD+ (reduces to NADH) 4 ATP form by substrate-level phosphorylation ...
... Enzymes of glycolysis use two ATP to convert one molecule of glucose to two molecules of three-carbon pyruvate Reactions transfer electrons and hydrogen atoms to two NAD+ (reduces to NADH) 4 ATP form by substrate-level phosphorylation ...
TOTAL POLYPHENOLIC CONTENT AND FREE RADICAL QUENCHING POTENTIAL OF DIOSCOREA ALATA
... and can be effectively utilized as source of natural antioxidants. DA is an important staple food as well as medicinal plant but its scientific authentication and mechanism of action has not been investigated. Methods: We investigated ethanolic and water extracts of DA for its polyphenolic content a ...
... and can be effectively utilized as source of natural antioxidants. DA is an important staple food as well as medicinal plant but its scientific authentication and mechanism of action has not been investigated. Methods: We investigated ethanolic and water extracts of DA for its polyphenolic content a ...
Chapter 2
... 2. Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form molecules 3. Weak chemical bonds play important roles in the chemistry of life 4. A molecule’s biological function is related to its shape 5. Chemical reactions make and break chemical bonds ...
... 2. Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form molecules 3. Weak chemical bonds play important roles in the chemistry of life 4. A molecule’s biological function is related to its shape 5. Chemical reactions make and break chemical bonds ...
7vitamin-and-minerals
... It is involved in fat and carbohydrate metabolism the body needs it to burn fat It is also a component of various enzymes that are essential for biochemical reactions of the body The body can synthesize biotin from intestinal bacteria if enough is not intaken o There is no need to suppleme ...
... It is involved in fat and carbohydrate metabolism the body needs it to burn fat It is also a component of various enzymes that are essential for biochemical reactions of the body The body can synthesize biotin from intestinal bacteria if enough is not intaken o There is no need to suppleme ...
Energy and Respiration
... 4 carbon compound to make a 6 carbon compound. A series of steps now transfer the 6C (citrate) back to the 4C (oxaloacetate) These steps include more decarboxylation and dehydrogenation ...
... 4 carbon compound to make a 6 carbon compound. A series of steps now transfer the 6C (citrate) back to the 4C (oxaloacetate) These steps include more decarboxylation and dehydrogenation ...
Citric Acid (or Krebs) Cycle - BYU
... In step 11, we learned that as high energy electrons passed down the chain of protein acceptors, energy was used to move H+ ions into the intermembranous space. This generates a proton gradient. This means that there will be a higher concentration of protons in the intermembranous space than there i ...
... In step 11, we learned that as high energy electrons passed down the chain of protein acceptors, energy was used to move H+ ions into the intermembranous space. This generates a proton gradient. This means that there will be a higher concentration of protons in the intermembranous space than there i ...
Electrophilic addition reactions of acids to alkenes double
... those circumstances, water adds, and now we’re on S1 manifold; is this just what we saw before. Or imagine that we had isobutylene, rather than as we had in other syntheses earlier, isobutanol, in the same conditions, protic methanol, so… a little few drops of concentrated acid or a few of gas in m ...
... those circumstances, water adds, and now we’re on S1 manifold; is this just what we saw before. Or imagine that we had isobutylene, rather than as we had in other syntheses earlier, isobutanol, in the same conditions, protic methanol, so… a little few drops of concentrated acid or a few of gas in m ...
Nikolai N. Semenov - Nobel Lecture
... chain reactions with degenerate branching. These reactions are characterized in that their primary product is a molecular intermediate which enters relatively slowly into the reaction leading to the formation of free radicals. The existence of such reactions was proved even in the thirties, when it ...
... chain reactions with degenerate branching. These reactions are characterized in that their primary product is a molecular intermediate which enters relatively slowly into the reaction leading to the formation of free radicals. The existence of such reactions was proved even in the thirties, when it ...
Radical (chemistry)

In chemistry, a radical (more precisely, a free radical) is an atom, molecule, or ion that has unpaired valency electrons.With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make free radicals highly chemically reactive towards other substances, or even towards themselves: their molecules will often spontaneously dimerize or polymerize if they come in contact with each other. Most radicals are reasonably stable only at very low concentrations in inert media or in a vacuum.A notable example of a free radical is the hydroxyl radical (HO•), a molecule that has one unpaired electron on the oxygen atom. Two other examples are triplet oxygen and triplet carbene (:CH2) which have two unpaired electrons. In contrast, the hydroxyl anion (HO−) is not a radical, since the unpaired electron is resolved by the addition of an electron; singlet oxygen and singlet carbene are not radicals as the two electrons are paired.Free radicals may be created in a number of ways, including synthesis with very dilute or rarefied reagents, reactions at very low temperatures, or breakup of larger molecules. The latter can be affected by any process that puts enough energy into the parent molecule, such as ionizing radiation, heat, electrical discharges, electrolysis, and chemical reactions. Indeed, radicals are intermediate stages in many chemical reactions.Free radicals play an important role in combustion, atmospheric chemistry, polymerization, plasma chemistry, biochemistry, and many other chemical processes. In living organisms, the free radicals superoxide and nitric oxide and their reaction products regulate many processes, such as control of vascular tone and thus blood pressure. They also play a key role in the intermediary metabolism of various biological compounds. Such radicals can even be messengers in a process dubbed redox signaling. A radical may be trapped within a solvent cage or be otherwise bound.Until late in the 20th century the word ""radical"" was used in chemistry to indicate any connected group of atoms, such as a methyl group or a carboxyl, whether it was part of a larger molecule or a molecule on its own. The qualifier ""free"" was then needed to specify the unbound case. Following recent nomenclature revisions, a part of a larger molecule is now called a functional group or substituent, and ""radical"" now implies ""free"". However, the old nomenclature may still occur in the literature.