Lab #7 Exoenzymes, Differential and Selective Media
... 25oC, the gelatin will be liquid (remember what happens to Jell-O at room temperature). If you cool the liquefied gelatin, it will resolidify. Gelatin hydrolysis has been correlated with pathogenicity of some microorganisms. It is thought that pathogenic bacteria may break down tissue and spread to ...
... 25oC, the gelatin will be liquid (remember what happens to Jell-O at room temperature). If you cool the liquefied gelatin, it will resolidify. Gelatin hydrolysis has been correlated with pathogenicity of some microorganisms. It is thought that pathogenic bacteria may break down tissue and spread to ...
Physiology PPT - MHC LEVEL 3 PED
... However, oxygen availability only determines the fate of the end product and is not required for the actual process of glycolysis itself. In fact, oxygen availability has been shown to have little to do with which of the two end products, lactate or pyruvate is produced. Hence the terms aerobic mean ...
... However, oxygen availability only determines the fate of the end product and is not required for the actual process of glycolysis itself. In fact, oxygen availability has been shown to have little to do with which of the two end products, lactate or pyruvate is produced. Hence the terms aerobic mean ...
Name - chem.uwec.edu
... 39. How is the structure of cellulose different from that of amylose? b a. Cellulose has α(14) glysidic bond, but amylose has (14) glysidic bond. b. Cellulose has (14) glysidic bond, but amylose has α(14) glysidic bond. c. Cellulose has no branches, but amylose has brances. d. Cellulose has br ...
... 39. How is the structure of cellulose different from that of amylose? b a. Cellulose has α(14) glysidic bond, but amylose has (14) glysidic bond. b. Cellulose has (14) glysidic bond, but amylose has α(14) glysidic bond. c. Cellulose has no branches, but amylose has brances. d. Cellulose has br ...
Zhang Yufeng - USD Biology
... • The energy requirements of the brain are very high • Lipids contain more energy compare to other substrate • Other organs use lipids as fuel • Fatty acid metabolism has a role in neurodevelopment, neurotransmission, and repair processes ...
... • The energy requirements of the brain are very high • Lipids contain more energy compare to other substrate • Other organs use lipids as fuel • Fatty acid metabolism has a role in neurodevelopment, neurotransmission, and repair processes ...
Types of Organic compounds
... reactions to occur • Catalysts speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy needed to get it started • Catalysts orient the colliding particles properly so that they touch at the spots that make the reaction happen • Catalyst molecules are unchanged and can be used repeatedly to spe ...
... reactions to occur • Catalysts speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy needed to get it started • Catalysts orient the colliding particles properly so that they touch at the spots that make the reaction happen • Catalyst molecules are unchanged and can be used repeatedly to spe ...
Encoding Amino Acids • mRNA codes for amino acids
... the amino acids they encode. Suppose we want to know the amino acid coded by the codon ACU. To read the chart, find the first nucleotide (A) in the red cells. Then, match it up with the second nucleotide (C) in the yellow cells. Finally, match those up with the 3rd nucleotide (U) in the green cells. ...
... the amino acids they encode. Suppose we want to know the amino acid coded by the codon ACU. To read the chart, find the first nucleotide (A) in the red cells. Then, match it up with the second nucleotide (C) in the yellow cells. Finally, match those up with the 3rd nucleotide (U) in the green cells. ...
2.2.5-H.2.2.10 Respiration - Intermediate School Biology
... the pyruvate molecule enters the mitochondrion and is broken down to one molecule of carbon dioxide and a two-carbon acetyl group, acetyl Co-enzyme A. ...
... the pyruvate molecule enters the mitochondrion and is broken down to one molecule of carbon dioxide and a two-carbon acetyl group, acetyl Co-enzyme A. ...
Document
... 27. If you measure the abundance of an enzyme (or any other protein) and it increases, that increase is most likely due to: a. decreased transcription. b. increased translation. c. posttranslational modification. d. allosteric regulation. e. two of the above ...
... 27. If you measure the abundance of an enzyme (or any other protein) and it increases, that increase is most likely due to: a. decreased transcription. b. increased translation. c. posttranslational modification. d. allosteric regulation. e. two of the above ...
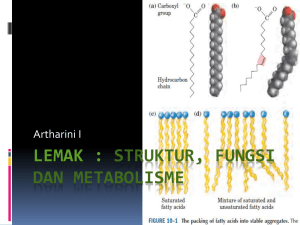
LEMAK : Struktur, Fungsi dan Metabolisme
... Besides the payout of ATP that comes from fatty acid oxidation, another benefit is the generation of H2O that occurs when O2 is reduced by the final reaction in the electron transport system, as well as, the formation of H2O in oxidative phosphorylation. 2 NADH + 2 H+ + O2 --> 2 H2O 2 FADH2 + O2 --> ...
... Besides the payout of ATP that comes from fatty acid oxidation, another benefit is the generation of H2O that occurs when O2 is reduced by the final reaction in the electron transport system, as well as, the formation of H2O in oxidative phosphorylation. 2 NADH + 2 H+ + O2 --> 2 H2O 2 FADH2 + O2 --> ...
27.1 Digestion of Proteins 27.2 Amino Acid Metabolism: An
... – Biologically, it lowers blood pressure, kills invading bacteria, and enhances memory. – Nitric oxide is synthesized from oxygen and the amino acid arginine. – In blood vessels, NO activates reactions in smooth muscle cells that cause dilation and a resulting decrease in blood pressure. © 2013 Pear ...
... – Biologically, it lowers blood pressure, kills invading bacteria, and enhances memory. – Nitric oxide is synthesized from oxygen and the amino acid arginine. – In blood vessels, NO activates reactions in smooth muscle cells that cause dilation and a resulting decrease in blood pressure. © 2013 Pear ...
Photosynthesis
... Photorespiration consumes O2 and organic fuel and releases CO2 without producing ATP or sugar ...
... Photorespiration consumes O2 and organic fuel and releases CO2 without producing ATP or sugar ...
2.21 Amino Acids.docx
... 2.21 Amino Acids Similar to carbohydrates, proteins contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). However, unlike carbohydrates (and lipids) proteins also contain nitrogen (N). Proteins are made up of smaller units called amino acids. This name amino acid signifies that each contains an amino (N ...
... 2.21 Amino Acids Similar to carbohydrates, proteins contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). However, unlike carbohydrates (and lipids) proteins also contain nitrogen (N). Proteins are made up of smaller units called amino acids. This name amino acid signifies that each contains an amino (N ...
Presentazione standard di PowerPoint
... The triglycerides of plants, such as corn oil, tend to have short or unsaturated fatty acids. Because of their kinks, these fatty acids pack together poorly and have low melting points, and these triglycerides are usually liquids at room temperature. ...
... The triglycerides of plants, such as corn oil, tend to have short or unsaturated fatty acids. Because of their kinks, these fatty acids pack together poorly and have low melting points, and these triglycerides are usually liquids at room temperature. ...
Ch. 6 Cell Respiration.notebook
... Both NADH & FADH2 are used to donate electrons an electron transport chain ...
... Both NADH & FADH2 are used to donate electrons an electron transport chain ...
Chapter 5 - Organic Chemistry, Biochemistry
... The oxygen or nitrogen atoms of the peptide bond are capable of hydrogen- bonding with hydrogen atoms elsewhere on the molecule. This bonding produces two common kinds of shapes seen in protein molecules, coils (helices) and pleated sheets. The helices and pleated sheets are referred to as a protein ...
... The oxygen or nitrogen atoms of the peptide bond are capable of hydrogen- bonding with hydrogen atoms elsewhere on the molecule. This bonding produces two common kinds of shapes seen in protein molecules, coils (helices) and pleated sheets. The helices and pleated sheets are referred to as a protein ...
Carbon Compounds
... • Functions of proteins: –Some proteins control the rate of reactions and regulate cell processes. –Some proteins are used to form bones and muscles. –Other proteins transport substances into or out of cells or help to fight disease. ...
... • Functions of proteins: –Some proteins control the rate of reactions and regulate cell processes. –Some proteins are used to form bones and muscles. –Other proteins transport substances into or out of cells or help to fight disease. ...
Secondary Fermentation: Malolactic Fermentation
... Amino acids and five carbon sugars Some inoculums have many of the necessary components present Wine is to be stabilized by ML fermentation so does not make sense to add nutrients which may encourage growth of spoilage organisms • Oxygen Bacteria like small amounts of oxygen but in practice ...
... Amino acids and five carbon sugars Some inoculums have many of the necessary components present Wine is to be stabilized by ML fermentation so does not make sense to add nutrients which may encourage growth of spoilage organisms • Oxygen Bacteria like small amounts of oxygen but in practice ...
Lipids WORD 1000 KB - Science Learning Hub
... unsaturated fatty acids such as oleic, linoleic and linolenic. Oleic acid is very similar in structure to stearic acid – the only difference being the presence of one carbon-carbon double bond in the chain. It is a monounsaturated fatty acid. O ...
... unsaturated fatty acids such as oleic, linoleic and linolenic. Oleic acid is very similar in structure to stearic acid – the only difference being the presence of one carbon-carbon double bond in the chain. It is a monounsaturated fatty acid. O ...
Guideline for the investigation of hyperammonaemia
... become apparent. The initial clinical deterioration is often mistaken for sepsis as the features of feeding difficulties and lethargy are non-specific. If untreated the neurological status progressively worsens with the development of vomiting, convulsions and coma. Infant and childhood presentation ...
... become apparent. The initial clinical deterioration is often mistaken for sepsis as the features of feeding difficulties and lethargy are non-specific. If untreated the neurological status progressively worsens with the development of vomiting, convulsions and coma. Infant and childhood presentation ...
Pre-workout / Nitric Oxide : SUPERNOVA 282GR
... Presenting the active ingredients of the product according to functional groups: Supernova Blend contains active ingredients which enhance nitrogen monoxide production in your body and carnosine production in your muscles, as well as a unique combination of two kinds of L-arginine, L-citrulline mala ...
... Presenting the active ingredients of the product according to functional groups: Supernova Blend contains active ingredients which enhance nitrogen monoxide production in your body and carnosine production in your muscles, as well as a unique combination of two kinds of L-arginine, L-citrulline mala ...
File - Serrano High School AP Biology
... ATP originates when anaerobic respiration (fermentation) takes place in the absence of oxygen. What happens is that sugar is broken down into smaller molecules and energy is released? The energy is used to generate ATP from ADP and P. ADP + P ----> ATP Sugar --------------------------> smaller molec ...
... ATP originates when anaerobic respiration (fermentation) takes place in the absence of oxygen. What happens is that sugar is broken down into smaller molecules and energy is released? The energy is used to generate ATP from ADP and P. ADP + P ----> ATP Sugar --------------------------> smaller molec ...
i. building blocks
... II. SYNTHESIS AND DEGRADATION A. Dehydration synthesis 1. Monomers are joined to form polymers by the removal or a water molecule (dehydration) a) This results in covalent attachment of the subunits (1) The bond forms when a hydrogen from one monomer is linked to a hydroxyl group from another monome ...
... II. SYNTHESIS AND DEGRADATION A. Dehydration synthesis 1. Monomers are joined to form polymers by the removal or a water molecule (dehydration) a) This results in covalent attachment of the subunits (1) The bond forms when a hydrogen from one monomer is linked to a hydroxyl group from another monome ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.