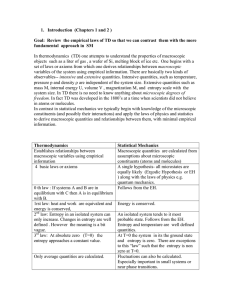
Heat and Energy
... The states of matter are the physical forms in which a substance can exist. The three states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. A substance’s state depends on the speed of its particles, the attraction between them, and the pressure around them ...
... The states of matter are the physical forms in which a substance can exist. The three states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. A substance’s state depends on the speed of its particles, the attraction between them, and the pressure around them ...
Silicone Heat Transfer Compound
... reliable thermal coupling of electrical and electronic components is required or between any surface where thermal conductivity of heat dissipation is important. A full range of heat transfer products are available from Electrolube. This range includes non-silicone based pastes (HTC), a RTV rubber ( ...
... reliable thermal coupling of electrical and electronic components is required or between any surface where thermal conductivity of heat dissipation is important. A full range of heat transfer products are available from Electrolube. This range includes non-silicone based pastes (HTC), a RTV rubber ( ...
Heat - Indian Institute of Technology Madras
... transfer occurs when there is relative motion between a fluid and an object. As the relative velocity increases, the rate of convective heat transfer also increases. Radiative heat exchange occurs through space. Even when two objects at different temperatures are not in physical contact, photons emi ...
... transfer occurs when there is relative motion between a fluid and an object. As the relative velocity increases, the rate of convective heat transfer also increases. Radiative heat exchange occurs through space. Even when two objects at different temperatures are not in physical contact, photons emi ...
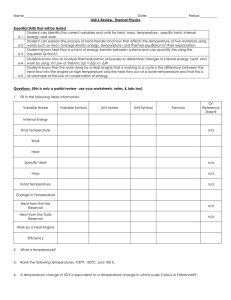
WORKSHOP 2: Dimensional Analysis and
... 7. A rubber stopper weighing 65.4 g is immersed into a graduated cylinder filled with 30.0 mL of liquid. The liquid level then rises to 48.8 mL. Calculate the density of the stopper. 3.48 g/mL 8. If the density of a liquid is known to be 0.785 g/mL, calculate the mass of the liquid if its volume is ...
... 7. A rubber stopper weighing 65.4 g is immersed into a graduated cylinder filled with 30.0 mL of liquid. The liquid level then rises to 48.8 mL. Calculate the density of the stopper. 3.48 g/mL 8. If the density of a liquid is known to be 0.785 g/mL, calculate the mass of the liquid if its volume is ...
September 26, 2012
... a. More than one phase (like oil and water) State: We need at least two intensive properties to define the state of a pure substance. Temperature: ...
... a. More than one phase (like oil and water) State: We need at least two intensive properties to define the state of a pure substance. Temperature: ...
WBL6_Lecture_Ch10-2djgx21
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
9. Entropy 2nd and 3rd laws/ Thermodynamic processes / Droplet
... (2pts) 2. Assume that all water has evaporated and that the temperature for the whole atmosphere is constant at 5◦ C. If all water vapour condenses out, what would be the increase in air temperature? Use the total mass of the atmosphere is 5 · 1018 kg. (2pts) 3. Explain different types (condensation ...
... (2pts) 2. Assume that all water has evaporated and that the temperature for the whole atmosphere is constant at 5◦ C. If all water vapour condenses out, what would be the increase in air temperature? Use the total mass of the atmosphere is 5 · 1018 kg. (2pts) 3. Explain different types (condensation ...
Temperature
... • Using a Thermometer Thermometers can measure temperature because of a property called thermal expansion. • Thermal expansion is the increase in volume of a substance in response to an increase in temperature. As a substance’s temperature increases, its particles move faster and spread out. ...
... • Using a Thermometer Thermometers can measure temperature because of a property called thermal expansion. • Thermal expansion is the increase in volume of a substance in response to an increase in temperature. As a substance’s temperature increases, its particles move faster and spread out. ...
Conceptual Physics. Tenth Edition
... liquid or a gas. Convection is the result of changes in density in parts of a liquid or gas. This change in density is the result of change in temperature. This process is called natural convection whereas in a forced convection the speed of the heat transfer is being increased by wind or other forc ...
... liquid or a gas. Convection is the result of changes in density in parts of a liquid or gas. This change in density is the result of change in temperature. This process is called natural convection whereas in a forced convection the speed of the heat transfer is being increased by wind or other forc ...
The Specific Heat Capacity of Metals
... it to boil for about five minutes so that the metal reaches the temperature of the boiling water. Take the temperature of the water. Assume this is also the temperature of the metal. Record this temperature in the table. 3. Add 100 g of cold water to an insulated cup. Quickly remove the metal sample ...
... it to boil for about five minutes so that the metal reaches the temperature of the boiling water. Take the temperature of the water. Assume this is also the temperature of the metal. Record this temperature in the table. 3. Add 100 g of cold water to an insulated cup. Quickly remove the metal sample ...
Problem set #2: 5
... (b) Do you expect the temperature to increase, decrease, or remain constant. Justify your answer with molecular arguments. Be specific about the nature of the forces involved. (c) What is the temperature of the final state? (d) What is the entropy change of the universe for this process? ...
... (b) Do you expect the temperature to increase, decrease, or remain constant. Justify your answer with molecular arguments. Be specific about the nature of the forces involved. (c) What is the temperature of the final state? (d) What is the entropy change of the universe for this process? ...