HNRS 227 Lecture #2 Chapters 2 and 3
... to measure the chemical energy of foodstuff is to find out how much heat is released by complete oxidation. A Calorie (kcal) is a measure of the heat release and thus is a measure of the chemical energy released. ...
... to measure the chemical energy of foodstuff is to find out how much heat is released by complete oxidation. A Calorie (kcal) is a measure of the heat release and thus is a measure of the chemical energy released. ...
Energy
... What is heat transfer by convection? •Heat is transferred through a substance through currents. This occurs in fluids (liquids AND gases) •Convection currents are caused by heating of a liquid or gas, the liquid or gas rises, then cools and falls. This occurs in the mantle of the earth. •And in the ...
... What is heat transfer by convection? •Heat is transferred through a substance through currents. This occurs in fluids (liquids AND gases) •Convection currents are caused by heating of a liquid or gas, the liquid or gas rises, then cools and falls. This occurs in the mantle of the earth. •And in the ...
Effect of temperature dependent specific heats
... This paper presents thermodynamics analysis of spark-ignition (SI) engine. A theoretical model of air-standard Otto cycle having temperature dependent specific heats has been implemented. It was compared to that which uses constant temperature specific heats. Wide range of engine parameters was stud ...
... This paper presents thermodynamics analysis of spark-ignition (SI) engine. A theoretical model of air-standard Otto cycle having temperature dependent specific heats has been implemented. It was compared to that which uses constant temperature specific heats. Wide range of engine parameters was stud ...
Journal of Special Topics - Department of Physics and Astronomy
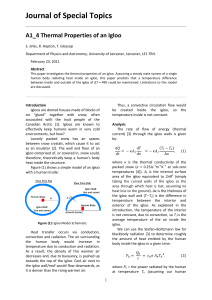
... where κ is the thermal conductivity of the packed snow (κ ≈ 0.25Js−1m−1K−1 at sub-zero temperatures [4]). AI is the internal surface area of the igloo equivalent to 2πR2 (simply taking the curved walls of the igloo as the area through which heat is lost, assuming no heat loss to the ground). ∆x is t ...
... where κ is the thermal conductivity of the packed snow (κ ≈ 0.25Js−1m−1K−1 at sub-zero temperatures [4]). AI is the internal surface area of the igloo equivalent to 2πR2 (simply taking the curved walls of the igloo as the area through which heat is lost, assuming no heat loss to the ground). ∆x is t ...
Chapter 16 notes
... added. (heats & cools faster) Metals: low specific heat Nonmetals: high specific heat ...
... added. (heats & cools faster) Metals: low specific heat Nonmetals: high specific heat ...
Assessment of febrile child
... • 1 to 3 years : • 4 to 10 years: 15 to 25 breaths/ min 15 to 20 breaths/ min • Over 10 years: BE CONCERNED IF RR> 70 IN UNDER 1 YEAR OR > 50 IN OLDER CHILDREN PS rates are not reliable in crying infant ...
... • 1 to 3 years : • 4 to 10 years: 15 to 25 breaths/ min 15 to 20 breaths/ min • Over 10 years: BE CONCERNED IF RR> 70 IN UNDER 1 YEAR OR > 50 IN OLDER CHILDREN PS rates are not reliable in crying infant ...
Document
... It is possible to calculate a value for entropy using statistical mechanics with a zero entropy being a single particle at absolute zero as a reference. S= kB log W ...
... It is possible to calculate a value for entropy using statistical mechanics with a zero entropy being a single particle at absolute zero as a reference. S= kB log W ...
Electrical Equivalent of Heat
... In this activity, the Power Amplifier supplies electrical energy to a heating resistor at a set voltage. The energy dissipated by the resistor warms a measured quantity of water. The Temperature Sensor measures the change in temperature of the water. The Power Amplifier measures the current through ...
... In this activity, the Power Amplifier supplies electrical energy to a heating resistor at a set voltage. The energy dissipated by the resistor warms a measured quantity of water. The Temperature Sensor measures the change in temperature of the water. The Power Amplifier measures the current through ...
Answers to Test Your Knowledge questions for
... to a given stimulus as a function of changing internal state. In a state of dehydration, water has a high affective rating, whereas in overhydration it is much lower or even negative. Body fluid level is regulated since there are control actions instigated when it departs from normal. In functional ...
... to a given stimulus as a function of changing internal state. In a state of dehydration, water has a high affective rating, whereas in overhydration it is much lower or even negative. Body fluid level is regulated since there are control actions instigated when it departs from normal. In functional ...
Chemistry Goal 2 Study Guide
... A small research submarine with a volume of 1.2 x 105 L has an internal pressure of 1.0 atm and an internal temperature of 150 C. If the submarine descends to a depth where the pressure is 150 atm and the temperature is 30 C, what will the volume of the gas inside be if the hull of the submarine bre ...
... A small research submarine with a volume of 1.2 x 105 L has an internal pressure of 1.0 atm and an internal temperature of 150 C. If the submarine descends to a depth where the pressure is 150 atm and the temperature is 30 C, what will the volume of the gas inside be if the hull of the submarine bre ...
First Law of Thermodynamics 9.1 Heat and Work
... The air (γ=1.40) in an automobile engine is compressed quickly so that appreciable heat exchange does not occur. For a compression ratio V1/V2 =10. Find the temperature of the gas compressed from an initial temperature of 20o C. ...
... The air (γ=1.40) in an automobile engine is compressed quickly so that appreciable heat exchange does not occur. For a compression ratio V1/V2 =10. Find the temperature of the gas compressed from an initial temperature of 20o C. ...
Shrinking a power supply and the challenge to maintain high
... This approach, combined with better thermal management will allow you to maintain reliably and lifetime of the final solution. The most important factor is good, careful design based on sound experience, resulting in known safety margins. This does not necessarily show up in any predictions, and can ...
... This approach, combined with better thermal management will allow you to maintain reliably and lifetime of the final solution. The most important factor is good, careful design based on sound experience, resulting in known safety margins. This does not necessarily show up in any predictions, and can ...
Chapter 19 First Law of Thermodynamics 19.1 Specific Heat (I)
... The internal energy is a state function that depends on the equilibrium state of a system, whereas Q and W depend on the thermodynamic path between two equilibrium states. That is, Q and W are associated with processes. The heat absorbed by a system will increase its internal energy, only some of wh ...
... The internal energy is a state function that depends on the equilibrium state of a system, whereas Q and W depend on the thermodynamic path between two equilibrium states. That is, Q and W are associated with processes. The heat absorbed by a system will increase its internal energy, only some of wh ...
Lowering the sink temperature for a desert solar air
... the cover bottom and sink surface. The air gap provides cheap and excellent insulation properties to reduce heat conduction from cover to ground. Since gap height is small, and the hotter surface is the top one, convective effects (all natural) are negligible. After sunset and until next day sunrise ...
... the cover bottom and sink surface. The air gap provides cheap and excellent insulation properties to reduce heat conduction from cover to ground. Since gap height is small, and the hotter surface is the top one, convective effects (all natural) are negligible. After sunset and until next day sunrise ...
Heat Transfer - Concord Consortium
... and the area of a surface such as a wall. If a house had ten times as much wall area as it had window area, and the wall was ten times as insulating, what would be the relative heat loss from wall and window? They would be the same, because the higher conductivity of one balances the greater area of ...
... and the area of a surface such as a wall. If a house had ten times as much wall area as it had window area, and the wall was ten times as insulating, what would be the relative heat loss from wall and window? They would be the same, because the higher conductivity of one balances the greater area of ...