Heat Transfer - Concord Consortium
... and the area of a surface such as a wall. If a house had ten times as much wall area as it had window area, and the wall was ten times as insulating, what would be the relative heat loss from wall and window? They would be the same, because the higher conductivity of one balances the greater area of ...
... and the area of a surface such as a wall. If a house had ten times as much wall area as it had window area, and the wall was ten times as insulating, what would be the relative heat loss from wall and window? They would be the same, because the higher conductivity of one balances the greater area of ...
Project 1.3.4 Renewable Insulation R
... Amount of heat lost through the (un-insulated) bottom is not significant in this experiment (if a student should ask about it). We are ignoring the heat absorbed and released by the box and the insulating materials themselves. Cp: air=1000, Styrofoam=1300, and acrylic=1470 J/kg°C, which means that ...
... Amount of heat lost through the (un-insulated) bottom is not significant in this experiment (if a student should ask about it). We are ignoring the heat absorbed and released by the box and the insulating materials themselves. Cp: air=1000, Styrofoam=1300, and acrylic=1470 J/kg°C, which means that ...
Conceptual Summary/Outline of Topics
... i. Radiation: Continuum of E-M wavelengths and energies 1. Amount and wavelength is proportional to T 4 2. Wien’s law (T from max ) 3. Blackbody curves: Information from area and peak, units. 4. Kirchhoff: good absorbers are good emitters ii. Conduction: collisions of molecules with adjacent molecu ...
... i. Radiation: Continuum of E-M wavelengths and energies 1. Amount and wavelength is proportional to T 4 2. Wien’s law (T from max ) 3. Blackbody curves: Information from area and peak, units. 4. Kirchhoff: good absorbers are good emitters ii. Conduction: collisions of molecules with adjacent molecu ...
Lecture 4
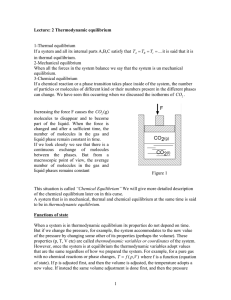
... • When there is a reversible flow of heat between a system and its surroundings, the temperatures of the system and the surroundings are essentially equal. • The heat flow out of the surroundings will be equal to the heat flow into the system. ...
... • When there is a reversible flow of heat between a system and its surroundings, the temperatures of the system and the surroundings are essentially equal. • The heat flow out of the surroundings will be equal to the heat flow into the system. ...
Rates of biotic interactions scale predictably with
... 1984, Englund et al. 2011), most of them operate most of the time within a biologically relevant range of approximately 0–40° C, and many use behavior to seek out optimal temperatures and avoid extremes (Martin and Huey 2008, Stevenson 1985, and additional detail in the Discussion). Within an organi ...
... 1984, Englund et al. 2011), most of them operate most of the time within a biologically relevant range of approximately 0–40° C, and many use behavior to seek out optimal temperatures and avoid extremes (Martin and Huey 2008, Stevenson 1985, and additional detail in the Discussion). Within an organi ...
Many_8 - USU physics
... electron charge, e , times the drift speed, vd , times the number of conduction (i.e., able to move when the field is turned on) electrons per unit volume, ne : J = evd ne . Combining these results with (1) we find m v ...
... electron charge, e , times the drift speed, vd , times the number of conduction (i.e., able to move when the field is turned on) electrons per unit volume, ne : J = evd ne . Combining these results with (1) we find m v ...
Thermometry in Fire Investigation and Analysis
... thermometer or a meat thermometer) uses a bimetallic strip wrapped into a coil. The two dissimilar metal strips which form the coil expand and contract at different rates when exposed to changes in temperature. One end of the coil is fixed to the housing of the device and the other drives an indicat ...
... thermometer or a meat thermometer) uses a bimetallic strip wrapped into a coil. The two dissimilar metal strips which form the coil expand and contract at different rates when exposed to changes in temperature. One end of the coil is fixed to the housing of the device and the other drives an indicat ...
CH 105 -- TAKE-HOME LAB The Vapor Pressure and Heat of
... liquid to a vapor. The ∆H vap value for water is very large at 540 calories per gram. This number explains why perspiration is such a good coolant for the body. Each single gram of water that evaporates removes almost three times more heat than ethanol (200 cal/g) would even though alcohols evaporat ...
... liquid to a vapor. The ∆H vap value for water is very large at 540 calories per gram. This number explains why perspiration is such a good coolant for the body. Each single gram of water that evaporates removes almost three times more heat than ethanol (200 cal/g) would even though alcohols evaporat ...