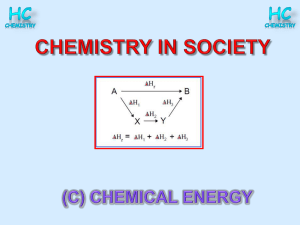
AOSS_401_20070919_L06_Thermo_Energy
... immediately assumes the pressure of the altitude to which it is displaced. • Temperature changes according to the adiabatic lapse rate ...
... immediately assumes the pressure of the altitude to which it is displaced. • Temperature changes according to the adiabatic lapse rate ...
Lecture 8 notes, ppt file
... (born, 1821-1895, first estimation of Avogadro number, Boltzmann’s colleague) ...
... (born, 1821-1895, first estimation of Avogadro number, Boltzmann’s colleague) ...
Specific Heat and Phase Change - CK
... • The amount of heat capacitance (and thus its specific heat value) is related to something called ’degrees of freedom,’ which basically says how free is the object to move in different ways (and thus how much kinetic energy can it store inside itself without breaking apart). For example, solids hav ...
... • The amount of heat capacitance (and thus its specific heat value) is related to something called ’degrees of freedom,’ which basically says how free is the object to move in different ways (and thus how much kinetic energy can it store inside itself without breaking apart). For example, solids hav ...
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTORY REMARKS 1.1 Introduction
... Intensive quantities do not depend on the amount of material. Temperature and pressure are examples. Another would be the specific heat capacity of a substance, which is the amount of heat required to raise unit mass of it through one degree, and it might be expressed in J kg−1 Co −1. This is what i ...
... Intensive quantities do not depend on the amount of material. Temperature and pressure are examples. Another would be the specific heat capacity of a substance, which is the amount of heat required to raise unit mass of it through one degree, and it might be expressed in J kg−1 Co −1. This is what i ...
ILQ-Ch - KFUPM Faculty List
... 18.6.1. An artist wishes to insert a gold pin into a hole in an iron sculpture and have it held permanently. The pin is slightly larger than the hole. The coefficient of linear thermal expansion of gold is slightly larger than that of iron. Consider the following options: (1) increase the temperatu ...
... 18.6.1. An artist wishes to insert a gold pin into a hole in an iron sculpture and have it held permanently. The pin is slightly larger than the hole. The coefficient of linear thermal expansion of gold is slightly larger than that of iron. Consider the following options: (1) increase the temperatu ...
floor level coverage charts
... floor temperature eventually will be reached. The amount of time it takes to reach “thermal equilibrium” is in direct correlation to the distance between the heaters. B. Location In most applications, 70 to 80 percent of the building heat loss is around the outside perimeter walls. The transmission ...
... floor temperature eventually will be reached. The amount of time it takes to reach “thermal equilibrium” is in direct correlation to the distance between the heaters. B. Location In most applications, 70 to 80 percent of the building heat loss is around the outside perimeter walls. The transmission ...
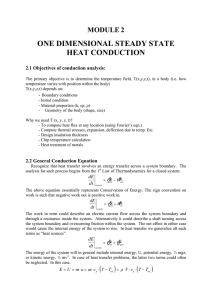
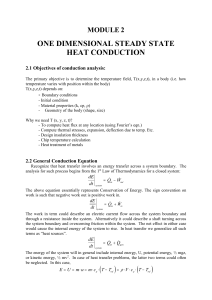
one dimensional steady state heat conduction
... The primary objective is to determine the temperature field, T(x,y,z,t), in a body (i.e. how temperature varies with position within the body) T(x,y,z,t) depends on: - Boundary conditions - Initial condition - Material properties (k, cp, ) - Geometry of the body (shape, size) Why we need T (x, y, z ...
... The primary objective is to determine the temperature field, T(x,y,z,t), in a body (i.e. how temperature varies with position within the body) T(x,y,z,t) depends on: - Boundary conditions - Initial condition - Material properties (k, cp, ) - Geometry of the body (shape, size) Why we need T (x, y, z ...