Exercises - Madison County Schools
... a certain temperature than most substances, and it takes longer to cool. 44. Explain why Europe is much warmer than northeastern Canada, even though they are at similar latitudes. ...
... a certain temperature than most substances, and it takes longer to cool. 44. Explain why Europe is much warmer than northeastern Canada, even though they are at similar latitudes. ...
Chapter 31 – Aves (Birds)
... Panting: releases water from nose & mouth, causing loss of body heat Sweat glands: moisture is secreted onto skin’s surface; as moisture evaporates, heat from body is transferred to air ...
... Panting: releases water from nose & mouth, causing loss of body heat Sweat glands: moisture is secreted onto skin’s surface; as moisture evaporates, heat from body is transferred to air ...
The Insatiable Appetite
... Next lectures will cover a bit of physiology – how do you keep an engine running at such high RPMs? And then seque into the annual cycle of birds. Because resources are not available at constant levels throughout the year (day length changes, winter, dry & wet seasons in the tropics, etc.), and bec ...
... Next lectures will cover a bit of physiology – how do you keep an engine running at such high RPMs? And then seque into the annual cycle of birds. Because resources are not available at constant levels throughout the year (day length changes, winter, dry & wet seasons in the tropics, etc.), and bec ...
Lab 1: Temperature and Heat
... (g) Find the latent heat of vaporization of nitrogen by assuming that the electrical energy supplied by the resistor equals the thermal energy gained by the nitrogen as it boiled. (h) Put your value for the latent heat of vaporization on the white board. When all lab groups have reported their value ...
... (g) Find the latent heat of vaporization of nitrogen by assuming that the electrical energy supplied by the resistor equals the thermal energy gained by the nitrogen as it boiled. (h) Put your value for the latent heat of vaporization on the white board. When all lab groups have reported their value ...
How we Experience indoor and outdoor climates
... Fingers, toes, head and neck need special protection in cold environments ...
... Fingers, toes, head and neck need special protection in cold environments ...
Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function
... its environment. Sources of insulation include hair, feathers, and layers of fat formed by adipose tissue. Most land mammals and birds react to cold by raising their fur or feathers. Lacking feathers or fur, humans must rely primarily on fat for insulation. “Goose bumps” are a vestige of hair raisin ...
... its environment. Sources of insulation include hair, feathers, and layers of fat formed by adipose tissue. Most land mammals and birds react to cold by raising their fur or feathers. Lacking feathers or fur, humans must rely primarily on fat for insulation. “Goose bumps” are a vestige of hair raisin ...
Document
... • Human body stabilizes its T (i.e., prevents its T decrease) primarily by converting food into heat (metabolism) • The stronger the wind, the faster the body’s heat loss • High winds in below-freezing air can remove heat from exposed skin so quickly that the skin may actually freeze (called frostbi ...
... • Human body stabilizes its T (i.e., prevents its T decrease) primarily by converting food into heat (metabolism) • The stronger the wind, the faster the body’s heat loss • High winds in below-freezing air can remove heat from exposed skin so quickly that the skin may actually freeze (called frostbi ...
2nd law - WordPress.com
... •Heat transfer through a finite temperature difference. •Lack of pressure equilibrium between system and surroundings. •Free expansion. (b) Involvement of dissipative effects. •Friction •Paddle wheel work transfer •Transfer of electricity through a resistor. ...
... •Heat transfer through a finite temperature difference. •Lack of pressure equilibrium between system and surroundings. •Free expansion. (b) Involvement of dissipative effects. •Friction •Paddle wheel work transfer •Transfer of electricity through a resistor. ...
Chapter16
... Picture the Problem: A steel gasoline tank is completely filled with gasoline, such that the gasoline and the tank have the same initial volumes. When the gas and tank are heated, the gas expands more than the tank, causing some of the gas to spill out of the tank. Strategy: Since the initial volume ...
... Picture the Problem: A steel gasoline tank is completely filled with gasoline, such that the gasoline and the tank have the same initial volumes. When the gas and tank are heated, the gas expands more than the tank, causing some of the gas to spill out of the tank. Strategy: Since the initial volume ...
Physics 1301, Exam 4 Review
... On the scantron sheet provided, write and bubble in your name. In the identification number field, write and bubble in the 7 digits from your student id number from your black cougar 1 card, or from your fee bill (do not try to fill the first two characters, which are letters.) Each of the following ...
... On the scantron sheet provided, write and bubble in your name. In the identification number field, write and bubble in the 7 digits from your student id number from your black cougar 1 card, or from your fee bill (do not try to fill the first two characters, which are letters.) Each of the following ...
Homeostasis Flashcards
... prolonged exposure to heat and high humidity prolonged immersion in cold water ...
... prolonged exposure to heat and high humidity prolonged immersion in cold water ...
Practice Problems and Solutions for Quiz: 100g of water was
... Practice Problems and Solutions for Quiz: 1. 100g of water was warmed 50 degrees C. Find the energy in Joules and calories. ...
... Practice Problems and Solutions for Quiz: 1. 100g of water was warmed 50 degrees C. Find the energy in Joules and calories. ...
Thermoregulation
... subcutaneous fat during cold winter. Endotherms produce more metabolic heat than ectotherms as they posses different types of mitochondria and concentra
... subcutaneous fat during cold winter. Endotherms produce more metabolic heat than ectotherms as they posses different types of mitochondria and concentra
Document
... • A lumped system is one in which the dependent variables of interest are a function of time alone. In general, this will mean solving a set of ordinary differential equations (ODEs) • A distributed system is one in which all dependent variables are functions of time and one or more spatial variable ...
... • A lumped system is one in which the dependent variables of interest are a function of time alone. In general, this will mean solving a set of ordinary differential equations (ODEs) • A distributed system is one in which all dependent variables are functions of time and one or more spatial variable ...
2, 5, 9, 11, 18, 20 / 3, 9, 10, 16, 19, 24
... 18. REASONING AND SOLUTION The thermal conductivity of the bottom of the pot is greater than the thermal conductivity of air; therefore, the portion of the heating element beneath the pot loses heat by conduction through the bottom of the pot. The exposed portion of the heating element loses some he ...
... 18. REASONING AND SOLUTION The thermal conductivity of the bottom of the pot is greater than the thermal conductivity of air; therefore, the portion of the heating element beneath the pot loses heat by conduction through the bottom of the pot. The exposed portion of the heating element loses some he ...
Abstract
... solar furnace in the James. S. Markiewicz Solar Energy Research Facility in order to substitute solar thermal energy for electric energy. A major challenge of the research effort is to develop an interface that allows the integration of the solar thermal energy into the electrolytic cell where the M ...
... solar furnace in the James. S. Markiewicz Solar Energy Research Facility in order to substitute solar thermal energy for electric energy. A major challenge of the research effort is to develop an interface that allows the integration of the solar thermal energy into the electrolytic cell where the M ...
Slide 1
... failed. The bottom TEG should follow the temperature of the water closely as seen in the 24 hour test. If this were the case this would have produced a workable temperature difference capable of creating a large voltage. ...
... failed. The bottom TEG should follow the temperature of the water closely as seen in the 24 hour test. If this were the case this would have produced a workable temperature difference capable of creating a large voltage. ...
Heat
... •Each of the three regions represents a pure phase (not a mix). •Each line represents the temp & pressure conditions where the phases exist in equilibrium. •Triple point: set of conditions in which all phases exist in equilibrium ...
... •Each of the three regions represents a pure phase (not a mix). •Each line represents the temp & pressure conditions where the phases exist in equilibrium. •Triple point: set of conditions in which all phases exist in equilibrium ...
Document
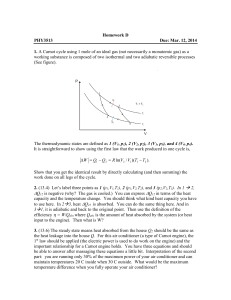
... 2. (13.4) Let’s label three points as 1 (p1,V1,T1), 2 (p1,V2,T2), and 3 (p2,V2,T3). In 1 2, ∆Q12 is negative (why? The gas is cooled.) You can express ∆Q12 in terms of the heat capacity and the temperature change. You should think what kind heat capacity you have to use here. In 23, heat ∆Q23 is ...
... 2. (13.4) Let’s label three points as 1 (p1,V1,T1), 2 (p1,V2,T2), and 3 (p2,V2,T3). In 1 2, ∆Q12 is negative (why? The gas is cooled.) You can express ∆Q12 in terms of the heat capacity and the temperature change. You should think what kind heat capacity you have to use here. In 23, heat ∆Q23 is ...
Nats 101 S00 #8
... heat away. That is why you appear flushed after being in the sun. In addition, you sweat. The water absorbs heat in order to evaporate. When the body gets too cold, the blood vessels contract so that less heat is carried to the surface. This can lead to frostbite where the skin dies from lack of b ...
... heat away. That is why you appear flushed after being in the sun. In addition, you sweat. The water absorbs heat in order to evaporate. When the body gets too cold, the blood vessels contract so that less heat is carried to the surface. This can lead to frostbite where the skin dies from lack of b ...
Heat - Cobb Learning
... What is thermal energy? • Thermal energy is the total kinetic energy of all particles in a substance. Which is measured by temperature. • For example, a glass of water can have the same temperature as a lake, but the lake has much more thermal energy because the lake contains many more water molecu ...
... What is thermal energy? • Thermal energy is the total kinetic energy of all particles in a substance. Which is measured by temperature. • For example, a glass of water can have the same temperature as a lake, but the lake has much more thermal energy because the lake contains many more water molecu ...
Heat Transfer Powerpoint 1/6/15
... from the bottom of the teapot rise and spread their heat energy to the cooler molecules above them through direct contact. This convection current also pushes cooler molecules of water down to the bottom where they come in contact with the heated bottom of the teapot. While all of this is occurring, ...
... from the bottom of the teapot rise and spread their heat energy to the cooler molecules above them through direct contact. This convection current also pushes cooler molecules of water down to the bottom where they come in contact with the heated bottom of the teapot. While all of this is occurring, ...
WS- Specific heat
... 1. How many calories of heat are required to raise the temperature of 550 g of water from 12.0 oC to 18.0 oC? (remember the specific heat of water is 1.00 cal/g x oC) 2. How much heat is lost when a 640 g piece of copper cools from 375 oC, to 26 oC? (The specific heat of copper is 0.38452 J/g x oC) ...
... 1. How many calories of heat are required to raise the temperature of 550 g of water from 12.0 oC to 18.0 oC? (remember the specific heat of water is 1.00 cal/g x oC) 2. How much heat is lost when a 640 g piece of copper cools from 375 oC, to 26 oC? (The specific heat of copper is 0.38452 J/g x oC) ...
Chapter 10 Power Point
... Hot liquids and gases expand and rise while the cooler liquid or gas falls (all caused by a difference in densities!) 2. Goes across ...
... Hot liquids and gases expand and rise while the cooler liquid or gas falls (all caused by a difference in densities!) 2. Goes across ...
Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia is elevated body temperature due to failed thermoregulation that occurs when a body produces or absorbs more heat than it dissipates. Extreme temperature elevation then becomes a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment to prevent disability or death.The most common causes include heat stroke and adverse reactions to drugs. The former is an acute temperature elevation caused by exposure to excessive heat, or combination of heat and humidity, that overwhelms the heat-regulating mechanisms. The latter is a relatively rare side effect of many drugs, particularly those that affect the central nervous system. Malignant hyperthermia is a rare complication of some types of general anesthesia.Hyperthermia differs from fever in that the body's temperature set point remains unchanged. The opposite is hypothermia, which occurs when the temperature drops below that required to maintain normal metabolism.