Presentation
... Specific Heat- the amount of heat that is needed to raise the temperature of 1kg of a material by 1˚C. This measurement determines how things conduct heat. Example- Plastic has a higher specific heat than metal which is why we use plastic spoons when we cook. ...
... Specific Heat- the amount of heat that is needed to raise the temperature of 1kg of a material by 1˚C. This measurement determines how things conduct heat. Example- Plastic has a higher specific heat than metal which is why we use plastic spoons when we cook. ...
5,6 Quiz - mvhs
... when an electron drops from the n=4 to the n=2 level in a hydrogen atom. 4. Write/Draw the following for Ag atom and Ag+ ion. a. Condensed electron configuration b. Condensed Orbital Notation c. Number of valence electrons 5. A student is asked to determine the molar enthalpy of neutralization, ∆Hne ...
... when an electron drops from the n=4 to the n=2 level in a hydrogen atom. 4. Write/Draw the following for Ag atom and Ag+ ion. a. Condensed electron configuration b. Condensed Orbital Notation c. Number of valence electrons 5. A student is asked to determine the molar enthalpy of neutralization, ∆Hne ...
Calorimetry In all physical and chemical reactions energy is either
... In all physical and chemical reactions energy is either released or absorbed. If energy is released in a reaction, it is said to be exothermic and the potential energy of the reactants will be higher than the potential energy of the products. If energy is absorbed in a reaction, it is said to be end ...
... In all physical and chemical reactions energy is either released or absorbed. If energy is released in a reaction, it is said to be exothermic and the potential energy of the reactants will be higher than the potential energy of the products. If energy is absorbed in a reaction, it is said to be end ...
Worksheet – Measuring Heat
... 1. A fast-food item contains 544 nutritional Calories. Convert this energy to calories and to joules. (544,000 cal ; 2.28 x 106 J) 2. An endothermic process absorbs 138 kJ. How many calories of heat are absorbed?(3.30 x 104 cal) 3. An exothermic reaction releases 325000 calories. Convert this energy ...
... 1. A fast-food item contains 544 nutritional Calories. Convert this energy to calories and to joules. (544,000 cal ; 2.28 x 106 J) 2. An endothermic process absorbs 138 kJ. How many calories of heat are absorbed?(3.30 x 104 cal) 3. An exothermic reaction releases 325000 calories. Convert this energy ...
Class 4a
... • Absolute humidity: ratio of water vapor to a given volume of air • Specific humidity: ratio of water vapor to a given mass of air ...
... • Absolute humidity: ratio of water vapor to a given volume of air • Specific humidity: ratio of water vapor to a given mass of air ...
Ch 10 Review activity
... 2. A 97 g sample of gold at 785oC is dropped into 323 g of water, which has an initial temperature of 15oC. If gold and water have specific heats of 0.129 J/goC and 4.184 J/goC respectively, what is the final temperature of the mixture? Assume that the gold and the water experience no change in sta ...
... 2. A 97 g sample of gold at 785oC is dropped into 323 g of water, which has an initial temperature of 15oC. If gold and water have specific heats of 0.129 J/goC and 4.184 J/goC respectively, what is the final temperature of the mixture? Assume that the gold and the water experience no change in sta ...
The fundamental principles of radiant heat barrier
... radiant heat barrier / reflective foil Reflective insulation materials work on a different concept than conventional bulk insulation like rigid foam boards or fibrous blankets. Unlike conventional bulk insulation, reflective insulation has very low emittance values “e-values” (typically 0.03, compar ...
... radiant heat barrier / reflective foil Reflective insulation materials work on a different concept than conventional bulk insulation like rigid foam boards or fibrous blankets. Unlike conventional bulk insulation, reflective insulation has very low emittance values “e-values” (typically 0.03, compar ...
Name - Net Start Class
... temperature of 25oC. The final temperature of both the metal and the water is 45oC. a. What will happen to the temperature of the piece of metal? decrease b. What will happen to the temperature of the water? increase c. What is the specific heat of the metal? Q = m Cp T 2500 g * 4.184 j/goC * 20oC ...
... temperature of 25oC. The final temperature of both the metal and the water is 45oC. a. What will happen to the temperature of the piece of metal? decrease b. What will happen to the temperature of the water? increase c. What is the specific heat of the metal? Q = m Cp T 2500 g * 4.184 j/goC * 20oC ...
2 - D STEADY STATE HEAT CONDUCTION
... then T1 + T2 + T3 + T4 - 4To = l These equations may be solved by spreadsheet iteration 'updating' each temperature 'cell' in sequence . Alternatively an array of simultaneous equations may be set up and solved by Gaussian elimination, either by hand (!) or by computer. BOUNDARY CONDITIONS The above ...
... then T1 + T2 + T3 + T4 - 4To = l These equations may be solved by spreadsheet iteration 'updating' each temperature 'cell' in sequence . Alternatively an array of simultaneous equations may be set up and solved by Gaussian elimination, either by hand (!) or by computer. BOUNDARY CONDITIONS The above ...
Transfer of Thermal Energy worksheet
... If you have stood in front of a fireplace or near a campfire, you have felt the heat transfer known as radiation. The side of you nearest the fire warms, while your other side remains unaffected by the heat. Although you are surrounded by air, the air has nothing to do with this transfer of heat. He ...
... If you have stood in front of a fireplace or near a campfire, you have felt the heat transfer known as radiation. The side of you nearest the fire warms, while your other side remains unaffected by the heat. Although you are surrounded by air, the air has nothing to do with this transfer of heat. He ...
Study Guide Answers
... 1. A change of state is a _c__ a. Process by which two states of matter co-exist b. Chemical change c. Physical change that converts a substance from one physical form to another 2. Particles in a ___solid_______ move slower than particles in a ____liquid or gas______. 3. Particles in a _a__ vibrate ...
... 1. A change of state is a _c__ a. Process by which two states of matter co-exist b. Chemical change c. Physical change that converts a substance from one physical form to another 2. Particles in a ___solid_______ move slower than particles in a ____liquid or gas______. 3. Particles in a _a__ vibrate ...
Name Date Class THE FLOW OF ENERGY—HEAT AND WORK
... Use this completion exercise to check your understanding of the concepts and terms that are introduced in this section. Each blank can be completed with a term, short phrase, or number. The energy that flows from a warm object to a cool object is called ...
... Use this completion exercise to check your understanding of the concepts and terms that are introduced in this section. Each blank can be completed with a term, short phrase, or number. The energy that flows from a warm object to a cool object is called ...
Practice Problems and Solutions for Quiz: 100g of water was
... 2. 50g of gold was warmed from 30 degrees C to 590 degrees C. If the specific heat of gold is 0.129J/gC, how much energy was used to heat the gold? Q=gCpT Q=(50g)( 0.129J/gC)(560C)= 3,612J 3. A student took 40g of a metal at 5C and added it to 30g of water at 50C. The final temp was 40C. Find ...
... 2. 50g of gold was warmed from 30 degrees C to 590 degrees C. If the specific heat of gold is 0.129J/gC, how much energy was used to heat the gold? Q=gCpT Q=(50g)( 0.129J/gC)(560C)= 3,612J 3. A student took 40g of a metal at 5C and added it to 30g of water at 50C. The final temp was 40C. Find ...
Our design for the heating and cooling system is centered upon two
... The second heating and cooling area includes the classrooms, study spaces, offices and other spaces located on the upper floors. Since the classrooms and office spaces will be used mainly between 8am and 6pm, only during this period they will be constantly conditioned. After those hours, as well as ...
... The second heating and cooling area includes the classrooms, study spaces, offices and other spaces located on the upper floors. Since the classrooms and office spaces will be used mainly between 8am and 6pm, only during this period they will be constantly conditioned. After those hours, as well as ...
Heat Heat Capacity Latent Heat Latent Heat
... A phase change occurs when a solid melts to a liquid, a liquid boils to a gas, a gas condenses to a liquid, and a liquid freezes to a solid. Each of these phase changes requires a certain amount of heat, although the temperature does not change. If a solid becomes liquid, or vice versa, the amou ...
... A phase change occurs when a solid melts to a liquid, a liquid boils to a gas, a gas condenses to a liquid, and a liquid freezes to a solid. Each of these phase changes requires a certain amount of heat, although the temperature does not change. If a solid becomes liquid, or vice versa, the amou ...
NÁZEV PROJEKTU
... Adiabatic · Isoentropic · Isoenthalpic Quasistatic · Polytropic Reversible vs. irreversible ...
... Adiabatic · Isoentropic · Isoenthalpic Quasistatic · Polytropic Reversible vs. irreversible ...
Teacher`s notes 22 Specific Heat Capacity of a solid
... this reason it is best to purchase a block and heater that are matched. Ideally several blocks are required, aluminium, brass and iron. Glycerol is mentioned as the heat conductive medium to surround the heater this reduces the risk or fire. Oil with a very high boiling point and flash point can be ...
... this reason it is best to purchase a block and heater that are matched. Ideally several blocks are required, aluminium, brass and iron. Glycerol is mentioned as the heat conductive medium to surround the heater this reduces the risk or fire. Oil with a very high boiling point and flash point can be ...
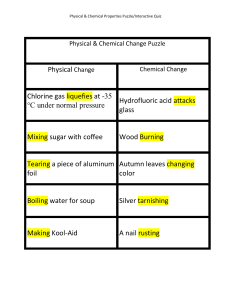
Physical Change Chlorine gas liquefies at
... Chlorine gas liquefies at -35 Hydrofluoric acid attacks °C under normal pressure glass ...
... Chlorine gas liquefies at -35 Hydrofluoric acid attacks °C under normal pressure glass ...
CHM 111: General Physical Chemistry 3 Units
... Historical development of the atom: definition of atoms, Daltons atomic theory, relative atomic masses. Fundamental particles of the atom and atomic structure. Modern electronic theory of atoms; electronic configuration of the elements. Periodicity of the elements. Radioactivity: Stoichiometry: mole ...
... Historical development of the atom: definition of atoms, Daltons atomic theory, relative atomic masses. Fundamental particles of the atom and atomic structure. Modern electronic theory of atoms; electronic configuration of the elements. Periodicity of the elements. Radioactivity: Stoichiometry: mole ...
The Functional Form of the Internal Energy
... Note that at Room Temperature, JT is positive for most gases; the cryogenic gases H2 and He being the exception. This means that most gases will cool when throttled at Room Temperature. The so called Inversion Temperature is the temperature at which JT inverts from positive to negative. The Joule ...
... Note that at Room Temperature, JT is positive for most gases; the cryogenic gases H2 and He being the exception. This means that most gases will cool when throttled at Room Temperature. The so called Inversion Temperature is the temperature at which JT inverts from positive to negative. The Joule ...
THE WATER CYCLE
... On average, the molecules in a glass of water do not have enough heat energy to escape from the liquid, or else the liquid would turn into vapor quickly (see boil). When the molecules collide, they transfer energy to each other in varying degrees, based on how they collide. Sometimes the transfer i ...
... On average, the molecules in a glass of water do not have enough heat energy to escape from the liquid, or else the liquid would turn into vapor quickly (see boil). When the molecules collide, they transfer energy to each other in varying degrees, based on how they collide. Sometimes the transfer i ...
Nats 101 S00 #8
... 1. Conduction: the movement of heat by atomic vibrations. If a piece of metal is heated at one end then the rest of the piece will get hot as the atoms vibrate with large amplitudes and bump into their neighbors and thus increase their vibrations. This is the major way that heat loss occurs in build ...
... 1. Conduction: the movement of heat by atomic vibrations. If a piece of metal is heated at one end then the rest of the piece will get hot as the atoms vibrate with large amplitudes and bump into their neighbors and thus increase their vibrations. This is the major way that heat loss occurs in build ...
ideal gas law
... that has neither definite shape nor definite volume. Like liquids, they are fluids and assume the shape of their containers. Unlike liquids, they will expand to fill any container, regardless of its size. They also condense into liquids or solids when sufficiently cooled or compressed. ...
... that has neither definite shape nor definite volume. Like liquids, they are fluids and assume the shape of their containers. Unlike liquids, they will expand to fill any container, regardless of its size. They also condense into liquids or solids when sufficiently cooled or compressed. ...