Nitric oxide—Important messenger in human body
... arterial part of cardiovascular system, and also regulates tonus of small arteries and venules within microcirculation [9]. Main stimuli responsible for NO release are shear stress and distension of the vessels. The role of NO in regulation of the vascular tone is well defined, based on the concepti ...
... arterial part of cardiovascular system, and also regulates tonus of small arteries and venules within microcirculation [9]. Main stimuli responsible for NO release are shear stress and distension of the vessels. The role of NO in regulation of the vascular tone is well defined, based on the concepti ...
An introduction to immunology
... • Important to study what parts of a protein that binds to MHC molecules. • MHC I binds peptides with 8-10 aa • MHC II bind peptides with 12-25 aa • Potentials of peptide vaccines • Prediction of peptides is important!!!! ...
... • Important to study what parts of a protein that binds to MHC molecules. • MHC I binds peptides with 8-10 aa • MHC II bind peptides with 12-25 aa • Potentials of peptide vaccines • Prediction of peptides is important!!!! ...
CNS-CPC - Trinity College Dublin
... special problems in pregnancy and in children. It can be due to multiple causes. Repeated hemolysis of infected red cells is the most important cause for a reduction in haemoglobin levels. Anaemia depends on the degree of parasitemia, duration of the acute illness and the number of febrile paroxysms ...
... special problems in pregnancy and in children. It can be due to multiple causes. Repeated hemolysis of infected red cells is the most important cause for a reduction in haemoglobin levels. Anaemia depends on the degree of parasitemia, duration of the acute illness and the number of febrile paroxysms ...
Placental regulation of maternal-fetal interactions and
... immunosuppression. Trophoblast cells secrete a variety of immunosuppressive factors and harbor surface ligands to control immune reactivity through cell– cell interactions. Shedding of trophoblast antigens and trafficking of fetal cells into the maternal circulation are believed to promote classical ...
... immunosuppression. Trophoblast cells secrete a variety of immunosuppressive factors and harbor surface ligands to control immune reactivity through cell– cell interactions. Shedding of trophoblast antigens and trafficking of fetal cells into the maternal circulation are believed to promote classical ...
Autoimmunity and Apoptosis – Therapeutic Implications Iran Rashedi , Soumya Panigrahi
... however, since the autoantigen cannot be eliminated, the effector Tand B-cells are constantly recruited and activated, and the immune response will not end. In addition to the role of the adaptive immune system and its multiple players in the pathogenesis of autoimmunity, which has been vastly inves ...
... however, since the autoantigen cannot be eliminated, the effector Tand B-cells are constantly recruited and activated, and the immune response will not end. In addition to the role of the adaptive immune system and its multiple players in the pathogenesis of autoimmunity, which has been vastly inves ...
Goblet Cells and Mucins: Role in Innate Defense
... stem cells and differentiation into specific cell lineages in the intestine involves a complex interplay of multiple developmental pathways including Wnt/β-catenin, bone morphogenic protein (BMP), and PI3-kinase/Akt signaling [20]. Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) gene Math1 is a mammalian homolog of t ...
... stem cells and differentiation into specific cell lineages in the intestine involves a complex interplay of multiple developmental pathways including Wnt/β-catenin, bone morphogenic protein (BMP), and PI3-kinase/Akt signaling [20]. Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) gene Math1 is a mammalian homolog of t ...
Chapter 12 ppt
... Our cells in another person’s body can trigger an immune response because they are foreign Restricts donors for transplants ...
... Our cells in another person’s body can trigger an immune response because they are foreign Restricts donors for transplants ...
Chapter 22 PPT. - HCC Learning Web
... • 22-6 Discuss the mechanisms of B cell activation and differentiation, describe the structure and function of antibodies, and explain the primary and secondary responses to antigen exposure. • 22-7 Describe the development of immunological competence, list and explain examples of immune disorders a ...
... • 22-6 Discuss the mechanisms of B cell activation and differentiation, describe the structure and function of antibodies, and explain the primary and secondary responses to antigen exposure. • 22-7 Describe the development of immunological competence, list and explain examples of immune disorders a ...
Surfactant proteins and the inflammatory and immune response in
... Surfactant protein A prevents inhibition of surfactant activity by blood proteins. Leakage of blood components into the alveolar space as a result of lung injury has been implicated in the pathology of respiratory distress syndrome. Plasma proteins have been shown to inhibit surfactant activity both ...
... Surfactant protein A prevents inhibition of surfactant activity by blood proteins. Leakage of blood components into the alveolar space as a result of lung injury has been implicated in the pathology of respiratory distress syndrome. Plasma proteins have been shown to inhibit surfactant activity both ...
Vaccine development strategies Plasmodium falciparum
... total serum antibodies and are associated with phagocytosis (mainly IgG1 and IgG3), activation of complement system (IgG3 and IgG1, to a smaller extent IgG2), and the release of immune effectors, including highly reactive oxygen- and nitrogen compounds, and immunoregulatory polypeptides (chemokines) ...
... total serum antibodies and are associated with phagocytosis (mainly IgG1 and IgG3), activation of complement system (IgG3 and IgG1, to a smaller extent IgG2), and the release of immune effectors, including highly reactive oxygen- and nitrogen compounds, and immunoregulatory polypeptides (chemokines) ...
Initial depletion of regulatory T cells: the missing
... sponse to allogeneic stimulation. An increased detection of Foxp3 at mRNA and protein levels in the cultures confirmed the Treg expansion. Overall, we demonstrate that T-cell cultures promote Treg expansion over effector T cells, leading to deleterious immune functions, and that this imbalance can b ...
... sponse to allogeneic stimulation. An increased detection of Foxp3 at mRNA and protein levels in the cultures confirmed the Treg expansion. Overall, we demonstrate that T-cell cultures promote Treg expansion over effector T cells, leading to deleterious immune functions, and that this imbalance can b ...
Natural Antimicrobial Peptides: Pleiotropic Molecules in Host Defense
... parasites, bacteria and viruses. But it is the innate immunity that is responsible for the rapid initial defense against the pathogen. The co-evolution of hosts and pathogens has led to a diverse group of peptides that the host produces in order to kill or reduce the infective microbes. These peptid ...
... parasites, bacteria and viruses. But it is the innate immunity that is responsible for the rapid initial defense against the pathogen. The co-evolution of hosts and pathogens has led to a diverse group of peptides that the host produces in order to kill or reduce the infective microbes. These peptid ...
An Identification Guide for Avian Blood Components
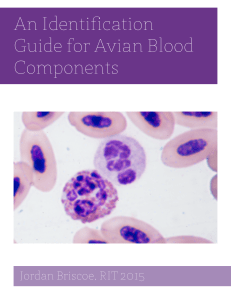
... of the heterophils can be used to infer the severity of an immune response. These toxic heterophils were present in a bird that was infected with blood parasites. Toxic heterophils appear more basophilic overall, with hypersegmented nuclei, and varying degrees of basophilic granules depending on the ...
... of the heterophils can be used to infer the severity of an immune response. These toxic heterophils were present in a bird that was infected with blood parasites. Toxic heterophils appear more basophilic overall, with hypersegmented nuclei, and varying degrees of basophilic granules depending on the ...
Progress in the fight against Inflammatory Diseases and Cancer
... Recent years have seen dramatic advances in our understanding of the molecular basis for immune defense. Studies of the molecular interactions that contribute to innate and adaptive immunity keep providing new insights of the mechanisms by which our body responds to infection and injury. Detailed an ...
... Recent years have seen dramatic advances in our understanding of the molecular basis for immune defense. Studies of the molecular interactions that contribute to innate and adaptive immunity keep providing new insights of the mechanisms by which our body responds to infection and injury. Detailed an ...
Licentiate thesis from the Department of Immunology, Wenner-Gren Institute,
... Perhaps the most essential task for the immune system is to be able to distinguish what is to be regarded as friendly and what is to be regarded as dangerous. To solve this task, an array of receptors has evolved to recognize components that are essential and unique to microbes. An example is the ce ...
... Perhaps the most essential task for the immune system is to be able to distinguish what is to be regarded as friendly and what is to be regarded as dangerous. To solve this task, an array of receptors has evolved to recognize components that are essential and unique to microbes. An example is the ce ...
Latent Infection with Cytomegalovirus Is Associated with Poor
... virus respond as well as the young. Hence, advanced chronological age plays a role in depressed responses to influenza but only in concert with CMV infection. Our data also suggest that contrary to the widely accepted concept, a more late-differentiated CD4 compartment is not detrimental but is asso ...
... virus respond as well as the young. Hence, advanced chronological age plays a role in depressed responses to influenza but only in concert with CMV infection. Our data also suggest that contrary to the widely accepted concept, a more late-differentiated CD4 compartment is not detrimental but is asso ...
Review Article Bridging Innate and Adaptive Antitumor Immunity
... has modified ideas on the chemical nature of molecules recognized by T cells [68]. In the early years, it was suggested that hapten-specific T cells recognize haptenmodified peptides [69]. Chemical haptens and metal ions interact with proteins and thereby become recognizable by T and B lymphocytes. ...
... has modified ideas on the chemical nature of molecules recognized by T cells [68]. In the early years, it was suggested that hapten-specific T cells recognize haptenmodified peptides [69]. Chemical haptens and metal ions interact with proteins and thereby become recognizable by T and B lymphocytes. ...
Andrea Cerutti Regulation of B cell Responses by the Innate Immune System
... The immune system is comprised of a series of highly integrated physical structures and biological processes that protect our body against disease. This protection involves the recognition and clearance of foreign agents also referred to as antigens that range from toxic molecules to complex microor ...
... The immune system is comprised of a series of highly integrated physical structures and biological processes that protect our body against disease. This protection involves the recognition and clearance of foreign agents also referred to as antigens that range from toxic molecules to complex microor ...
Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating
... Vector Construct and Virtual Protein Modeling. Mouse IL-2 and GMIntroduction CSF cDNAs were obtained from the National Gene Vector Laboratories (The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI), excised by restriction digest and The delivery of cytokines, or their encoding cDNA sequences, has inserted int ...
... Vector Construct and Virtual Protein Modeling. Mouse IL-2 and GMIntroduction CSF cDNAs were obtained from the National Gene Vector Laboratories (The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI), excised by restriction digest and The delivery of cytokines, or their encoding cDNA sequences, has inserted int ...
Mucosal Immunity in Mycobacterial Infections Anna Tjärnlund
... way the bacteria not only remain viable, but bacterial antigens are prevented from being presented to T cells. Mycobacteria appear to increase the retention of the tryptophan-aspartate containing coat (TACO) protein on the surface of the mycobacterial phagosome, thereby preventing phagosome-lysosom ...
... way the bacteria not only remain viable, but bacterial antigens are prevented from being presented to T cells. Mycobacteria appear to increase the retention of the tryptophan-aspartate containing coat (TACO) protein on the surface of the mycobacterial phagosome, thereby preventing phagosome-lysosom ...
Memorizing innate instructions requires a sufficiently specific
... Fig. 2. A simple example of a simulation. After self-tolerance induction most clonotypes are naive (i.e. mode 0), except clonotypes 6 and 12 which have been initialized in the tolerant mode (i.e. mode 1). Each pathogen consists of e = 3 different epitopes. The ®rst pathogen has to be rejected by an ...
... Fig. 2. A simple example of a simulation. After self-tolerance induction most clonotypes are naive (i.e. mode 0), except clonotypes 6 and 12 which have been initialized in the tolerant mode (i.e. mode 1). Each pathogen consists of e = 3 different epitopes. The ®rst pathogen has to be rejected by an ...
Author`s personal copy
... cells. Viral replication appears to occur in dendritic cells, monocytes, and possibly circulating lymphoid cells, and damage to these and other target cells occurs through immune-mediated mechanisms related to cross-reacting antibodies and cytokines released by dendritic cells, monocytes, and vascul ...
... cells. Viral replication appears to occur in dendritic cells, monocytes, and possibly circulating lymphoid cells, and damage to these and other target cells occurs through immune-mediated mechanisms related to cross-reacting antibodies and cytokines released by dendritic cells, monocytes, and vascul ...
Phagocyte

Phagocytes are cells that protect the body by ingesting (phagocytosing) harmful foreign particles, bacteria, and dead or dying cells. Their name comes from the Greek phagein, ""to eat"" or ""devour"", and ""-cyte"", the suffix in biology denoting ""cell"", from the Greek kutos, ""hollow vessel"". They are essential for fighting infections and for subsequent immunity. Phagocytes are important throughout the animal kingdom and are highly developed within vertebrates. One litre of human blood contains about six billion phagocytes. They were first discovered in 1882 by Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov while he was studying starfish larvae. Mechnikov was awarded the 1908 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his discovery. Phagocytes occur in many species; some amoebae behave like macrophage phagocytes, which suggests that phagocytes appeared early in the evolution of life.Phagocytes of humans and other animals are called ""professional"" or ""non-professional"" depending on how effective they are at phagocytosis. The professional phagocytes include many types of white blood cells (such as neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, mast cells, and dendritic cells). The main difference between professional and non-professional phagocytes is that the professional phagocytes have molecules called receptors on their surfaces that can detect harmful objects, such as bacteria, that are not normally found in the body. Phagocytes are crucial in fighting infections, as well as in maintaining healthy tissues by removing dead and dying cells that have reached the end of their lifespan.During an infection, chemical signals attract phagocytes to places where the pathogen has invaded the body. These chemicals may come from bacteria or from other phagocytes already present. The phagocytes move by a method called chemotaxis. When phagocytes come into contact with bacteria, the receptors on the phagocyte's surface will bind to them. This binding will lead to the engulfing of the bacteria by the phagocyte. Some phagocytes kill the ingested pathogen with oxidants and nitric oxide. After phagocytosis, macrophages and dendritic cells can also participate in antigen presentation, a process in which a phagocyte moves parts of the ingested material back to its surface. This material is then displayed to other cells of the immune system. Some phagocytes then travel to the body's lymph nodes and display the material to white blood cells called lymphocytes. This process is important in building immunity, and many pathogens have evolved methods to evade attacks by phagocytes.