Electronics Formal Homework 2
... The seat belt sensor produces logic 1 when the seat belt is fastened and logic 0 when the car ignition is off. (a) (i) Suggest a suitable output device that will illuminate the warning display. (ii) Complete the truth table for the logic levels P,Q and S in the circuit. ...
... The seat belt sensor produces logic 1 when the seat belt is fastened and logic 0 when the car ignition is off. (a) (i) Suggest a suitable output device that will illuminate the warning display. (ii) Complete the truth table for the logic levels P,Q and S in the circuit. ...
A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 4e
... Total amount of power needed to operate an electrical device Measured in watts Calculated by multiplying volts by amps in a system (W = V x A) ...
... Total amount of power needed to operate an electrical device Measured in watts Calculated by multiplying volts by amps in a system (W = V x A) ...
Current - PHS Regents Physics
... Voltage V is measured with a _________________, which DMM is often part of a _________. Its symbol is: V In an electrical circuit, voltmeters are connected NOT "in parallel" __________________ . This means the circuit is _______ opened up , but the _______________ must be voltmeter connected _______ ...
... Voltage V is measured with a _________________, which DMM is often part of a _________. Its symbol is: V In an electrical circuit, voltmeters are connected NOT "in parallel" __________________ . This means the circuit is _______ opened up , but the _______________ must be voltmeter connected _______ ...
Superconducting Fault Current Limiter for Energy Storage Protection
... for a stable operation of the distribution system has been recognized as one of the promising solutions for fault current problems, because of its fast fault current limiting and automatic characteristics of recovery. The devices in electronics and electrical circuits are sensitive to disturbance an ...
... for a stable operation of the distribution system has been recognized as one of the promising solutions for fault current problems, because of its fast fault current limiting and automatic characteristics of recovery. The devices in electronics and electrical circuits are sensitive to disturbance an ...
Solid State Relays Accessories.POWER Type RV
... Solid State Relays Accessories.POWER Type RV • Transient protection devices for Solid State Relays ...
... Solid State Relays Accessories.POWER Type RV • Transient protection devices for Solid State Relays ...
Demo Activity: Understanding Circuits Series Circuit: 1. Build the
... series circuit? Why do you think the brightness is different? - They are brighter because there is easier/multiple pathways for the current to move. ...
... series circuit? Why do you think the brightness is different? - They are brighter because there is easier/multiple pathways for the current to move. ...
Earth Fault Currents in Three Phase systems
... In TN systems, the earth fault current returns to the power supply node through a direct metal connection (PE or PEN conductor) without practically affecting the earth electrode. The main applications of TN Network can be found in industries and big installations with MV (Medium Voltage) power suppl ...
... In TN systems, the earth fault current returns to the power supply node through a direct metal connection (PE or PEN conductor) without practically affecting the earth electrode. The main applications of TN Network can be found in industries and big installations with MV (Medium Voltage) power suppl ...
G8SC_Test10 - Secondary Science Wiki
... mass decreases and the gravitational pull from Earth increases weight increases and the gravitational pull from Earth stays the same mass remains the same and the gravitational pull from Earth decreases weight remains the same and the gravitational pull from Earth changes ...
... mass decreases and the gravitational pull from Earth increases weight increases and the gravitational pull from Earth stays the same mass remains the same and the gravitational pull from Earth decreases weight remains the same and the gravitational pull from Earth changes ...
10.3 The ideal transformer
... ① Used for changing AC voltage levels. ② Transmission line : high voltage levels are used to decrease power loss due to ...
... ① Used for changing AC voltage levels. ② Transmission line : high voltage levels are used to decrease power loss due to ...
experiment 1 - UniMAP Portal
... Grounding System 1. Equipment Grounding (Body Grounding) 2. System grounding (Neutral grounding) ...
... Grounding System 1. Equipment Grounding (Body Grounding) 2. System grounding (Neutral grounding) ...
FINALLY…. an that actually means something!
... a valuable safety message! Don’t settle for less. This design also incorporates the unique Hubbell “Comprehensive Whole System Test Function” that has been a proven GFCI feature for many years. ...
... a valuable safety message! Don’t settle for less. This design also incorporates the unique Hubbell “Comprehensive Whole System Test Function” that has been a proven GFCI feature for many years. ...
Document
... Protoboard Connections Connections underneath: •Long rows across the top is connected •Each row of 5 is connected ...
... Protoboard Connections Connections underneath: •Long rows across the top is connected •Each row of 5 is connected ...
CN-0010 利用AD5381 DAC实现40通道可编程电压以及出色的温度漂移性能
... It is recommended to decouple each power pin close to the device with a 0.1 μF ceramic and a 10 μF tantalum capacitor. In this circuit, the reference for the AD5380 is provided externally from either an ADR421 or ADR431 2.5 V reference. The ADR431 provides a lower output voltage noise specification ...
... It is recommended to decouple each power pin close to the device with a 0.1 μF ceramic and a 10 μF tantalum capacitor. In this circuit, the reference for the AD5380 is provided externally from either an ADR421 or ADR431 2.5 V reference. The ADR431 provides a lower output voltage noise specification ...
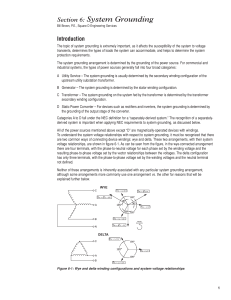
06 System Grounding
... The ground fault current is not large enough to force its removal by taking the system off-line. Therefore, the high-resistance grounded system has the same operational advantage in this respect as the ungrounded system. However, in addition to the improved voltage transient response as discussed ab ...
... The ground fault current is not large enough to force its removal by taking the system off-line. Therefore, the high-resistance grounded system has the same operational advantage in this respect as the ungrounded system. However, in addition to the improved voltage transient response as discussed ab ...
ground bond - high voltage insulation resistance
... check this. The user can select either automatic or manual mode connectivity check. The parameters can be adjusted in order to meet high quality control standards and optimum yield. OUTPUT VOLTAGE 50 - 1000V DC Quanti measures insulation resistance in electrical systems and equipment such as: electr ...
... check this. The user can select either automatic or manual mode connectivity check. The parameters can be adjusted in order to meet high quality control standards and optimum yield. OUTPUT VOLTAGE 50 - 1000V DC Quanti measures insulation resistance in electrical systems and equipment such as: electr ...
Science Study Guide
... ● A permanent magnet cannot be “turned on and off”. ●The magnetic field is strongest around the ends of a magnet. Objects that are magnetic will be pulled by a magnet, for example: paper clips, steel wool, tack. Some metals are nonmagnetic, for example aluminum, brass, copper, silver and gold. Magne ...
... ● A permanent magnet cannot be “turned on and off”. ●The magnetic field is strongest around the ends of a magnet. Objects that are magnetic will be pulled by a magnet, for example: paper clips, steel wool, tack. Some metals are nonmagnetic, for example aluminum, brass, copper, silver and gold. Magne ...