SET 1 - contentcarry
... 33:- (d) As the terminal voltage should fall with increase in the arc current for welding work, the differentially compounded generator is quite suited for this purpose. 34:- (b) In power station practice “spinning reserve” is to reserve generating capacity that is connected to bus and ready to take ...
... 33:- (d) As the terminal voltage should fall with increase in the arc current for welding work, the differentially compounded generator is quite suited for this purpose. 34:- (b) In power station practice “spinning reserve” is to reserve generating capacity that is connected to bus and ready to take ...
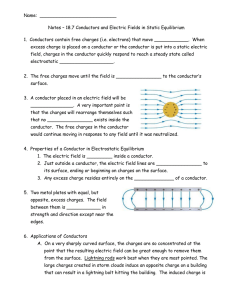
Name: Notes – 18.7 Conductors and Electric Fields in Static
... C. Another device that makes use of some of these principles is a Faraday cage. This is a metal shield that encloses a volume. All electrical charges will reside on the outside surface of this shield, and there will be no electrical field inside. A Faraday cage is used to prohibit stray electrical f ...
... C. Another device that makes use of some of these principles is a Faraday cage. This is a metal shield that encloses a volume. All electrical charges will reside on the outside surface of this shield, and there will be no electrical field inside. A Faraday cage is used to prohibit stray electrical f ...
I - R
... Ammeters and voltmeters can be either analog (read out with the deflection of a needle) or digital devices. We will study how the analog devices work since they’re easier to understand from basic principles. Galvanometer -- an analog device that responds to electrical currents flowing through it by ...
... Ammeters and voltmeters can be either analog (read out with the deflection of a needle) or digital devices. We will study how the analog devices work since they’re easier to understand from basic principles. Galvanometer -- an analog device that responds to electrical currents flowing through it by ...
Document
... c. As temperature increases, a metal’s resistance increases because electrons collide more often. 6. Battery – a device that converts chemical energy to electrical energy a. Batteries have different voltages, depending on the difference in energy at the two terminals b. Increasing the voltage increa ...
... c. As temperature increases, a metal’s resistance increases because electrons collide more often. 6. Battery – a device that converts chemical energy to electrical energy a. Batteries have different voltages, depending on the difference in energy at the two terminals b. Increasing the voltage increa ...
QM-13d: Electricity Elective
... Max amps for chassis wiring – 22 Max amps for power xmsn – 3.7 Max freq – 11,000 Hz Breaking strength – 75 pounds ...
... Max amps for chassis wiring – 22 Max amps for power xmsn – 3.7 Max freq – 11,000 Hz Breaking strength – 75 pounds ...
KidWind Kit Inventory List:
... • Some materials (insulators) do not share or release electrons easily – they have high resistance; Conductors easily share electrons and have low resistance • It takes about 40 volts or more to be dangerous (this is enough to overcome the resistance of the human body); but high voltage is really ...
... • Some materials (insulators) do not share or release electrons easily – they have high resistance; Conductors easily share electrons and have low resistance • It takes about 40 volts or more to be dangerous (this is enough to overcome the resistance of the human body); but high voltage is really ...
2Pro AC Devices Provide Overcurrent Overvoltage
... Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, users should independently evaluate the suitability of and test each product selected for their own applications. Littelfuse products are not designed for, and shall not be used for, any purpose (including, without limitation, ...
... Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, users should independently evaluate the suitability of and test each product selected for their own applications. Littelfuse products are not designed for, and shall not be used for, any purpose (including, without limitation, ...
The Importance of the X/R Ratio in Low
... equipment to the available fault current at the equipment. What is not always realized is that when lowvoltage gear is tested, it is tested at a certain X/R ratio. The X/R ratio is important because it determines the peak asymmetrical fault current. The asymmetrical fault current can be much larger ...
... equipment to the available fault current at the equipment. What is not always realized is that when lowvoltage gear is tested, it is tested at a certain X/R ratio. The X/R ratio is important because it determines the peak asymmetrical fault current. The asymmetrical fault current can be much larger ...
– APPENDIX F AESO TRANSMISSION PLANNING CRITERIA BASIS AND ASSUMPTIONS
... The AESO applies the following Alberta Reliability Standards to ensure that the transmission system is planned to meet applicable performance requirements under a defined set of system conditions and contingencies. A brief description of each of these standards is given below: 1. TPL-001-AB-0: Syste ...
... The AESO applies the following Alberta Reliability Standards to ensure that the transmission system is planned to meet applicable performance requirements under a defined set of system conditions and contingencies. A brief description of each of these standards is given below: 1. TPL-001-AB-0: Syste ...
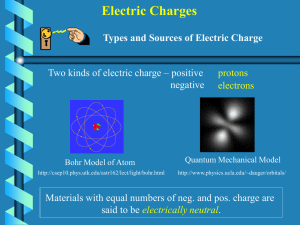
Physics 242 2 Electric Charges (1)
... • The magnitude of the electric current that flows through a closed circuit depends directly on the voltage between the battery terminals and inversely to the circuit resistance. The relationship that connects current, voltage and resistance is known as OHM'S LAW and is written as follows: ...
... • The magnitude of the electric current that flows through a closed circuit depends directly on the voltage between the battery terminals and inversely to the circuit resistance. The relationship that connects current, voltage and resistance is known as OHM'S LAW and is written as follows: ...
AC Power Quality and Standards
... • SC 77A/WG 2: Voltage fluctuations and other lowfrequency disturbances • SC 77A/WG 8: Electromagnetic interference related to the network frequency • SC 77A/WG 9: Power Quality measurement ...
... • SC 77A/WG 2: Voltage fluctuations and other lowfrequency disturbances • SC 77A/WG 8: Electromagnetic interference related to the network frequency • SC 77A/WG 9: Power Quality measurement ...