TB6551FAG Application Note
... in this document, and related hardware, software and systems (collectively "Product") without notice. This document and any information herein may not be reproduced without prior written permission from TOSHIBA. Even with TOSHIBA's written permission, reproduction is permissible only if reproducti ...
... in this document, and related hardware, software and systems (collectively "Product") without notice. This document and any information herein may not be reproduced without prior written permission from TOSHIBA. Even with TOSHIBA's written permission, reproduction is permissible only if reproducti ...
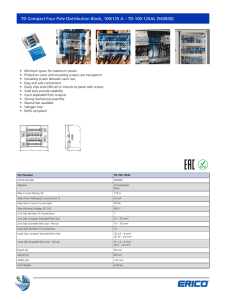
TD Compact Four Pole Distribution Block, 100/125 A – TD
... Derating according to Ambient* Temperature (°C) to maintain working temperature of 85°C ...
... Derating according to Ambient* Temperature (°C) to maintain working temperature of 85°C ...
Amateur Radio Technician Class Element 2 Course
... VHF and UHF radio signals are non-ionizing radiation. • Quite different from X-ray, gamma ray, and ultra violet radiation ...
... VHF and UHF radio signals are non-ionizing radiation. • Quite different from X-ray, gamma ray, and ultra violet radiation ...
P6 Revision Questions Motors and Generators
... How is electricity generated at a power station? Put a tick ( ) in the box next to the correct answer. A bar magnet rotates inside coils of wire. An electromagnet rotates around a permanent magnet. ...
... How is electricity generated at a power station? Put a tick ( ) in the box next to the correct answer. A bar magnet rotates inside coils of wire. An electromagnet rotates around a permanent magnet. ...
Generation of electricity
... railway and tramway systems and other motor driven applications where a smooth and wide range of speed control is required. It is generally more economical to transmit and distribute electricity in alternating current (AC) form, therefore all electricity generated at is AC.
The exce ...
... railway and tramway systems and other motor driven applications where a smooth and wide range of speed control is required. It is generally more economical to transmit and distribute electricity in alternating current (AC) form, therefore all electricity generated at
Potential Difference - Farid Minawi`s Physics zone
... (remember that they are identical, so there is no reason for the charge not to be redistributed equally), then these two balls are said to be in identical electric states. In general, the displacement of electric charges from an object to another takes place only if the two objects are connected by ...
... (remember that they are identical, so there is no reason for the charge not to be redistributed equally), then these two balls are said to be in identical electric states. In general, the displacement of electric charges from an object to another takes place only if the two objects are connected by ...
NRF Series Circuit Protectors - Flexi
... manually turning OFF, make sure that the current is not applied (under no-load condition). ...
... manually turning OFF, make sure that the current is not applied (under no-load condition). ...
Voltage Rating
... the two ratings is for overcurrents at line-to-ground voltages, intended to be cleared by one pole of the device. The higher of the two ratings is for overcurrents at line-to-line voltages, intended to be cleared by two or three poles of the circuit breaker or other mechanical overcurrent device. Sl ...
... the two ratings is for overcurrents at line-to-ground voltages, intended to be cleared by one pole of the device. The higher of the two ratings is for overcurrents at line-to-line voltages, intended to be cleared by two or three poles of the circuit breaker or other mechanical overcurrent device. Sl ...
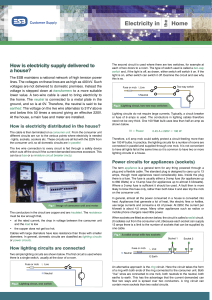
Electricity in Home
... reducing the risk of overheating and fire Other types of domestic load use large currents and are supplied byFuse connected in parallel and supplied through one mcb. It is not convenient customers with services which meet their needs (for The live wire connection to every circuit is fed through a saf ...
... reducing the risk of overheating and fire Other types of domestic load use large currents and are supplied byFuse connected in parallel and supplied through one mcb. It is not convenient customers with services which meet their needs (for The live wire connection to every circuit is fed through a saf ...
Latchable Negative Floating Hot Swap Power
... The UCC3921 family of negative floating hot swap power managers provides complete power management, hot swap, and fault handling capability. The IC is referenced to the negative input voltage and is powered through an external resistor connected to ground, which is essentially a current drive as opp ...
... The UCC3921 family of negative floating hot swap power managers provides complete power management, hot swap, and fault handling capability. The IC is referenced to the negative input voltage and is powered through an external resistor connected to ground, which is essentially a current drive as opp ...
Times-Protect Brochure
... When lightning strikes the tower, the shield and center conductor at the antenna are simultaneously elevated in potential. Since there is more surface area on the shield, the propagation velocity will be faster, and high frequencies will not be as attenuated as on the slower propagating center condu ...
... When lightning strikes the tower, the shield and center conductor at the antenna are simultaneously elevated in potential. Since there is more surface area on the shield, the propagation velocity will be faster, and high frequencies will not be as attenuated as on the slower propagating center condu ...