CIRCUIT THEORY
... 7. State two salient points of a series combination of resistance. 8. State two salient points of a parallel combination of resistance. 9. Give two applications of both series and parallel combination. 10. A bulb is as rated 230V, 230W. Find the rated current, resistance of the filament and the ener ...
... 7. State two salient points of a series combination of resistance. 8. State two salient points of a parallel combination of resistance. 9. Give two applications of both series and parallel combination. 10. A bulb is as rated 230V, 230W. Find the rated current, resistance of the filament and the ener ...
Critical Points of Simplified Model for Ferroresonance Phenomenon in Single Phase Power Transformers
... The calculated results dictate a jump up in primary induced voltage V2 from 80.19V to 128.73V due to ferroresonance at supply voltage V1 of 42.59 V. The calculated results dictate a jump down in primary induced voltage V2 from 115.1V to 44.86V due to ferroresonance at supply voltage V1 of 30.42 ...
... The calculated results dictate a jump up in primary induced voltage V2 from 80.19V to 128.73V due to ferroresonance at supply voltage V1 of 42.59 V. The calculated results dictate a jump down in primary induced voltage V2 from 115.1V to 44.86V due to ferroresonance at supply voltage V1 of 30.42 ...
User Manual
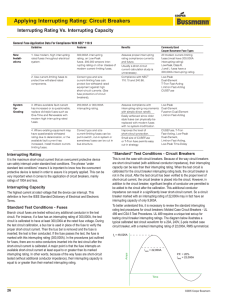
... NOTE: This test has no meaning for equipment that does not use a grounded cord. Selecting this function automatically opens the connection to Earth/Ground and passes any leakage current through a 1000 Ω load with either AAMI ES1-1993 or IEC 601 frequency compensation as selected by the Load Selectio ...
... NOTE: This test has no meaning for equipment that does not use a grounded cord. Selecting this function automatically opens the connection to Earth/Ground and passes any leakage current through a 1000 Ω load with either AAMI ES1-1993 or IEC 601 frequency compensation as selected by the Load Selectio ...
UEENEEE104A Solve problems in dc circuits
... affect the change in ‘length’ has on the resistance of a conductor. affect the change in ‘cross-sectional area’ has on the resistance of a conductor. effects of temperature change on the resistance of various conducting materials effects of resistance on the current-carrying capacity and voltage dro ...
... affect the change in ‘length’ has on the resistance of a conductor. affect the change in ‘cross-sectional area’ has on the resistance of a conductor. effects of temperature change on the resistance of various conducting materials effects of resistance on the current-carrying capacity and voltage dro ...
Guidelines for Modernizing Existing Electrical
... However, investment limitations and operating budget constraints are leading electrical distribution operators to extend the life of their switchgear from 10- 30 years on average to 50-60 years. At the same time, electrical switchgear manufacturers are renewing their technology offerings 3 to 5 time ...
... However, investment limitations and operating budget constraints are leading electrical distribution operators to extend the life of their switchgear from 10- 30 years on average to 50-60 years. At the same time, electrical switchgear manufacturers are renewing their technology offerings 3 to 5 time ...
260553-H: SUPPLEMENTAL ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT IDENTIFICATION (16195-H) Related Sections Standards
... Third part is a sequential letter if there is more than one panel of this type in the given area. Last part of name to reflect floor number. An example is CRP-BA-2: critical receptacle power, in section B, ("A" denotes second panel in area), on second floor - first such panel would have been CRP-B-2 ...
... Third part is a sequential letter if there is more than one panel of this type in the given area. Last part of name to reflect floor number. An example is CRP-BA-2: critical receptacle power, in section B, ("A" denotes second panel in area), on second floor - first such panel would have been CRP-B-2 ...
ELECRICAL CIRCUITS
... except they can be reset either mechanically or automatically Circuit breakers are normally located inside the fuse box, However some circuit such as headlights and power windows can have circuit breaker built into the switch or motor. ...
... except they can be reset either mechanically or automatically Circuit breakers are normally located inside the fuse box, However some circuit such as headlights and power windows can have circuit breaker built into the switch or motor. ...
Understanding Generator Stator Ground Faults
... current for a single-phase-to-ground fault at the terminals would be no greater than the charging current of the generator stator windings plus the associated cabling and surge capacitors. If the ground fault is bolted and not intermittent, then the potential difference of the unfaulted phases incre ...
... current for a single-phase-to-ground fault at the terminals would be no greater than the charging current of the generator stator windings plus the associated cabling and surge capacitors. If the ground fault is bolted and not intermittent, then the potential difference of the unfaulted phases incre ...
Safety First! - Lake Area Radio Klub
... VHF and UHF radio signals are non-ionizing radiation. • Quite different from X-ray, gamma ray, and ultra violet radiation ...
... VHF and UHF radio signals are non-ionizing radiation. • Quite different from X-ray, gamma ray, and ultra violet radiation ...
Component Electronic Systems
... Electricity is one of the most important forms of energy available to man. It affects everyone’s lives in many ways. If you take time to think about your everyday life you will realise that our lives are full of devices that depend upon electricity. These devices depend on the electrical circuits in ...
... Electricity is one of the most important forms of energy available to man. It affects everyone’s lives in many ways. If you take time to think about your everyday life you will realise that our lives are full of devices that depend upon electricity. These devices depend on the electrical circuits in ...
PSS30S92F6-AG
... It is recommended to insert a Zener diode D1(24V/1W) between each pair of control supply terminals to prevent surge destruction. To prevent surge destruction, the wiring between the smoothing capacitor and the P, N1 terminals should be as short as possible. Generally a 0.1-0.22μF snubber capacitor C ...
... It is recommended to insert a Zener diode D1(24V/1W) between each pair of control supply terminals to prevent surge destruction. To prevent surge destruction, the wiring between the smoothing capacitor and the P, N1 terminals should be as short as possible. Generally a 0.1-0.22μF snubber capacitor C ...
Amateur Radio Technician Class Element 2 Course Presentation
... VHF and UHF radio signals are non-ionizing radiation. • Quite different from X-ray, gamma ray, and ultra violet radiation ...
... VHF and UHF radio signals are non-ionizing radiation. • Quite different from X-ray, gamma ray, and ultra violet radiation ...
CEDMCS ACTM 10V Current Sensor Nuclear Automation Background Description
... a gap within the toroid. The main current carrying conductor passes through the center of the toroid, generating a magnetic field. The HE sensor senses this field in the gap of the toroid. A sensor has been selected that offers advanced features, including temperature compensation and precision offs ...
... a gap within the toroid. The main current carrying conductor passes through the center of the toroid, generating a magnetic field. The HE sensor senses this field in the gap of the toroid. A sensor has been selected that offers advanced features, including temperature compensation and precision offs ...
Interrupting Capacity vs. Interrupting Rating
... not assure that the circuit breaker’s interrupting capacity equals its interrupting rating nor even that the circuit breaker is reusable. In this test, line and load terminals are connected to 10 inches of rated conductor. For single pole circuit breakers, these 10 inch leads are then connected to 4 ...
... not assure that the circuit breaker’s interrupting capacity equals its interrupting rating nor even that the circuit breaker is reusable. In this test, line and load terminals are connected to 10 inches of rated conductor. For single pole circuit breakers, these 10 inch leads are then connected to 4 ...
Lightning and Surge Protection – Technical Note
... and should be implemented according to installation requirements. The SolarEdge inverter internal SPD cannot replace external protection devices requirements. ...
... and should be implemented according to installation requirements. The SolarEdge inverter internal SPD cannot replace external protection devices requirements. ...
Smart Ground Test Report Springfield Energy
... This report describes the ground tests and analysis of the Springfield Power Station. The objective of the test and analysis was to evaluate the plant grounding system with respect to safety performance, and transfer voltage to control circuits and if necessary, to recommend grounding design enhance ...
... This report describes the ground tests and analysis of the Springfield Power Station. The objective of the test and analysis was to evaluate the plant grounding system with respect to safety performance, and transfer voltage to control circuits and if necessary, to recommend grounding design enhance ...
Electrical Technology 2015
... Explain the term human rights in the workplace with reference to the protection of a worker. ...
... Explain the term human rights in the workplace with reference to the protection of a worker. ...