Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E Chapter 22
... (now called Standard Precautions) were mandated, exposure to latex by health care workers has dramatically increased. By June, 1996, 28 latex-related deaths had been reported to the FDA. ...
... (now called Standard Precautions) were mandated, exposure to latex by health care workers has dramatically increased. By June, 1996, 28 latex-related deaths had been reported to the FDA. ...
PPT Version - OMICS International
... • Due to the level of detail at which individual components are represented, ABMs can be computationally expensive and sometimes intractable. Population level approaches like ordinary differential equations (ODEs) are computationally tractable and can scale up to simulate host pathogen dynamics in l ...
... • Due to the level of detail at which individual components are represented, ABMs can be computationally expensive and sometimes intractable. Population level approaches like ordinary differential equations (ODEs) are computationally tractable and can scale up to simulate host pathogen dynamics in l ...
Lec.2 Dr.Maysem M.Alwash Hypersensitivity Reaction s (cont.)
... and B cells that recognize self antigens are either killed (negative selection) or rendered harmless during their maturation in central (generative) lymphoid organs (i.e., in the thymus for T cells and in the bone marrow for B cells). ...
... and B cells that recognize self antigens are either killed (negative selection) or rendered harmless during their maturation in central (generative) lymphoid organs (i.e., in the thymus for T cells and in the bone marrow for B cells). ...
MCB150 Beatty 1 MCB 150 Problem Set Inflammation
... neutrophils) whereas an inflammed endothelium will attract neutrophils/macs and ACTIVATED T cells. Q5. IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α play a crucial role in activating acute inflammation. On a systemic level they are capable of producing numerous effects on the host. How can IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α interact wi ...
... neutrophils) whereas an inflammed endothelium will attract neutrophils/macs and ACTIVATED T cells. Q5. IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α play a crucial role in activating acute inflammation. On a systemic level they are capable of producing numerous effects on the host. How can IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α interact wi ...
Office hours
... Course Objectives: Upon completion of this course students will be expected to: •Describe the various cells and organs of the immune system, including the role of each during the immune response. •Compare and contrast innate and acquired immunity, including their specific components and effector mec ...
... Course Objectives: Upon completion of this course students will be expected to: •Describe the various cells and organs of the immune system, including the role of each during the immune response. •Compare and contrast innate and acquired immunity, including their specific components and effector mec ...
c. Section 1.3 The Immune System
... • Any substance that causes an allergic reaction is called an allergen. • Side effects of an allergic reaction are a result of histamine. Histamine is a chemical that your body releases when you need to fight invaders. • Severe allergies can cause anaphylactic shock (swelling, breathing difficulties ...
... • Any substance that causes an allergic reaction is called an allergen. • Side effects of an allergic reaction are a result of histamine. Histamine is a chemical that your body releases when you need to fight invaders. • Severe allergies can cause anaphylactic shock (swelling, breathing difficulties ...
Third Semester M.Sc. Degree Examination (CSS)
... Explain the role of MHC proteins in cell mediated lysis. Give an account on the applications of monoclonal antibodies. Describe the role of cytokines in immunogenic reactions. Explain the immune responses shown to viral, bacterial and parasitic infections. Discuss the role of secondary lymphoid orga ...
... Explain the role of MHC proteins in cell mediated lysis. Give an account on the applications of monoclonal antibodies. Describe the role of cytokines in immunogenic reactions. Explain the immune responses shown to viral, bacterial and parasitic infections. Discuss the role of secondary lymphoid orga ...
Understanding HIV and AIDS
... •An infection in which HIV enters the blood and is multiplying in the person’s cells. ...
... •An infection in which HIV enters the blood and is multiplying in the person’s cells. ...
Lycera and Celgene Announce an Exclusive
... including Lycera's first-in-class RORgamma agonists for cancer immunotherapy, and clinicalstage candidate, LYC-30937, being studied for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) NEW YORK and ANN ARBOR, Mich., June 9, 2015 /PRNewswire/ -- Lycera Corp., a privately held biopharmaceutical company developing bre ...
... including Lycera's first-in-class RORgamma agonists for cancer immunotherapy, and clinicalstage candidate, LYC-30937, being studied for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) NEW YORK and ANN ARBOR, Mich., June 9, 2015 /PRNewswire/ -- Lycera Corp., a privately held biopharmaceutical company developing bre ...
Medical Biology
... and other invaders, through a series of steps called the immune response. On other words, the ability of an organism to resist infectious disease, it’s the sum of all naturally occurring defense mechanisms that protect humans from diseases. The immune system, which is made up of special cells, prote ...
... and other invaders, through a series of steps called the immune response. On other words, the ability of an organism to resist infectious disease, it’s the sum of all naturally occurring defense mechanisms that protect humans from diseases. The immune system, which is made up of special cells, prote ...
nonspecific defense
... Or make clones & memory cells Or release chemicals to attract monocytes Or release toxins or interferons ...
... Or make clones & memory cells Or release chemicals to attract monocytes Or release toxins or interferons ...
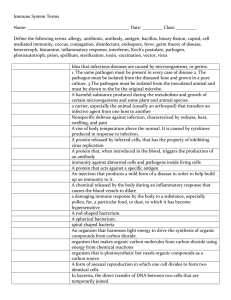
Immune Terms
... Idea that infectious diseases are caused by microorganisms, or germs. 1. The same pathogen must be present in every case of disease 2. The pathogen must be isolated from the diseased host and grown in a pure culture. 3.The pathogen must be isolated from the inoculated animal and must be shown to the ...
... Idea that infectious diseases are caused by microorganisms, or germs. 1. The same pathogen must be present in every case of disease 2. The pathogen must be isolated from the diseased host and grown in a pure culture. 3.The pathogen must be isolated from the inoculated animal and must be shown to the ...
Reading Guide for Week 9_10
... immune system works to fight off pathogenic microbes?” Chapter 3: Microscopy and Cell Structure (pg 68-78) You and your immune system are made out of eukaryotic cells. Make sure to review eukaryotic cell structure and function in Chapter 3. This is the basic foundation to help you understand how the ...
... immune system works to fight off pathogenic microbes?” Chapter 3: Microscopy and Cell Structure (pg 68-78) You and your immune system are made out of eukaryotic cells. Make sure to review eukaryotic cell structure and function in Chapter 3. This is the basic foundation to help you understand how the ...
3.6 Immune System
... 1. What are the two types of immune response in the second line of defense? 2. What are the characteristics of the innate immune response? 3. What type of blood cells are involved in the innate immune response? 4. What is the difference between a pathogen and a phagocyte? 5. When you are sick, w ...
... 1. What are the two types of immune response in the second line of defense? 2. What are the characteristics of the innate immune response? 3. What type of blood cells are involved in the innate immune response? 4. What is the difference between a pathogen and a phagocyte? 5. When you are sick, w ...
Immunology Terms Phagocytosis- method of engulfing and
... Epitope- the specific aspect of an antigen that is recognized by a T cell B cell or antibody Immunoglobulins (Igs)- B cells there are five families of B cells IgM, IgA, IgD, IgE, and IgG Monoclonal Antibodies- antibodies specifically generated for the purpose of binding to specific targets used ofte ...
... Epitope- the specific aspect of an antigen that is recognized by a T cell B cell or antibody Immunoglobulins (Igs)- B cells there are five families of B cells IgM, IgA, IgD, IgE, and IgG Monoclonal Antibodies- antibodies specifically generated for the purpose of binding to specific targets used ofte ...
There are
... water? How do they lose it? What adaptations do they have to minimize water loss and dehydration? What are nitrogenous wastes? What are the 3 types of nitrogenous wastes made by animals? Which ones do humans make? What are the advantages and disadvantages of each waste product? fig 25.6. What is Go ...
... water? How do they lose it? What adaptations do they have to minimize water loss and dehydration? What are nitrogenous wastes? What are the 3 types of nitrogenous wastes made by animals? Which ones do humans make? What are the advantages and disadvantages of each waste product? fig 25.6. What is Go ...
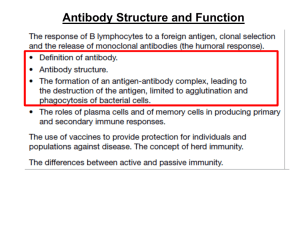
2 Antibodies - WordPress.com
... B-cell binds to antigen. B-cell divides by mitosis. Some cells formed are plasma cells – secrete antibodies. Some cells formed are memory cells – remain in blood for a period of time, providing ...
... B-cell binds to antigen. B-cell divides by mitosis. Some cells formed are plasma cells – secrete antibodies. Some cells formed are memory cells – remain in blood for a period of time, providing ...
VACCINES - Rovira i Virgili University
... Memory Cells and natural immunity After body eliminated the disease some of the B cells and T cells are converted into memory cells. Memory B cells can quickly divide into plasma cells and make more antibody if needed. Memory T cells can divide and grow into disease-fighting army. ...
... Memory Cells and natural immunity After body eliminated the disease some of the B cells and T cells are converted into memory cells. Memory B cells can quickly divide into plasma cells and make more antibody if needed. Memory T cells can divide and grow into disease-fighting army. ...
Immunology: Introduction and Overview
... inappropriately activated, they can attack the body’s own cells and tissues and lead to autoimmune responses. Several mechanisms exist also to eliminate or control potentially autoreactive lymphocytes providing protection against autoimmunity that is successful for most individuals. ...
... inappropriately activated, they can attack the body’s own cells and tissues and lead to autoimmune responses. Several mechanisms exist also to eliminate or control potentially autoreactive lymphocytes providing protection against autoimmunity that is successful for most individuals. ...
PA12-01 Galustian Lay summary Principal Investigator: Dr Christine
... How are you proposing to do it? There are a group of proteins known as cytokines, which can boost the immune system to help combat and destroy cancer cells. These cytokines are injected into the blood and can go freely around the body to activate cells of the immune system to kill tumour cells. Howe ...
... How are you proposing to do it? There are a group of proteins known as cytokines, which can boost the immune system to help combat and destroy cancer cells. These cytokines are injected into the blood and can go freely around the body to activate cells of the immune system to kill tumour cells. Howe ...
What is Mathematical Biology and How Useful is It?
... A model on the influence of age on immunity to infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis A. Friedman, J. Turner, B. Szomolay Experimental Gerontology Increasing susceptibility to many infectious diseases is highly associated with the loss or delay in the generation of antigen specific CD4+ T ce ...
... A model on the influence of age on immunity to infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis A. Friedman, J. Turner, B. Szomolay Experimental Gerontology Increasing susceptibility to many infectious diseases is highly associated with the loss or delay in the generation of antigen specific CD4+ T ce ...
Psychoneuroimmunology

Psychoneuroimmunology (PNI), also referred to as psychoendoneuroimmunology (PENI), is the study of the interaction between psychological processes and the nervous and immune systems of the human body. PNI takes an interdisciplinary approach, incorporating psychology, neuroscience, immunology, physiology, genetics, pharmacology, molecular biology, psychiatry, behavioral medicine, infectious diseases, endocrinology, and rheumatology.The main interests of PNI are the interactions between the nervous and immune systems and the relationships between mental processes and health. PNI studies, among other things, the physiological functioning of the neuroimmune system in health and disease; disorders of the neuroimmune system (autoimmune diseases; hypersensitivities; immune deficiency); and the physical, chemical and physiological characteristics of the components of the neuroimmune system in vitro, in situ, and in vivo.