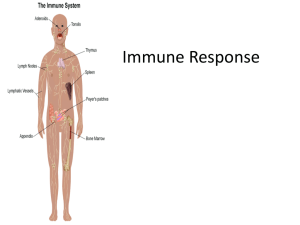
Immune System and Transpiration Practice Qui
... A. A body cell to present a viral antigen along with the MHC protein to a T cell B. The activation of B cells to secrete antibodies C. The activation of Memory T cells that were already present in the body D. The release of histamine from basophil and mast cells 10. The mature cytotoxic T cells will ...
... A. A body cell to present a viral antigen along with the MHC protein to a T cell B. The activation of B cells to secrete antibodies C. The activation of Memory T cells that were already present in the body D. The release of histamine from basophil and mast cells 10. The mature cytotoxic T cells will ...
... ____________________ bonds releases chemical energy ATP ATPase __________ + P + __________________ The phosphate bonds of the ATP molecule are _________ in energy. The energy from ATP can be used to perform an organism's _____________ processes. Enzymes are ________________ catalysts made mostly ...
Immunity web
... • Activated Killer T-Cells destroy pathogens and release chemicals called cytokines. Cytokines help to stimulate the immune system. Especially good at killing virus infected cells Pathogen ...
... • Activated Killer T-Cells destroy pathogens and release chemicals called cytokines. Cytokines help to stimulate the immune system. Especially good at killing virus infected cells Pathogen ...
Chapter 13 Physical Activity and the Immune System
... Monocytes are a type of white blood cell and are part of the innate immune system of vertebrates including all mammals (humans included), birds, reptiles, and fish. Monocytes play multiple roles in immune function. Such roles include: (1) replenish resident macrophages and dendritic cells under norm ...
... Monocytes are a type of white blood cell and are part of the innate immune system of vertebrates including all mammals (humans included), birds, reptiles, and fish. Monocytes play multiple roles in immune function. Such roles include: (1) replenish resident macrophages and dendritic cells under norm ...
body defenses
... Chemical and Mechanical Body Defenses……… • Intact skin • Respiratory system Bacteriostatic chemicals in saliva, low PH in the stomach and resident Flora In the intestine prevent infection ...
... Chemical and Mechanical Body Defenses……… • Intact skin • Respiratory system Bacteriostatic chemicals in saliva, low PH in the stomach and resident Flora In the intestine prevent infection ...
Immune Disorders notes
... Acquired Immune Deficiency Develops after birth Best example: AIDS, caused by the virus HIV Human Immunodeficiency virus ...
... Acquired Immune Deficiency Develops after birth Best example: AIDS, caused by the virus HIV Human Immunodeficiency virus ...
AIDS and its Effect on the Immune Response
... AIDS and its Effect on the Immune Response Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is a disease that results in the destruction of an individual’s immune system. The virus that causes AIDS is passed from an infected individual to another person by means of body fluids such as blood, semen, or vag ...
... AIDS and its Effect on the Immune Response Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is a disease that results in the destruction of an individual’s immune system. The virus that causes AIDS is passed from an infected individual to another person by means of body fluids such as blood, semen, or vag ...
A41-Immune Response
... – Damage to central nervous system, liver, digestive tract, kidneys, prolonged exposure leads to brain damage and death – Major sources – ingestion of contaminated food (mainly fish) and water, air pollution, improper use of items such as thermometers and fluorescent light ...
... – Damage to central nervous system, liver, digestive tract, kidneys, prolonged exposure leads to brain damage and death – Major sources – ingestion of contaminated food (mainly fish) and water, air pollution, improper use of items such as thermometers and fluorescent light ...
Cystatin 9: the key to effective treatment for bacterial lung disease?
... cysteine proteinase inhibitors called cystatins in the control of immune inflammatory responses in the lungs. These inhibitors may hold the key to limiting the damage done by an overzealous immune response to pathogens in diseases such as pneumonia and influenza. ...
... cysteine proteinase inhibitors called cystatins in the control of immune inflammatory responses in the lungs. These inhibitors may hold the key to limiting the damage done by an overzealous immune response to pathogens in diseases such as pneumonia and influenza. ...
Immune System
... • Failure of an organism in recognizing self • Immune response against its own cells/tissues • Autoimmune disease – Can be triggered by an infection (foreign antigens that are similar to human antigens) ...
... • Failure of an organism in recognizing self • Immune response against its own cells/tissues • Autoimmune disease – Can be triggered by an infection (foreign antigens that are similar to human antigens) ...
11.4: Immunity Healing and Protection Against Disease Recall that
... Specific immune system- variety of cells that recognize foreign substances and act to neutralize or destroy them; develops over time in each individual depending upon which diseases a person is exposed to. 3. Third-line defense- activated when pathogen gets by first- and second-line defenses and in ...
... Specific immune system- variety of cells that recognize foreign substances and act to neutralize or destroy them; develops over time in each individual depending upon which diseases a person is exposed to. 3. Third-line defense- activated when pathogen gets by first- and second-line defenses and in ...
Immune Response
... • Immunology- the study of host defense mechanisms • Immunity- ability of the host to protect itself against foreign organisms. Resistance to disease. • Antigen (Ag)- is a foreign substance that can elicit specific immune response (IR) when is immunogenic • Antibody (Ab)- protein produced by the bod ...
... • Immunology- the study of host defense mechanisms • Immunity- ability of the host to protect itself against foreign organisms. Resistance to disease. • Antigen (Ag)- is a foreign substance that can elicit specific immune response (IR) when is immunogenic • Antibody (Ab)- protein produced by the bod ...
Immune System Reading and Questions
... AIDS stands for Acquired Immunodeficient Syndrome. This virus lives in and kills helper T-cells. With fewer helper Tcells, the person’s immune system can’t form any new antibodies against any new invaders, thus people with AIDS usually die from some secondary infection or unusual form of cancer. The ...
... AIDS stands for Acquired Immunodeficient Syndrome. This virus lives in and kills helper T-cells. With fewer helper Tcells, the person’s immune system can’t form any new antibodies against any new invaders, thus people with AIDS usually die from some secondary infection or unusual form of cancer. The ...
Chapter 8 Immune Organs
... particular subsets of lymphocytes selectively enter some tissues but not others is called lymphocyte homing. (homing receptor on T lymphocyte and ligand on endothelial cell) ...
... particular subsets of lymphocytes selectively enter some tissues but not others is called lymphocyte homing. (homing receptor on T lymphocyte and ligand on endothelial cell) ...
IMMUNOCHEMISTRY OF THE EYE
... Graves’ disease is initially an autoimmune pathology that begins at the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland (shown on the right) controls basal metabolism by its secretion of T3 and T4 hormones. In the disease (generally in the 3rd or 4th decade of life) individuals begin to experience an increase in b ...
... Graves’ disease is initially an autoimmune pathology that begins at the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland (shown on the right) controls basal metabolism by its secretion of T3 and T4 hormones. In the disease (generally in the 3rd or 4th decade of life) individuals begin to experience an increase in b ...
Document
... • High levels of immunomodulatory factors: IL-10, TGF, TSLP, retinoic acid which can ‘condition’ local cells. • Reduced function of TLRs in intestinal DC. • Commensals are non-invasive. Whereas pathogens penetrate the epithelium and trigger inflammatory responses both locally and more widely, comme ...
... • High levels of immunomodulatory factors: IL-10, TGF, TSLP, retinoic acid which can ‘condition’ local cells. • Reduced function of TLRs in intestinal DC. • Commensals are non-invasive. Whereas pathogens penetrate the epithelium and trigger inflammatory responses both locally and more widely, comme ...
AJS_Paper3_Autoimmunity
... In a healthy human, the immune system works to identify and eradicate pathogens1. The human immune system is divided into two complement parts: the nonspecific or innate immune system and the specific or adaptive immune system. Each functions in a unique way and comprehension of these processes is i ...
... In a healthy human, the immune system works to identify and eradicate pathogens1. The human immune system is divided into two complement parts: the nonspecific or innate immune system and the specific or adaptive immune system. Each functions in a unique way and comprehension of these processes is i ...
Immunology – Immune System Overview
... Why is the immune system important? The immune system is important because it acts as barriers for pathogens to get through. If the pathogens do not find a break in our immune system – then they cannot prevail. Most pathogens initially find this break and incompatibility but eventually the body’s im ...
... Why is the immune system important? The immune system is important because it acts as barriers for pathogens to get through. If the pathogens do not find a break in our immune system – then they cannot prevail. Most pathogens initially find this break and incompatibility but eventually the body’s im ...
Chapter 36 - Immune System
... • Severe Combined Immune Deficiency is a genetic condition in which one or more genes for proteins crucial for the immune system are defective. Children born with SCID have no immune system. • Gene therapy has been used to inject a good copy of the defective gene into blood cells or bone marrow cell ...
... • Severe Combined Immune Deficiency is a genetic condition in which one or more genes for proteins crucial for the immune system are defective. Children born with SCID have no immune system. • Gene therapy has been used to inject a good copy of the defective gene into blood cells or bone marrow cell ...
Topic 19 - Roslyn Public Schools
... • B. Second line of Defense – 1. phagocyte –white blood cells engulfs pathogens and destroys them by the process of phagocytosis – several types of phagocytes - nonspecific – a. macrophages – develop from monocytes – engulf the microbe into a vacuole which fuses with a lysosome – b. eosinophils – p ...
... • B. Second line of Defense – 1. phagocyte –white blood cells engulfs pathogens and destroys them by the process of phagocytosis – several types of phagocytes - nonspecific – a. macrophages – develop from monocytes – engulf the microbe into a vacuole which fuses with a lysosome – b. eosinophils – p ...
Psychoneuroimmunology

Psychoneuroimmunology (PNI), also referred to as psychoendoneuroimmunology (PENI), is the study of the interaction between psychological processes and the nervous and immune systems of the human body. PNI takes an interdisciplinary approach, incorporating psychology, neuroscience, immunology, physiology, genetics, pharmacology, molecular biology, psychiatry, behavioral medicine, infectious diseases, endocrinology, and rheumatology.The main interests of PNI are the interactions between the nervous and immune systems and the relationships between mental processes and health. PNI studies, among other things, the physiological functioning of the neuroimmune system in health and disease; disorders of the neuroimmune system (autoimmune diseases; hypersensitivities; immune deficiency); and the physical, chemical and physiological characteristics of the components of the neuroimmune system in vitro, in situ, and in vivo.