Sci_ch9_Lesson_3_notes
... Energy is the ability to perform work or to change an object. Work is the measurement of the energy used to perform a task. Work = force x distance. The unit of measure for work and energy is joules (J). Potential Energy: Energy does not always involve motion. Potential energy is energy that is stor ...
... Energy is the ability to perform work or to change an object. Work is the measurement of the energy used to perform a task. Work = force x distance. The unit of measure for work and energy is joules (J). Potential Energy: Energy does not always involve motion. Potential energy is energy that is stor ...
SPH 4C - mackenziekim
... 22. Which are the most efficient types of light bulb in the home today? Which are the least efficient? 23. a) Where is most of your electricity used in the home? b) How can you as an individual reduce how much energy you use / waste in your home? 24. In energy conservation, no energy is actually “lo ...
... 22. Which are the most efficient types of light bulb in the home today? Which are the least efficient? 23. a) Where is most of your electricity used in the home? b) How can you as an individual reduce how much energy you use / waste in your home? 24. In energy conservation, no energy is actually “lo ...
Section 3 What is energy? Energy “Ability to do work” Anything that
... ME= PE + KE Chemical PE Formation and breaking of bonds Match releases energy as light and heat Kinetic energy The energy of an object due to its motion Depends on mass and speed Equation KE(J)=1/2 x mass(kg)x speed2(m/s)2 KE=1/2mv2 Radiant energy Energy from the Sun warms th ...
... ME= PE + KE Chemical PE Formation and breaking of bonds Match releases energy as light and heat Kinetic energy The energy of an object due to its motion Depends on mass and speed Equation KE(J)=1/2 x mass(kg)x speed2(m/s)2 KE=1/2mv2 Radiant energy Energy from the Sun warms th ...
Ideas about Work and Energy
... this is the dot product) Work can be positive or negative. Positive work increases the energy of an object. Negative work decreases the energy of an object (think of friction on a sliding object) ...
... this is the dot product) Work can be positive or negative. Positive work increases the energy of an object. Negative work decreases the energy of an object (think of friction on a sliding object) ...
Energy Assesment 1
... Q2. Energy cannot be destroyed, but it can be converted from one form to another. Give 3 examples. ...
... Q2. Energy cannot be destroyed, but it can be converted from one form to another. Give 3 examples. ...
What is Energy?
... change in itself or the world around it. Whenever work is done, energy is transformed or is transferred from one system to another. ...
... change in itself or the world around it. Whenever work is done, energy is transformed or is transferred from one system to another. ...
Energy
... • All of the kinetic energy due to random motion of particles that make up an object – Depends on speed & number of particles – Examples: boiling water, rubbing hands together ...
... • All of the kinetic energy due to random motion of particles that make up an object – Depends on speed & number of particles – Examples: boiling water, rubbing hands together ...
Forms of energy
... Fill in the blanks with the words at the bottom of the page. You can use words more than once. 1. Energy that is stored within an object is called ________ energy. 2. Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands store_________ energy. 3. The vibration and movements of the atoms and molecules within ...
... Fill in the blanks with the words at the bottom of the page. You can use words more than once. 1. Energy that is stored within an object is called ________ energy. 2. Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands store_________ energy. 3. The vibration and movements of the atoms and molecules within ...
Chapter 13
... • Energy is a property of an object due to its motion or its position • When work is done, energy is transferred or transformed from one system to another – Carry a tennis ball up in the stadium – You add potential energy to it by carrying it up ...
... • Energy is a property of an object due to its motion or its position • When work is done, energy is transferred or transformed from one system to another – Carry a tennis ball up in the stadium – You add potential energy to it by carrying it up ...
The Down-Low On Energy
... There are many ways to measure energy but one of the main constant units of measure is the: • BTU: British Thermal Unit • 1 BTU is the amount of energy it takes to heat 1 pound of water 1 degrees F. ...
... There are many ways to measure energy but one of the main constant units of measure is the: • BTU: British Thermal Unit • 1 BTU is the amount of energy it takes to heat 1 pound of water 1 degrees F. ...
Chapter 13
... • Energy is measured also in Joules ( J ) • Potential energy – energy of position ...
... • Energy is measured also in Joules ( J ) • Potential energy – energy of position ...
Additional Energy Terms
... Name and describe different types of energy. • Potential: chemical, gravitational, elastic, nuclear, magnetic • Kinetic: motion, heat, electric, light, sound What can happen to energy? • Transfer or transformation. Always conserved. Heat energy: movement/vibration of molecules. Measured by temperatu ...
... Name and describe different types of energy. • Potential: chemical, gravitational, elastic, nuclear, magnetic • Kinetic: motion, heat, electric, light, sound What can happen to energy? • Transfer or transformation. Always conserved. Heat energy: movement/vibration of molecules. Measured by temperatu ...
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Survey
... and attenders concerned about the impact that burning fossil fuels has on the Earth’s environment and the long-term sustainability of human life on the planet. We believe that humans are called and have an obligation to preserve and protect the natural environment The Climate Change Action Working G ...
... and attenders concerned about the impact that burning fossil fuels has on the Earth’s environment and the long-term sustainability of human life on the planet. We believe that humans are called and have an obligation to preserve and protect the natural environment The Climate Change Action Working G ...
Energy and Power - Reeths
... • Example 1- A bike on top of a hill waiting to get the energy out by going down the hill. • Example 2- Sleeping before awakening to alarm ...
... • Example 1- A bike on top of a hill waiting to get the energy out by going down the hill. • Example 2- Sleeping before awakening to alarm ...
Chemical Energy
... mechanical energy of the cart? What do you think the potential and kinetic energy at points w and x would be based on your answer from #3? What is mechanical energy? ...
... mechanical energy of the cart? What do you think the potential and kinetic energy at points w and x would be based on your answer from #3? What is mechanical energy? ...
Energy Worksheet
... 1. Energy that is stored within an object is called ________ energy. 2. Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands store_________ energy. 3. The vibration and movements of the atoms and molecules within substances is called heat or ________ energy. 4. The energy stored in the centre of atoms is c ...
... 1. Energy that is stored within an object is called ________ energy. 2. Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands store_________ energy. 3. The vibration and movements of the atoms and molecules within substances is called heat or ________ energy. 4. The energy stored in the centre of atoms is c ...
Energy Transformations
... 4 - Cite evidence to support the Law of Conservation of Energy. 3 - Investigate and describe the transformation of energy that occurs in given examples. 2 - Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. 1 - Identify examples of kinetic and potential energy. ...
... 4 - Cite evidence to support the Law of Conservation of Energy. 3 - Investigate and describe the transformation of energy that occurs in given examples. 2 - Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. 1 - Identify examples of kinetic and potential energy. ...
No Slide Title
... resources, rather than as an expense • The facility manager is being elevated to the role of asset manager, supporting the organization's overall business goals ...
... resources, rather than as an expense • The facility manager is being elevated to the role of asset manager, supporting the organization's overall business goals ...
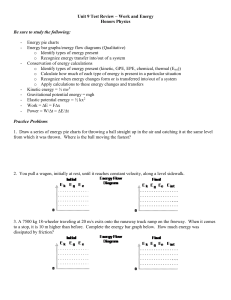
Unit 9 Test Review – Work and Energy
... 2. You pull a wagon, initially at rest, until it reaches constant velocity, along a level sidewalk. ...
... 2. You pull a wagon, initially at rest, until it reaches constant velocity, along a level sidewalk. ...
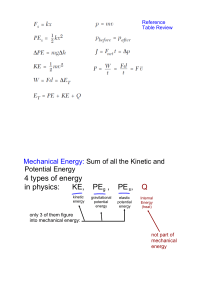
4 types of energy in physics: KE, PEg , PEs, Q
... Mechanical Energy: Sum of all the Kinetic and Potential Energy ...
... Mechanical Energy: Sum of all the Kinetic and Potential Energy ...
Law of the Conservation of Energy
... falling or rolling. Kinetic energy is the energy of movement. Moving cars and bikes have kinetic energy. Chemical energy is a form of potential energy; it is stored in food, batteries and gasoline. All of these types of energy interact with one another. The chemical energy from food can be turned in ...
... falling or rolling. Kinetic energy is the energy of movement. Moving cars and bikes have kinetic energy. Chemical energy is a form of potential energy; it is stored in food, batteries and gasoline. All of these types of energy interact with one another. The chemical energy from food can be turned in ...
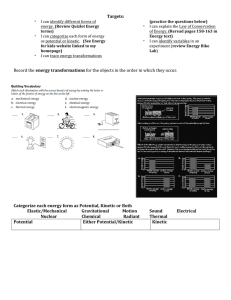
Targets: * I can identify different forms of energy. (Review Quizlet
... Categorize each energy form as Potential, Kinetic or Both ...
... Categorize each energy form as Potential, Kinetic or Both ...
Efficient energy use

Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the goal to reduce the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a home allows a building to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a comfortable temperature. Installing fluorescent lights , LED lights or natural skylights reduces the amount of energy required to attain the same level of illumination compared with using traditional incandescent light bulbs. Compact fluorescent lights use one-third the energy of incandescent lights and may last from 6 to 10 times longer. Improvements in energy efficiency are generally achieved by adopting a more efficient technology or production processes or by application of commonly accepted methods to reduce energy losses.There are many motivations to improve energy efficiency. Reducing energy use reduces energy costs and may result in a financial cost saving to consumers if the energy savings offset any additional costs of implementing an energy efficient technology. Reducing energy use is also seen as a solution to the problem of reducing carbon dioxide emissions. According to the International Energy Agency, improved energy efficiency in buildings, industrial processes and transportation could reduce the world's energy needs in 2050 by one third, and help control global emissions of greenhouse gases.Energy efficiency and renewable energy are said to be the twin pillars of sustainable energy policy and are high priorities in the sustainable energy hierarchy. In many countries energy efficiency is also seen to have a national security benefit because it can be used to reduce the level of energy imports from foreign countries and may slow down the rate at which domestic energy resources are depleted.