The advantages of being small Stockholm University
... The lipid shape is another important property that will affect the bilayer. There are three major classes of lipid structures, inverted cone, cylindrical, and cone shaped (Fig. 1). The first type is most common for lysophospholipids, having only one acyl chain, phospholipids with short akyl chains, ...
... The lipid shape is another important property that will affect the bilayer. There are three major classes of lipid structures, inverted cone, cylindrical, and cone shaped (Fig. 1). The first type is most common for lysophospholipids, having only one acyl chain, phospholipids with short akyl chains, ...
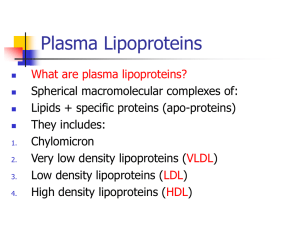
Plasma Lipoproteins
... LDL receptor deficiency plasma LDL & cholesterol type II hyperlipidemia (familial hypercholest.) T3 cause +ve effect on LDL binding to its receptors Hypothyroidism hypercholesterolemia ...
... LDL receptor deficiency plasma LDL & cholesterol type II hyperlipidemia (familial hypercholest.) T3 cause +ve effect on LDL binding to its receptors Hypothyroidism hypercholesterolemia ...
File
... Option 2 Directions and RubricI will provide you with the basic structure of a unit plan that you must complete. All activities must connect to each other and make sense in the flow of the unit. For each activity you must provide supple- ...
... Option 2 Directions and RubricI will provide you with the basic structure of a unit plan that you must complete. All activities must connect to each other and make sense in the flow of the unit. For each activity you must provide supple- ...
Systemic methods for capturing protein–lipid interactions (PDF
... • 25% of the identified lipid interaction proteome is enriched in drug targets, while 12% of total human proteome is drugged. lipid probes may preferentially interact with proteins that can bind other small molecule ligands ...
... • 25% of the identified lipid interaction proteome is enriched in drug targets, while 12% of total human proteome is drugged. lipid probes may preferentially interact with proteins that can bind other small molecule ligands ...
IGF-1 induces rat glomerular mesangial cells to accumulate
... 1C, no significant differences in AcLDL binding were detected over a period of 7 days. Similarly, in Fig. 1D, although a slight decrease in degradation occurred the first day, this was not sustained. This is in agreement with our previous data in which we found no change in the uptake of fluorescent ...
... 1C, no significant differences in AcLDL binding were detected over a period of 7 days. Similarly, in Fig. 1D, although a slight decrease in degradation occurred the first day, this was not sustained. This is in agreement with our previous data in which we found no change in the uptake of fluorescent ...
A, B, C… γ!
... HDL particle.11 Upregulation of ABC1 expression is likely to enhance cholesterol efflux from macrophage foam cells and may also result in increased HDL levels, especially in settings in which there is increased formation of free apoA-I or small HDL in the bloodstream. This might include the common a ...
... HDL particle.11 Upregulation of ABC1 expression is likely to enhance cholesterol efflux from macrophage foam cells and may also result in increased HDL levels, especially in settings in which there is increased formation of free apoA-I or small HDL in the bloodstream. This might include the common a ...
Effect of the Viral Proteins on the Fluidity of the Membrane Lipids in
... in the absence of the viral proteins, is shown in Figure 1, curve C. The viral lipids were much more fluid (had a lower order parameter) after extraction than they were in the intact virion. It thus appeared that the rigidity of the viral membrane relative to either the chick cell plasma membrane or ...
... in the absence of the viral proteins, is shown in Figure 1, curve C. The viral lipids were much more fluid (had a lower order parameter) after extraction than they were in the intact virion. It thus appeared that the rigidity of the viral membrane relative to either the chick cell plasma membrane or ...
Membrane proteins and the import business of mitochondria
... cent of all proteins required by the mitochondria are produced outside the outer mitochondrial membrane. How are these proteins transported across the membrane and how do they find their way into the mitochondria? A group of researchers led by Prof. Dr. Chris Meisinger at the University of Freiburg ...
... cent of all proteins required by the mitochondria are produced outside the outer mitochondrial membrane. How are these proteins transported across the membrane and how do they find their way into the mitochondria? A group of researchers led by Prof. Dr. Chris Meisinger at the University of Freiburg ...
3.3 Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two
... • The fluid mosaic model describes the membrane. cell membrane ...
... • The fluid mosaic model describes the membrane. cell membrane ...
A Proteomics Approach to Membrane Trafficking1
... to find the proteins colocalizing with many membrane compartments. As is evident from several Update articles in this issue, ambiguity exists when employing cytological techniques to identify specific endomembrane compartments, while markers identified based on homology may behave differently in pla ...
... to find the proteins colocalizing with many membrane compartments. As is evident from several Update articles in this issue, ambiguity exists when employing cytological techniques to identify specific endomembrane compartments, while markers identified based on homology may behave differently in pla ...
elucidate the contribution of proteins to tears. a challenge for
... Meibomian lipids alone, are needed for lowering the surface tension to that found in whole tears. Moreover, these proteins include the major tear proteins such as lysozyme and mucins (3,4). Enigmatically lipocalin is giving confounding results (unpublished) which are indicating that apolipocalin is ...
... Meibomian lipids alone, are needed for lowering the surface tension to that found in whole tears. Moreover, these proteins include the major tear proteins such as lysozyme and mucins (3,4). Enigmatically lipocalin is giving confounding results (unpublished) which are indicating that apolipocalin is ...
Chapter 7 Review Sheet
... how they differ from each other. Which is the most specific? Explain. Which uses pseudopods and why not just pinch in? Which use ATP? 9. Why would a cell want to perform endocytosis in general? Where does the vesicle with the ingested material first go? Explain why. Your white blood cells will do en ...
... how they differ from each other. Which is the most specific? Explain. Which uses pseudopods and why not just pinch in? Which use ATP? 9. Why would a cell want to perform endocytosis in general? Where does the vesicle with the ingested material first go? Explain why. Your white blood cells will do en ...
Imaging T-tubules: dynamic membrane
... clusters by counting the number of electron dense RyR2 ‘feet’ in crosssections and extrapolating cluster sizes based on presumed circular geometries of jSR domains.12 Furthermore, 3D EM has been applied to study local TT diameters, membrane branching and to estimate the size of junctions.13 As with ...
... clusters by counting the number of electron dense RyR2 ‘feet’ in crosssections and extrapolating cluster sizes based on presumed circular geometries of jSR domains.12 Furthermore, 3D EM has been applied to study local TT diameters, membrane branching and to estimate the size of junctions.13 As with ...
Is host lipidation of pathogen effector proteins a general virulence
... The involvement of lipidation in some and modified by N-myristoylation and severe human diseases (cancer, genetic S-palmitoylation (Dowen et al., 2009). In blindness, premature aging, or osteo- 2003, we showed that the Salmonella effecpetrosis; Perez-Sala, 2007) underlies the tor protein SifA has a ...
... The involvement of lipidation in some and modified by N-myristoylation and severe human diseases (cancer, genetic S-palmitoylation (Dowen et al., 2009). In blindness, premature aging, or osteo- 2003, we showed that the Salmonella effecpetrosis; Perez-Sala, 2007) underlies the tor protein SifA has a ...
Introduction 1.1 The Importance of Homeostasis in Maintaining
... fission, and that form sexual states which are not enclosed in a fruiting body." (Boekhout and Kurtzman, 1996). Yeast cell membranes acts as impermeable barriers against hydrophilic molecules to prevent the mixing of the cytoplasm and external environment. Around 7.5 n thick, the cell membrane is co ...
... fission, and that form sexual states which are not enclosed in a fruiting body." (Boekhout and Kurtzman, 1996). Yeast cell membranes acts as impermeable barriers against hydrophilic molecules to prevent the mixing of the cytoplasm and external environment. Around 7.5 n thick, the cell membrane is co ...
cell communication powerpoint
... Steps of Cellular Communication 1. Reception: “detection” of signal by a receptor molecule on a target cell (or receptor molecule within cell, depending on type of signal). PRIMARY MESSENGER. Signal does not participate in the actual pathway. In most cases, doesn’t even get into the cell! 2. Transd ...
... Steps of Cellular Communication 1. Reception: “detection” of signal by a receptor molecule on a target cell (or receptor molecule within cell, depending on type of signal). PRIMARY MESSENGER. Signal does not participate in the actual pathway. In most cases, doesn’t even get into the cell! 2. Transd ...
Phospholipid Class and Fatty Acid Composition of Golgi Apparatus
... endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and plasma membrane exhibited the highest percentage of saturated acids when compared to other lipid classes from the respective membrane fraction. Overall, sphingomyelin of Golgi apparatus and plasma membrane contained the highest percentage of saturated acid ...
... endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and plasma membrane exhibited the highest percentage of saturated acids when compared to other lipid classes from the respective membrane fraction. Overall, sphingomyelin of Golgi apparatus and plasma membrane contained the highest percentage of saturated acid ...
the Endoplasmic Reticulum CD1d1 with Cellular Phospholipids
... phosphatidylinositol-glycans are not V␣14J␣15 natural T cell Ags. Therefore, we predict that cellular lipids occlude the hydrophobic Ag-binding groove of CD1 during assembly until they are exchanged for a glycolipid Ag(s) within the recycling compartment for display on the plasma membrane. In this m ...
... phosphatidylinositol-glycans are not V␣14J␣15 natural T cell Ags. Therefore, we predict that cellular lipids occlude the hydrophobic Ag-binding groove of CD1 during assembly until they are exchanged for a glycolipid Ag(s) within the recycling compartment for display on the plasma membrane. In this m ...
Lipid transfer and metabolism across the endolysosomal
... Lysosomes (vacuoles in yeast) represent the most important catabolic compartment of eukaryotic cells, containing a wide set of acidic hydrolases able to digest not only macromolecules (such as proteins, lipids, sugars, nucleic acids), but also entire organelles and pathogenic organisms [14,15]. A co ...
... Lysosomes (vacuoles in yeast) represent the most important catabolic compartment of eukaryotic cells, containing a wide set of acidic hydrolases able to digest not only macromolecules (such as proteins, lipids, sugars, nucleic acids), but also entire organelles and pathogenic organisms [14,15]. A co ...
Cells and Tissues Part 1
... Nucleus contains one or more nucleoli Sites of ribosome assembly Ribosomes migrate into the cytoplasm through nuclear pores ...
... Nucleus contains one or more nucleoli Sites of ribosome assembly Ribosomes migrate into the cytoplasm through nuclear pores ...
Poster
... in endocytosis by helping to determine the curvature of the formed vesicle. To do this, certain positively charged residues on the concave surface of the FBAR domain of CIP4 interact with the negatively charged membrane phospholipids. CIP4 is important to the lab we are collaborating with because th ...
... in endocytosis by helping to determine the curvature of the formed vesicle. To do this, certain positively charged residues on the concave surface of the FBAR domain of CIP4 interact with the negatively charged membrane phospholipids. CIP4 is important to the lab we are collaborating with because th ...
A cellular backline: specialization of host membranes for defence
... Callose synthesis as a membraneanchored response The deposition of callose in the apoplast is triggered in a number of different contexts during plant–pathogen interactions. Callose is a β-1,3-glucan and has been hypothesized to fortify cell walls and tissues against an invading pathogen. Callose sy ...
... Callose synthesis as a membraneanchored response The deposition of callose in the apoplast is triggered in a number of different contexts during plant–pathogen interactions. Callose is a β-1,3-glucan and has been hypothesized to fortify cell walls and tissues against an invading pathogen. Callose sy ...
Lipid raft
The plasma membranes of cells contain combinations of glycosphingolipids and protein receptors organized in glycolipoprotein microdomains termed lipid rafts. These specialized membrane microdomains compartmentalize cellular processes by serving as organizing centers for the assembly of signaling molecules, influencing membrane fluidity and membrane protein trafficking, and regulating neurotransmission and receptor trafficking. Lipid rafts are more ordered and tightly packed than the surrounding bilayer, but float freely in the membrane bilayer. Although more common in plasma membrane, lipid rafts have also been reported in other parts of the cell, such as Golgi and lysosomes.